Fossil Evidence - Definition, Facts, Example, Quiz, Trivia
Discover the clues from the past that tell us about Earth's history and the evolution of life!
What are Fossils?
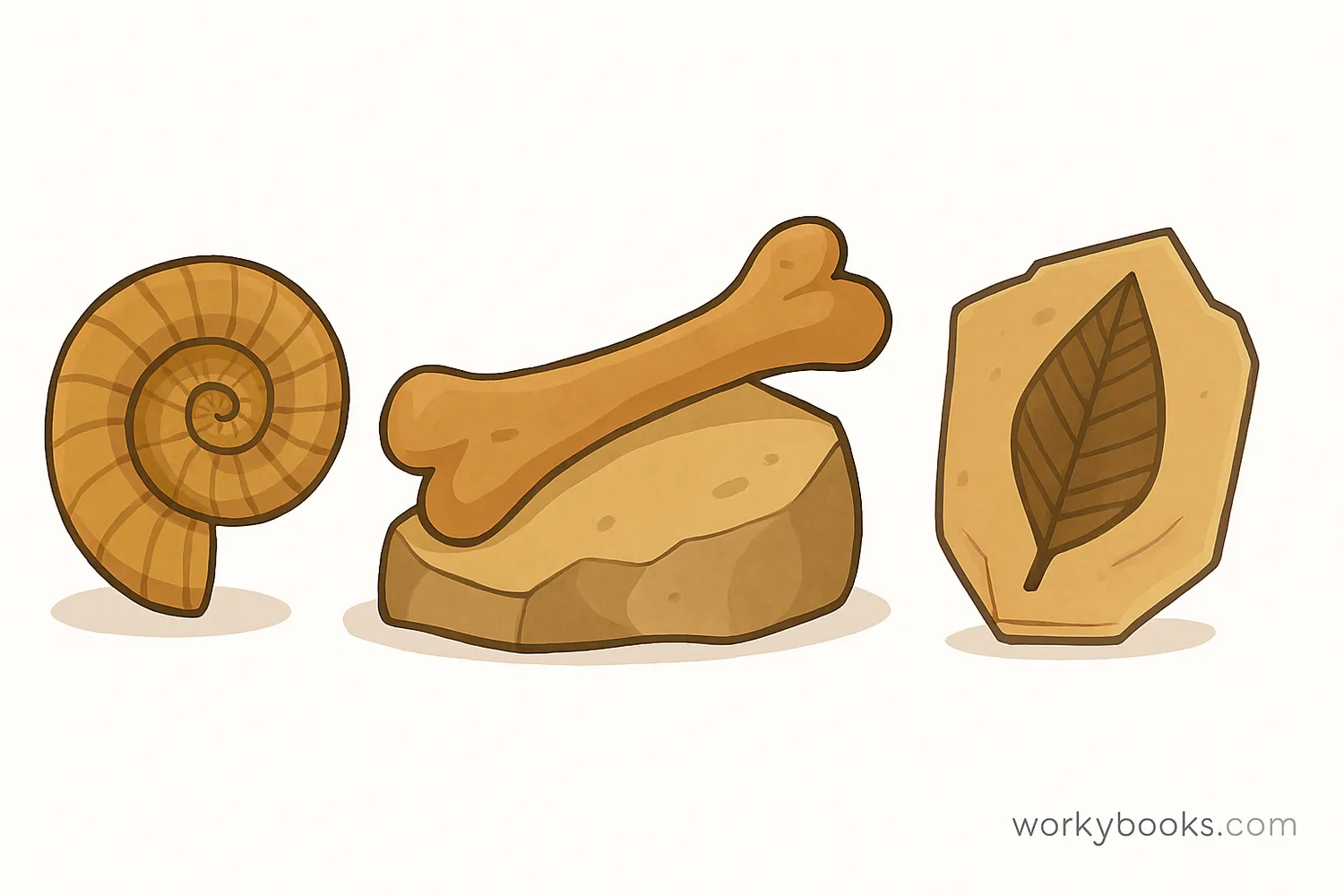

Fossils are like nature's history books! They are the preserved remains or traces of animals, plants, and other organisms from the past. The word "fossil" comes from the Latin word "fossilis" which means "dug up."
Most fossils form when living things die and are quickly buried by sediment like mud or sand. Over millions of years, the hard parts of these organisms become preserved in rock. Fossils help scientists understand what life was like long before humans existed.
Science Fact!
