Ohm's Law - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how voltage, current, and resistance work together in electrical circuits!
What is Ohm's Law?
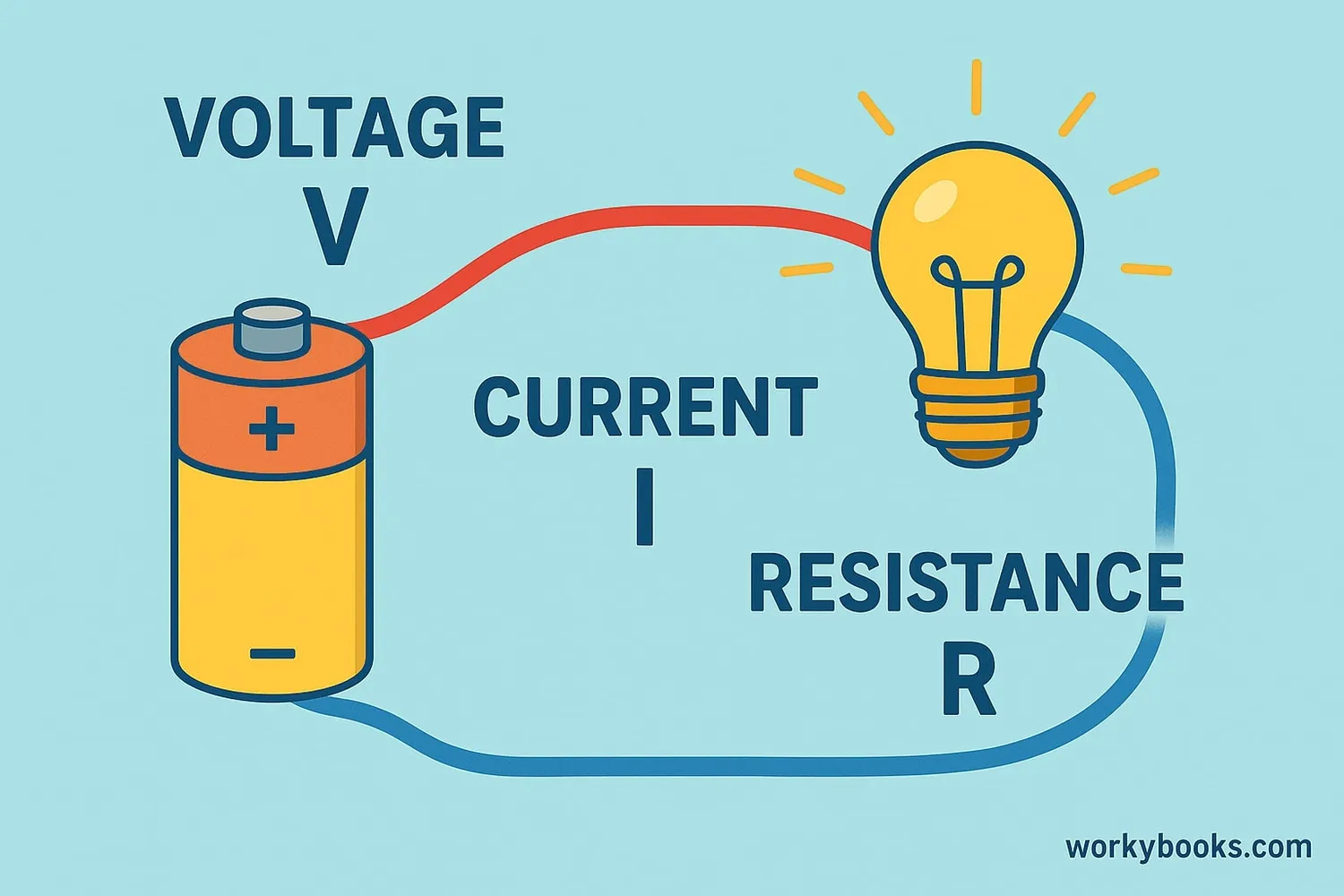
Ohm's Law is a fundamental rule in electricity that explains how voltage, current, and resistance work together in electrical circuits. It was discovered by German physicist Georg Ohm in the 1820s.
