Phenology - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how nature's calendar works with seasonal changes in plants and animals
What is Phenology?

Phenology is the study of how plants and animals change with the seasons throughout the year. It's like nature's calendar!
Scientists who study phenology observe and record seasonal events like when flowers bloom, when birds migrate, when leaves change color, or when animals hibernate. These events happen in a pattern that repeats every year, following nature's biological rhythms.
For example, in many places:
• Cherry blossoms appear in spring
• Fireflies light up summer nights
• Maple leaves turn red in autumn
• Geese fly south for winter
Nature's Calendar
Phenology comes from Greek words: "phaino" (to show or appear) and "logos" (to study). It's literally the study of appearances!
How Phenology Works
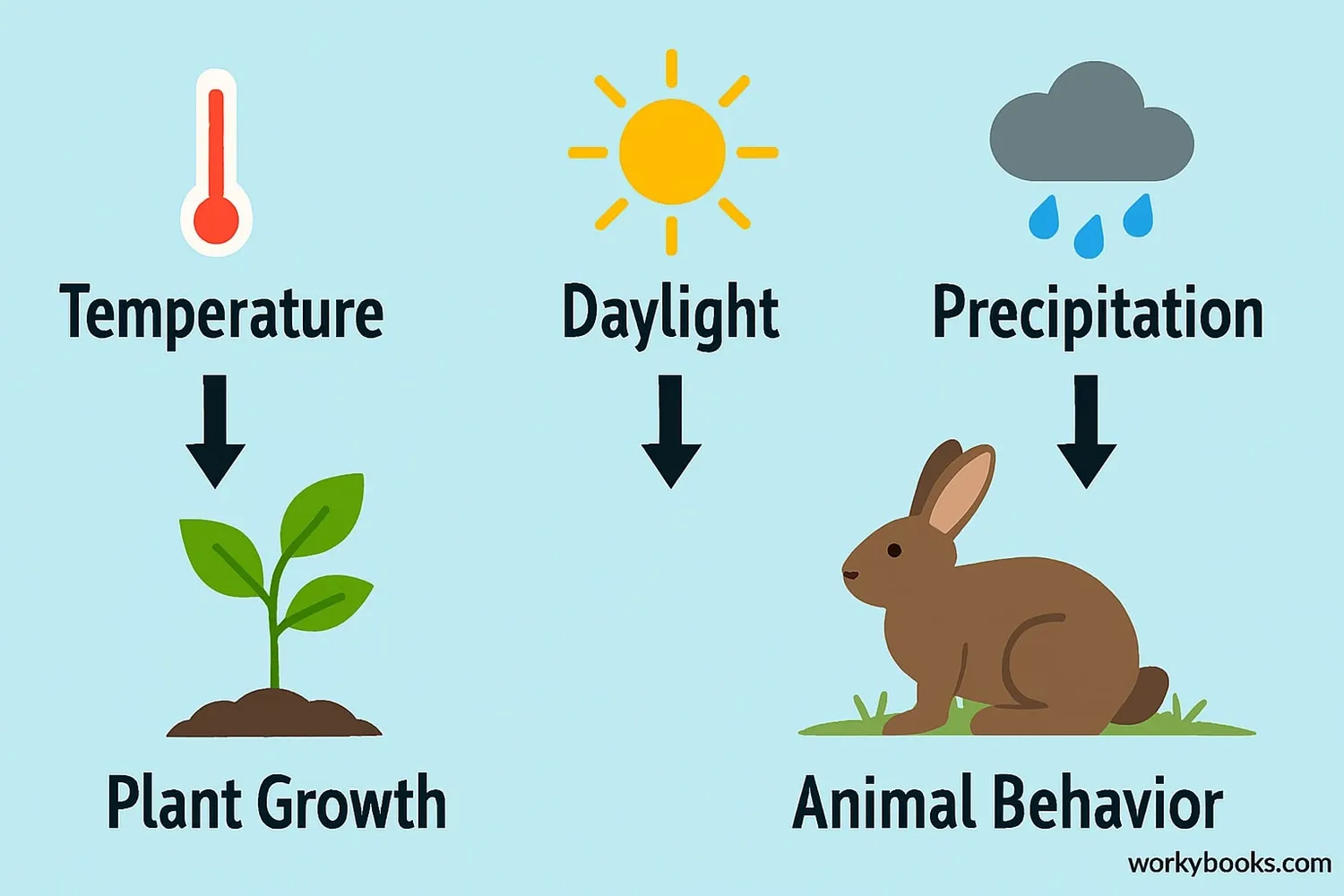
Plants and animals respond to environmental cues that signal when it's time to change their behavior or life cycle. The main triggers are:
Temperature
Warmer temperatures signal plants to bloom and animals to become active
Daylight
Changing day length triggers migration and hibernation
Precipitation
Rain patterns determine when plants grow and animals breed
These environmental signals create seasonal patterns in nature. For example:
• When days get longer and warmer in spring, trees grow new leaves
• When days shorten and cool in fall, animals prepare for winter
• After winter rains, desert flowers bloom in spectacular displays
Phenologists track these changes year after year to understand nature's timing.
Nature's Clock
Some plants are so sensitive to temperature that scientists can predict bloom times by adding up "growing degree days" - a measure of accumulated warmth.