The oldest fossils are about 3.5 billion years old! These are fossils of microscopic organisms called cyanobacteria that lived in the oceans.
Types of Fossils
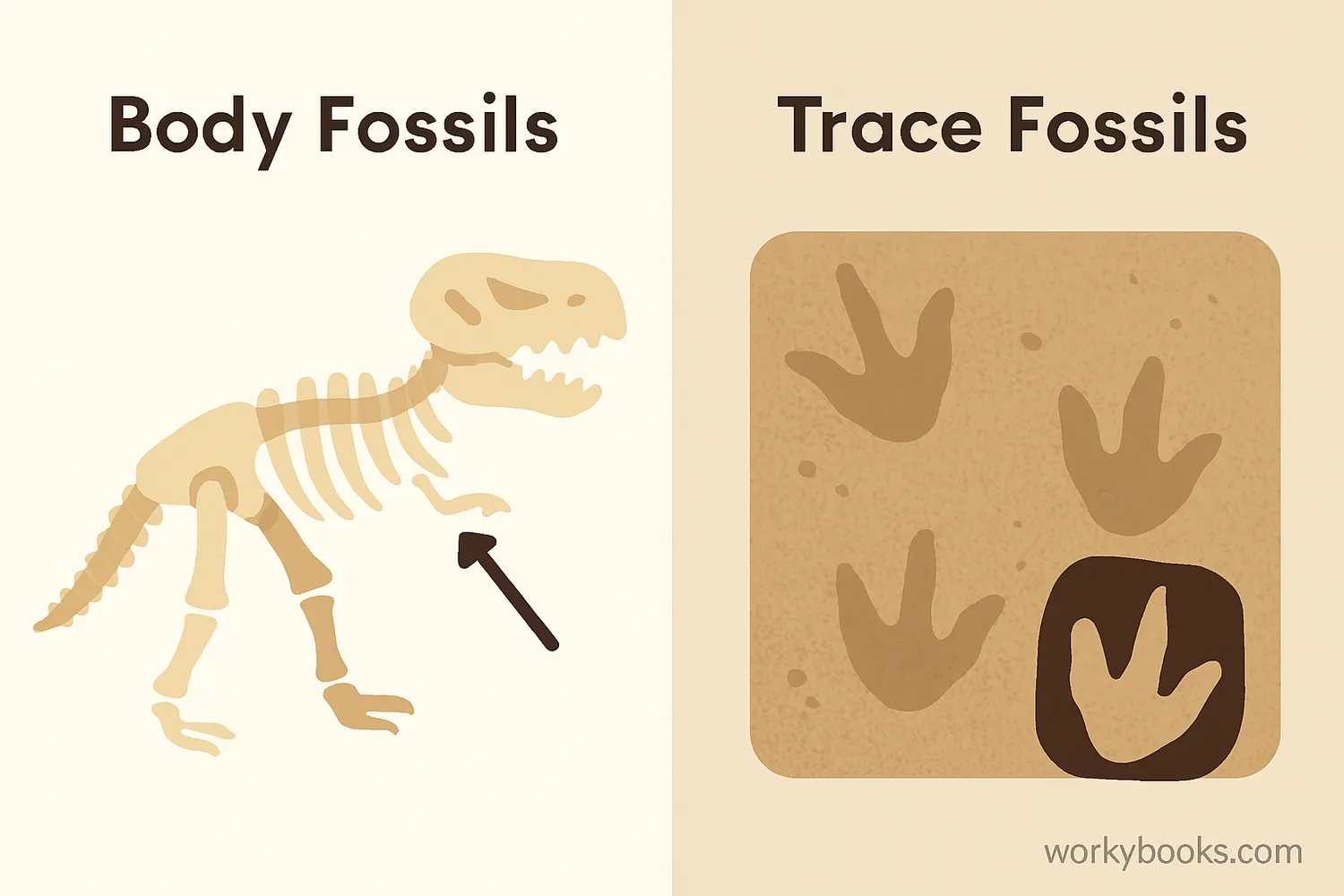
Fossils come in many different forms. Scientists classify them into two main categories: body fossils and trace fossils. Each type gives us different clues about life in the past.
Body Fossils
These are the actual preserved parts of an organism. They include bones, teeth, shells, and sometimes even whole animals preserved in amber or ice.
Trace Fossils
These are evidence of an organism's activity rather than the organism itself. They include footprints, burrows, bite marks, and fossilized droppings (called coprolites).