Think of electricity flowing through a wire like water flowing through a pipe. Voltage is like the water pressure that pushes the water through the pipe. Current is how much water is flowing through the pipe. Resistance is anything that makes it harder for the water to flow, like a narrow section of pipe.
Ohm's Law tells us that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage applied across it and inversely proportional to its resistance. This relationship helps us understand and design electrical circuits.
Did You Know?
Ohm's Law is used by electricians, engineers, and scientists to design everything from tiny electronic devices to large power grids!
Key Components of Ohm's Law
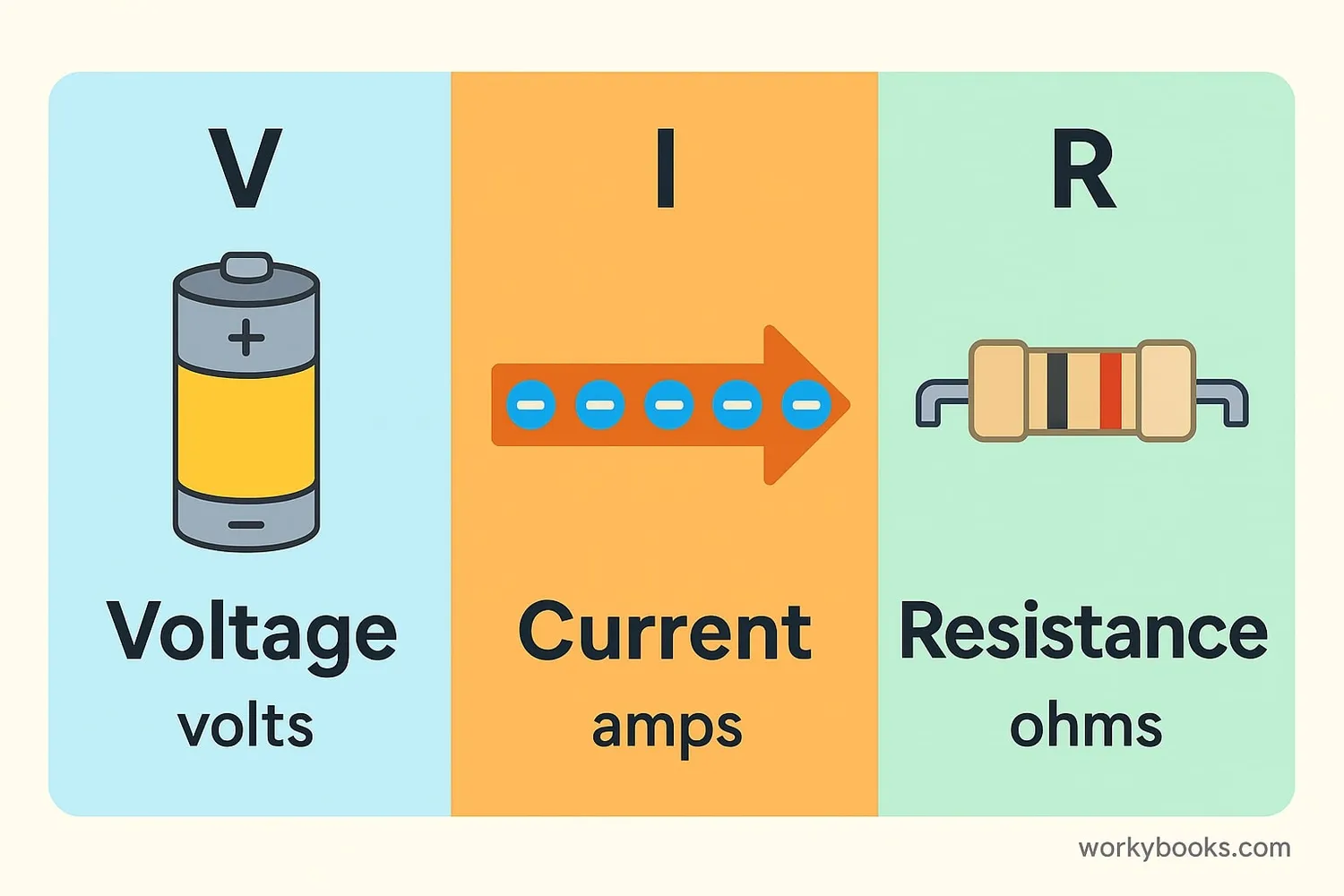
To understand Ohm's Law, we need to know its three main components:
Voltage (V)
Measured in volts (V)
The "push" that moves electrons through a circuit
Current (I)
Measured in amperes (A)
The flow of electric charge (electrons)
Resistance (R)
Measured in ohms (Ω)
How much a material opposes electric current
Voltage is like the pressure in a water hose - it pushes the electricity through the circuit. Current is how much electricity is flowing - like how much water comes out of the hose. Resistance is anything that slows down the flow of electricity - like a kink in the hose that reduces water flow.
