The Cryosphere - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Exploring Earth's Frozen Water Systems
What is the Cryosphere?

The cryosphere is the frozen water part of the Earth's system. It includes all the places where water is in its solid form, like snow, ice, glaciers, and permafrost. The word "cryosphere" comes from the Greek word "kryos" which means cold or frost.
Think of the cryosphere as Earth's freezer! It stores water in its frozen state, and it's found in many different places around our planet - from the polar ice caps to high mountain tops, and even in frozen ground in cold regions.
Cryosphere Fact!
About 10% of Earth's land area is covered by glaciers or ice sheets, and they store about 75% of the world's freshwater!
Components of the Cryosphere
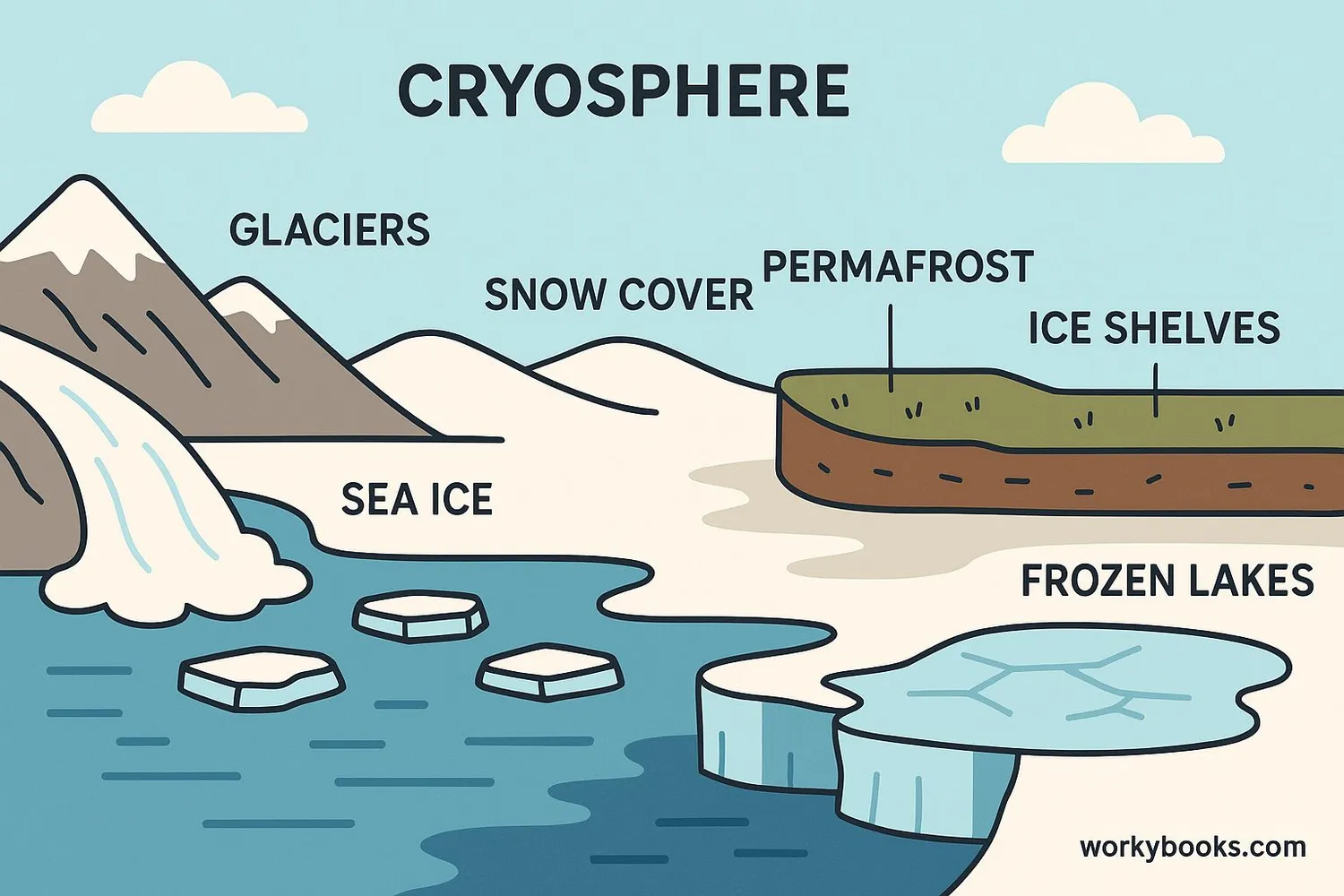
The cryosphere has several important parts that work together in Earth's climate system:
Snow
Seasonal snow cover that forms a temporary blanket over land
Sea Ice
Frozen ocean water that forms and melts with the seasons
Glaciers
Rivers of ice that slowly flow downhill under their own weight
Ice Sheets
Massive glaciers covering Greenland and Antarctica
Permafrost
Ground that remains frozen for two or more consecutive years
Each part of the cryosphere plays a special role in our planet's systems. For example, snow reflects sunlight back to space, helping to keep Earth cool. Sea ice creates habitat for polar animals, and glaciers store freshwater that millions of people depend on.
Ice Sheet Fact!