Why Phenology is Important
Understanding phenology helps us in many ways:
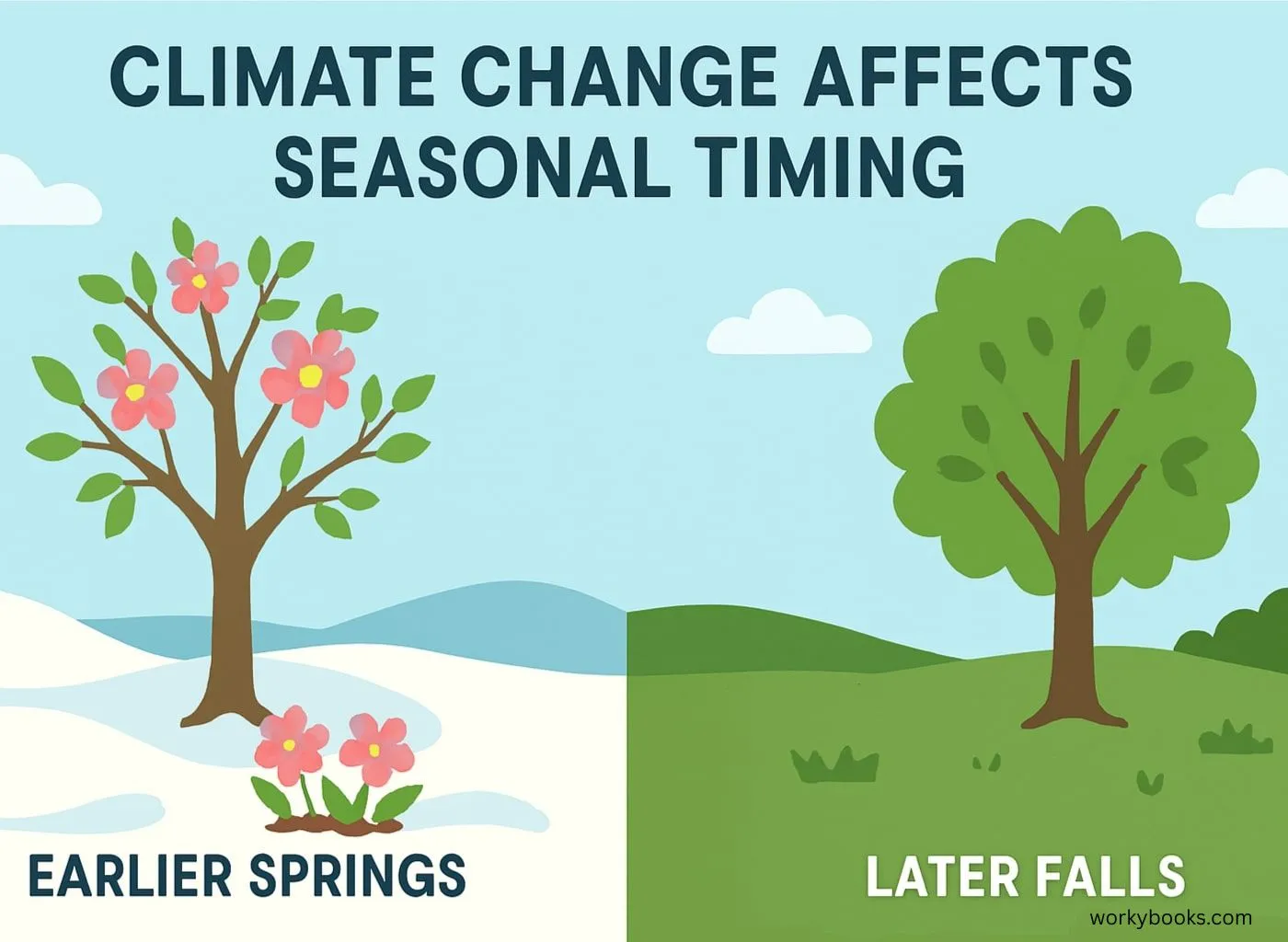
Climate Science
Reveals how climate change affects seasonal timing
Agriculture
Helps farmers know when to plant and harvest
Conservation
Protects ecosystems by understanding timing mismatches
As our climate changes, phenology helps scientists track important shifts:
• Springs are arriving earlier in many places
• Flowers are blooming before pollinators are active
• Migrating birds arrive after insect populations peak
• Growing seasons are becoming longer
By studying these seasonal phenomena, we can better understand how nature adapts to changing conditions and help protect ecosystems.
Phenology Quiz
Test your knowledge about seasonal changes in nature with this quiz!
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about phenology:
Nature Trivia
Discover fascinating facts about seasonal changes in nature:
Historical Records
Some of the longest phenology records come from Japan, where cherry blossom festivals have been documented for over 1,200 years!
Bird Migration
The Arctic Tern has the longest migration of any bird - flying from the Arctic to Antarctica and back each year, following seasonal changes.
Tree Rings
Each ring in a tree trunk represents one growing season. Wider rings mean better growing conditions that year - a form of natural phenology record!
Climate Clues
Phenology records from the 1700s and 1800s help scientists understand climate patterns before modern weather records existed.