These three components are related in a very special way, which we'll explore next with the Ohm's Law formula!
The Ohm's Law Formula

The Ohm's Law formula is a simple but powerful equation that shows the relationship between voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R):
This means: Voltage = Current × Resistance
We can rearrange this formula to solve for any of the three values:
Find Voltage (V)
V = I × R
Find Current (I)
I = V ÷ R
Find Resistance (R)
R = V ÷ I
Example: If a circuit has a 9V battery and a light bulb with 3Ω of resistance, how much current flows through the bulb?
Using the formula: I = V ÷ R = 9V ÷ 3Ω = 3A
So 3 amps of current flows through the bulb.
Remember the Triangle!
The Ohm's Law triangle helps you remember the formulas. Cover the letter you want to find, and the other two show how they relate!
Applications of Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law isn't just a theory - it has many practical applications in our daily lives:
Electrical Wiring
Electricians use Ohm's Law to design safe home wiring systems
Electronics Design
Engineers design smartphones and computers using Ohm's Law
Automotive Systems
Car electrical systems rely on Ohm's Law principles
Other important applications include:
• Calculating the right size resistors for circuits
• Troubleshooting electrical problems
• Designing power supplies
• Understanding how fuses and circuit breakers work
• Calculating electrical power (P = V × I)
Electricians use special tools called multimeters that measure voltage, current, and resistance based on Ohm's Law principles.
Limitations of Ohm's Law
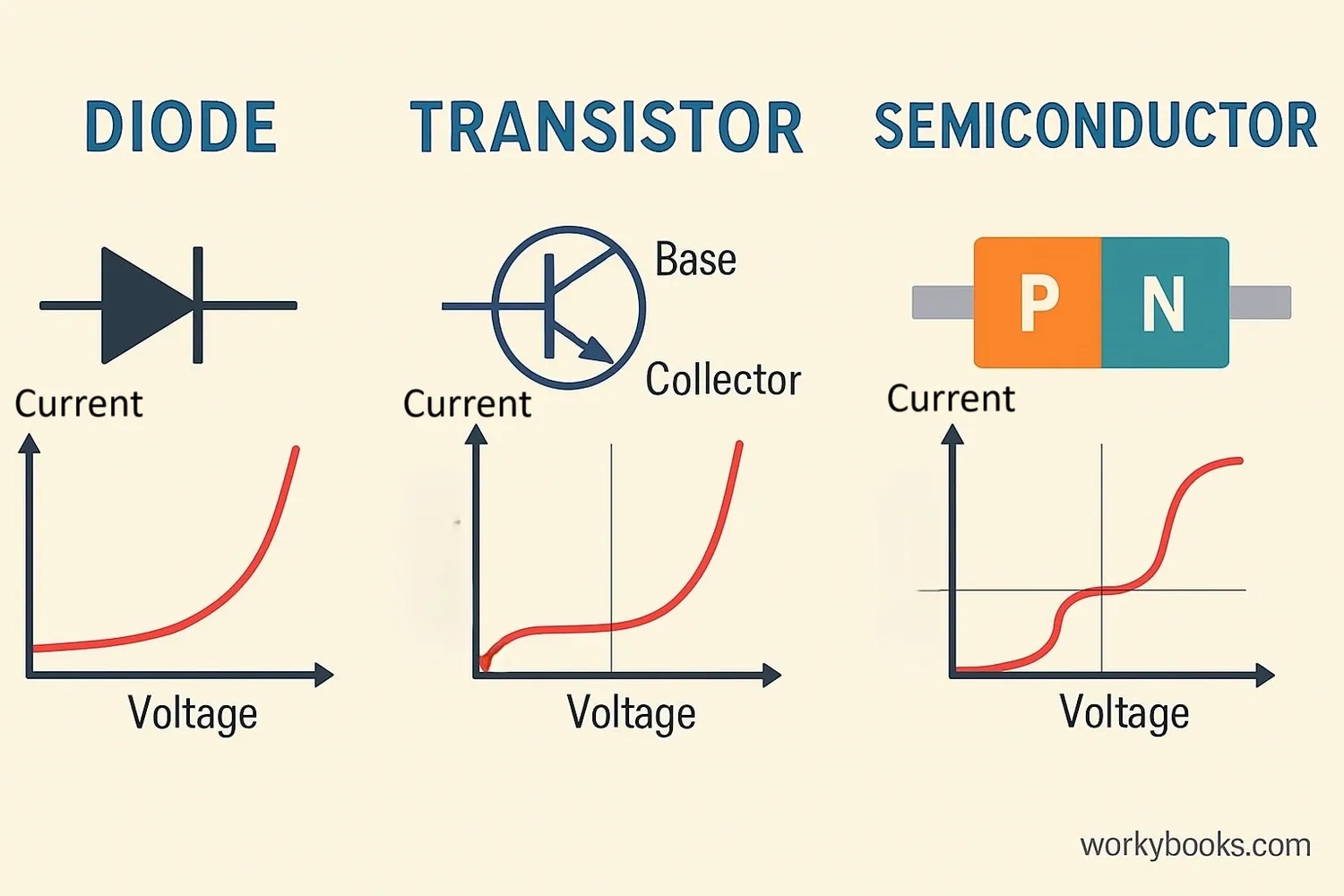