The Antarctic ice sheet is the largest single mass of ice on Earth, covering an area of almost 14 million square kilometers!
Importance of the Cryosphere
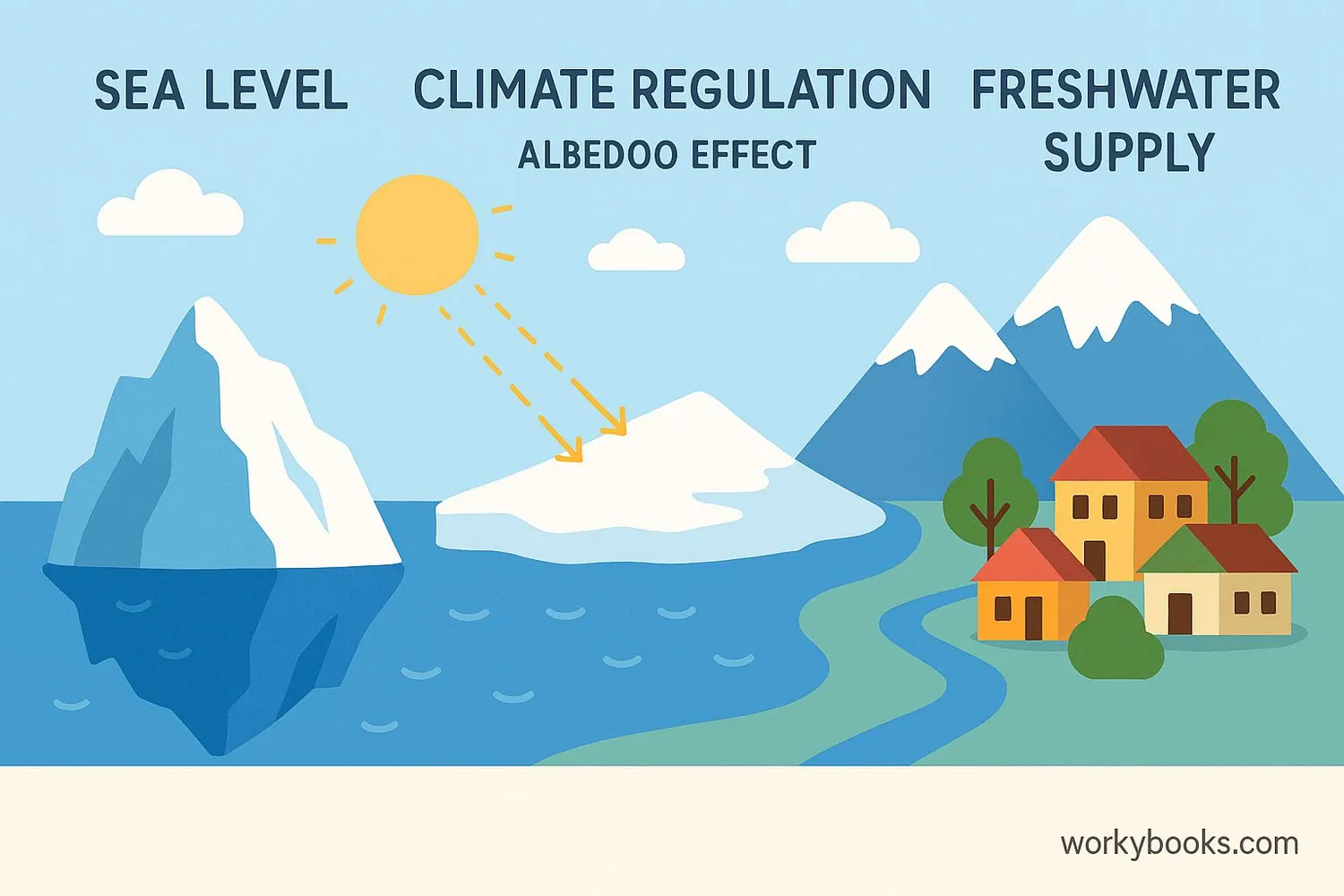
The cryosphere is incredibly important for our planet and for people. Here's why we need to understand and protect it:
Freshwater Storage
Glaciers and ice sheets store most of Earth's freshwater
Climate Regulation
Ice and snow reflect sunlight, helping to cool the planet
Sea Level Control
Ice on land regulates ocean levels worldwide
The cryosphere also supports unique ecosystems. Polar bears, seals, penguins, and many other animals depend on sea ice for their habitat. Many communities, especially indigenous peoples, have cultures and traditions built around the frozen parts of our planet.
Scientists study the cryosphere to understand past climates and predict future changes. Ice cores from glaciers contain bubbles of ancient air that tell us about Earth's atmosphere thousands of years ago!
Cryosphere and Climate Change

Climate change is having a major impact on the cryosphere. As Earth's temperature rises, ice and snow are melting at an accelerating rate. This creates important changes across our planet:
Melting Ice
Glaciers and ice sheets are shrinking worldwide
Sea Level Rise
Melting land ice adds water to the oceans
Less Reflection
Less ice means less sunlight reflected back to space
Thawing Permafrost
Frozen ground melts, releasing greenhouse gases
Ecosystem Changes
Animals lose habitat as sea ice disappears