Mold and Cast Fossils
A mold fossil forms when an organism is buried and then decays, leaving an empty space in the shape of the organism. If minerals fill this space, they create a cast fossil.
Petrified Fossils
These form when minerals replace the original organic material, turning it to stone. Petrified wood is a common example of this type of fossil.
How Fossils Form
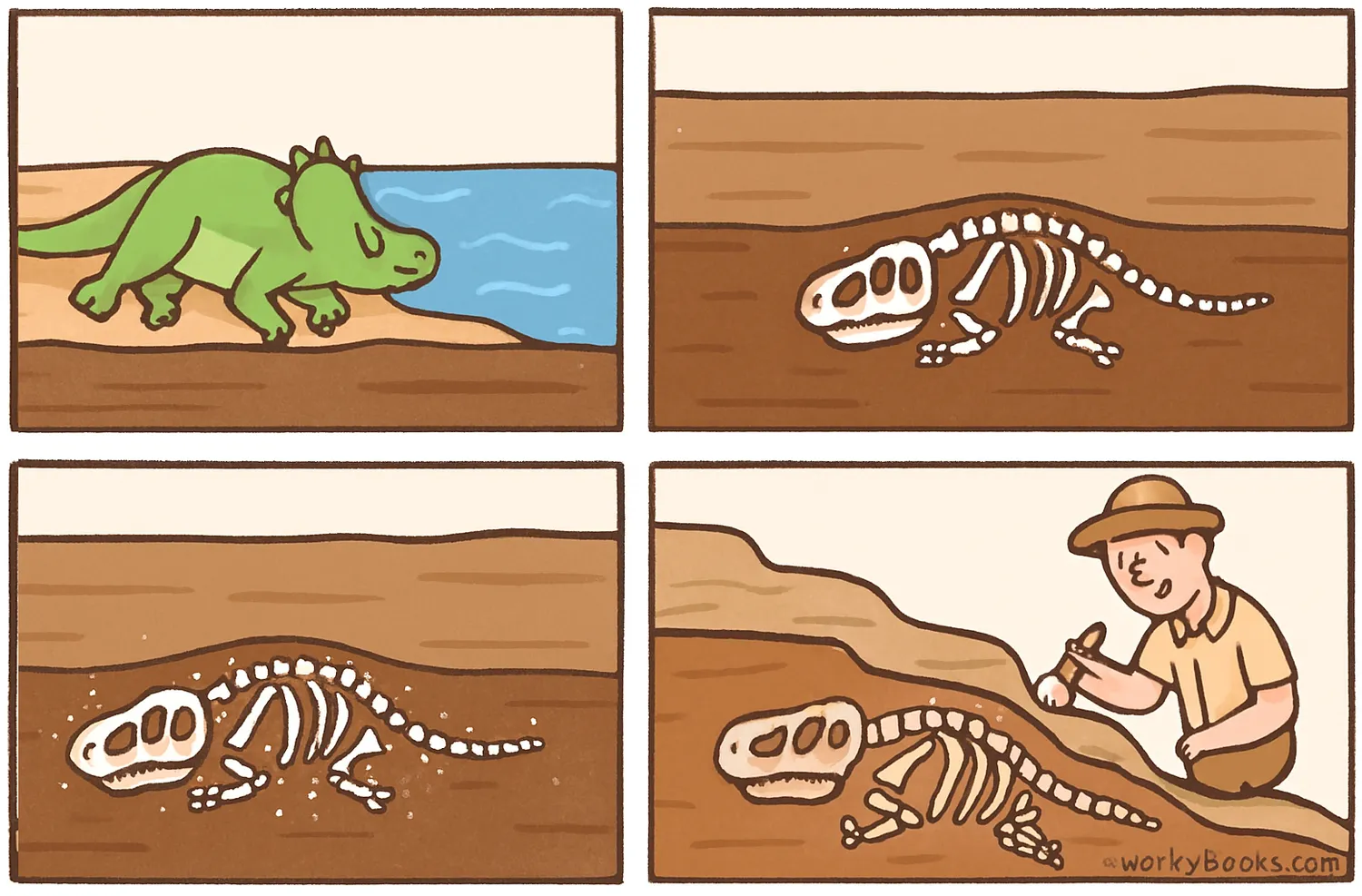
Fossil formation is a rare process that requires very specific conditions. Most living things decompose completely after death. Only a tiny fraction become fossils. Here's how it happens:
Death & Burial
An organism dies and is quickly buried by sediment like mud, sand, or volcanic ash. This protects it from scavengers and slows down decomposition.