While Ohm's Law is very useful, it doesn't apply to all materials and devices. Materials that follow Ohm's Law are called "ohmic" materials, while those that don't are "non-ohmic."
Ohmic Materials
Metals like copper and aluminum
Follow Ohm's Law at constant temperature
Non-Ohmic Materials
Diodes, transistors, semiconductors
Don't follow Ohm's Law
Why don't some materials follow Ohm's Law?
• Temperature changes: Resistance changes with temperature
• Semiconductor behavior: Current doesn't increase linearly with voltage
• Diode function: Allows current in only one direction
• Transistor action: Can amplify or switch electronic signals
Despite these limitations, Ohm's Law remains one of the most important principles in electrical engineering and is used in countless applications every day.
Ohm's Law Quiz
Test your knowledge with this fun quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about Ohm's Law:
Fun Ohm's Law Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about electricity and Ohm's Law!
Historical Resistance
When Georg Ohm first published his law in 1827, it was rejected by many scientists. It took years for his work to gain acceptance!
Human Resistance
Dry human skin has about 100,000 ohms of resistance, but when wet, it drops to just 1,000 ohms! That's why water and electricity are dangerous.
Superconductors
Some materials called superconductors have zero resistance when cooled to very low temperatures. Electricity flows through them perfectly!
Electric Eels
Electric eels use modified muscle cells to generate voltages up to 600 volts! They use Ohm's Law naturally to deliver powerful shocks to prey.