These changes create a feedback loop. As ice melts, darker ocean or land is exposed. These darker surfaces absorb more sunlight, causing more warming, which leads to more melting. This is called the ice-albedo feedback.
Scientists are closely monitoring these changes because what happens in the cryosphere affects the entire planet. Understanding these processes helps us prepare for future changes and work toward solutions.
Climate Fact!
Since 1979, Arctic sea ice has declined by about 13% per decade. The oldest and thickest Arctic ice has declined by 95% over the past 30 years.
Cryosphere Quiz
Test your knowledge about the cryosphere with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about the cryosphere:
Cryosphere Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about the cryosphere!
Ice Depth
The Antarctic ice sheet is so thick in places that it's over 4 kilometers (2.5 miles) deep! That's taller than 10 Empire State Buildings stacked on top of each other.
Ancient Ice
Some Antarctic ice is over 1 million years old! Scientists drill ice cores to study tiny air bubbles trapped in the ice, which reveal what Earth's atmosphere was like long ago.
Freshwater Storage
The cryosphere holds about 75% of the world's freshwater. If all of Earth's glaciers melted, sea levels would rise about 70 meters (230 feet), flooding coastal cities worldwide.
Not Always White
Ice isn't always clear or white! Glacier ice often appears blue because dense ice absorbs other colors of the spectrum and reflects blue light. Some Arctic ice appears green from algae growing within it.