Decomposition
Over time, the soft tissues decay, leaving only the hard parts like bones, teeth, or shells.
Mineralization
Minerals from groundwater seep into the remains and gradually replace the original material, turning it to stone.
Discovery
Millions of years later, erosion or human activity exposes the fossil, allowing scientists to find and study it.
Did You Know?
It takes at least 10,000 years for something to become a fossil. Most fossils are millions of years old!
Fossil Evidence of Evolution
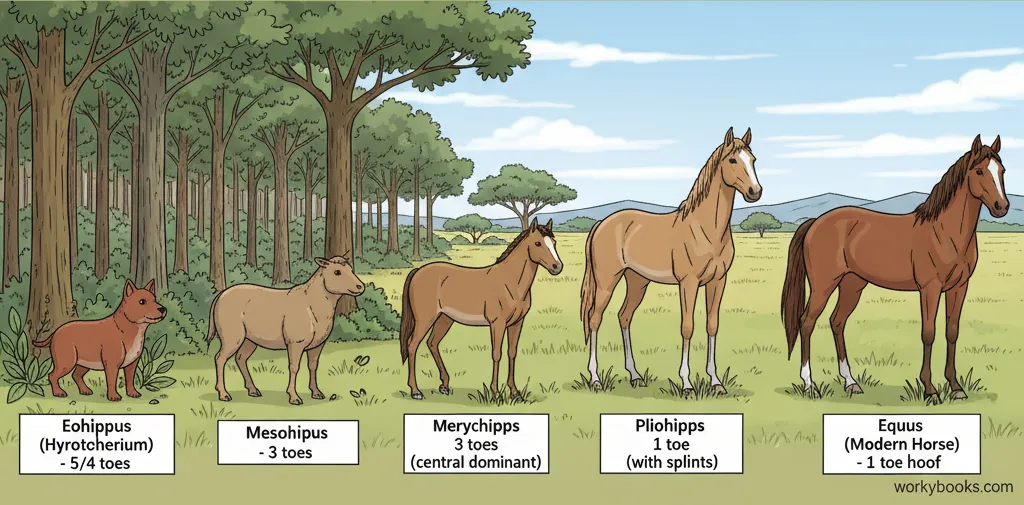
Fossils provide some of the most important evidence for evolution. They show us that life on Earth has changed dramatically over time. By studying fossils, scientists can see how species have evolved and how they're related to each other.
One of the most famous examples of fossil evidence for evolution is the horse. Fossil records show how horses evolved from small, dog-sized animals with multiple toes to the large, single-hoofed animals we know today.
Transitional Fossils
These fossils show intermediate forms between different groups of organisms. For example, Archaeopteryx has features of both dinosaurs and birds, showing the evolutionary link between them.
Extinction Events
Fossils show that many species have gone extinct throughout Earth's history. Mass extinction events, like the one that killed the dinosaurs, created opportunities for other species to evolve and diversify.
Biogeography
The geographic distribution of fossils shows how continents have moved and how species have migrated and evolved in different locations.
The Fossil Record

The fossil record is like a giant photo album of Earth's history. It's the collection of all fossils that have been found and the information we've gathered from them. While the fossil record is incomplete (because fossilization is so rare), it still provides overwhelming evidence for evolution and helps scientists understand the history of life on Earth.
The fossil record shows a clear pattern: simple life forms appear first in the rocks, with more complex forms appearing later. This supports the idea that life has evolved from simple to more complex forms over billions of years.
Science Fact!
Scientists have identified over 250,000 fossil species, but this is just a tiny fraction of all the species that have ever lived on Earth!
Fossil Evidence Quiz
Test your knowledge about fossils with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about fossil evidence:
Science Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about fossils and fossil evidence!
Dinosaur Giants
The largest dinosaur fossil ever found is a Titanosaur from Argentina. It was about 122 feet long and would have weighed around 70 tons - that's as much as 10 adult elephants!
Ancient Colors
Scientists have discovered fossils that preserve evidence of original colors! By studying microscopic structures in fossilized feathers, they can determine what colors dinosaurs had.
Shark Teeth Galore
Shark teeth are among the most common fossils because sharks shed thousands of teeth during their lifetime. Their teeth are made of durable dentin and enamel that fossilize well.
Frozen in Time
Some of the most complete fossils come from animals that were frozen in ice. Woolly mammoths found in Siberia have been so well preserved that scientists can study their skin, hair, and even stomach contents!





