Paleontology - Definition, Facts, Example, Quiz, Trivia
Discover the fascinating world of ancient life and how scientists study Earth's history!
What is Paleontology?
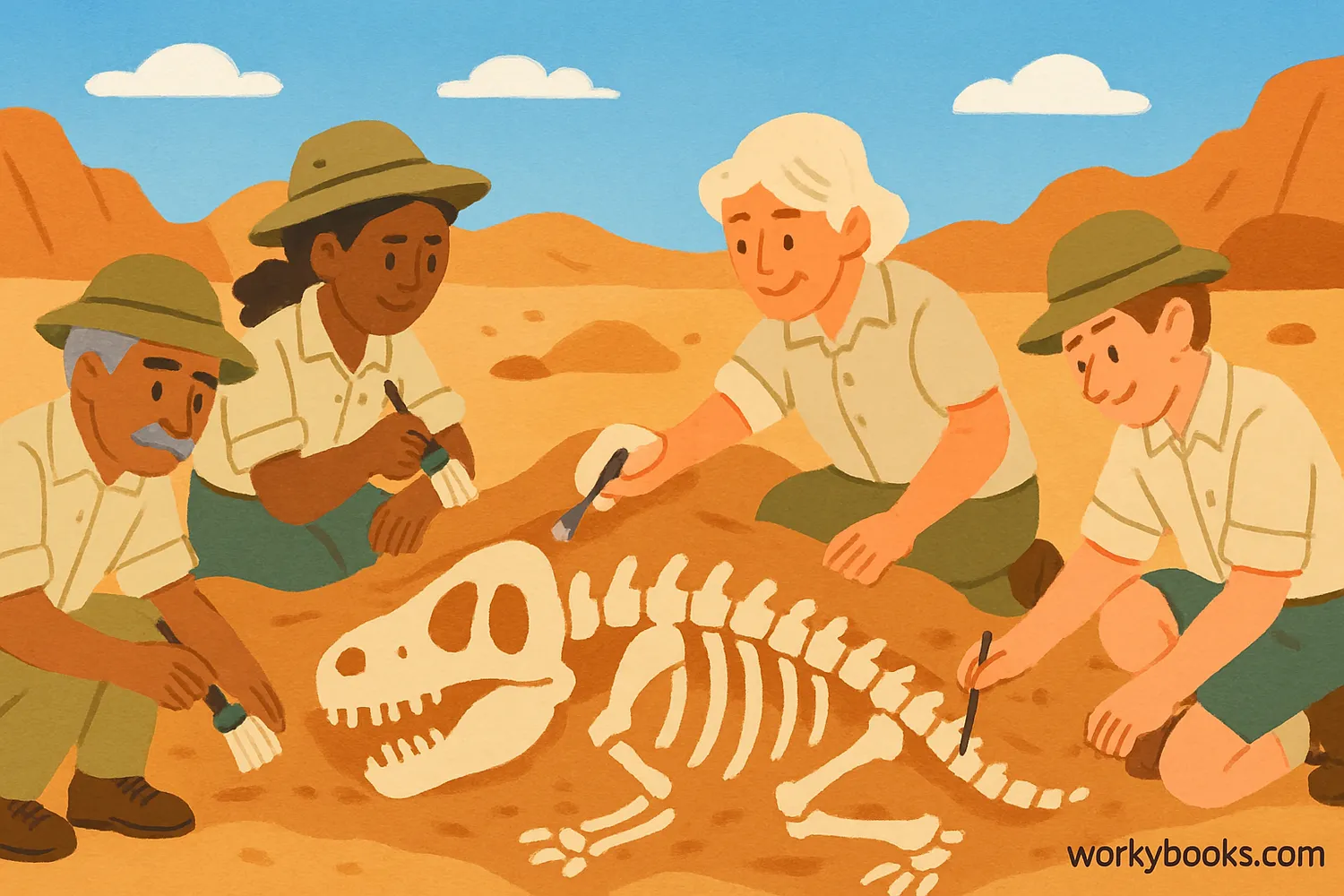

Paleontology is the scientific study of ancient life through the examination of plant and animal fossils. The word "paleontology" comes from Greek words meaning "ancient" (paleo), "being" (ontos), and "study" (logos).
Paleontologists are like detectives who piece together clues from the past to understand what life was like millions of years ago. They help us understand how life has changed over time and how living things are connected through evolution.
Science Fact!
Paleontology combines knowledge from biology, geology, chemistry, and even physics to understand ancient life forms!
What Are Fossils?

Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of ancient organisms. They form when plants or animals are buried quickly after death, and their remains are replaced by minerals over millions of years. This process is called fossilization.
Body Fossils
These are the actual preserved parts of an organism, like bones, teeth, or shells.
Trace Fossils
These are evidence of an organism's activity, like footprints, burrows, or droppings.
Imprint Fossils
These form when an organism leaves an impression in soft sediment that later hardens into rock.
Fossilization is a rare process. Most organisms decompose completely after death. Only under special conditions, like rapid burial in sediment with little oxygen, do remains become fossils.
The Fossil Record
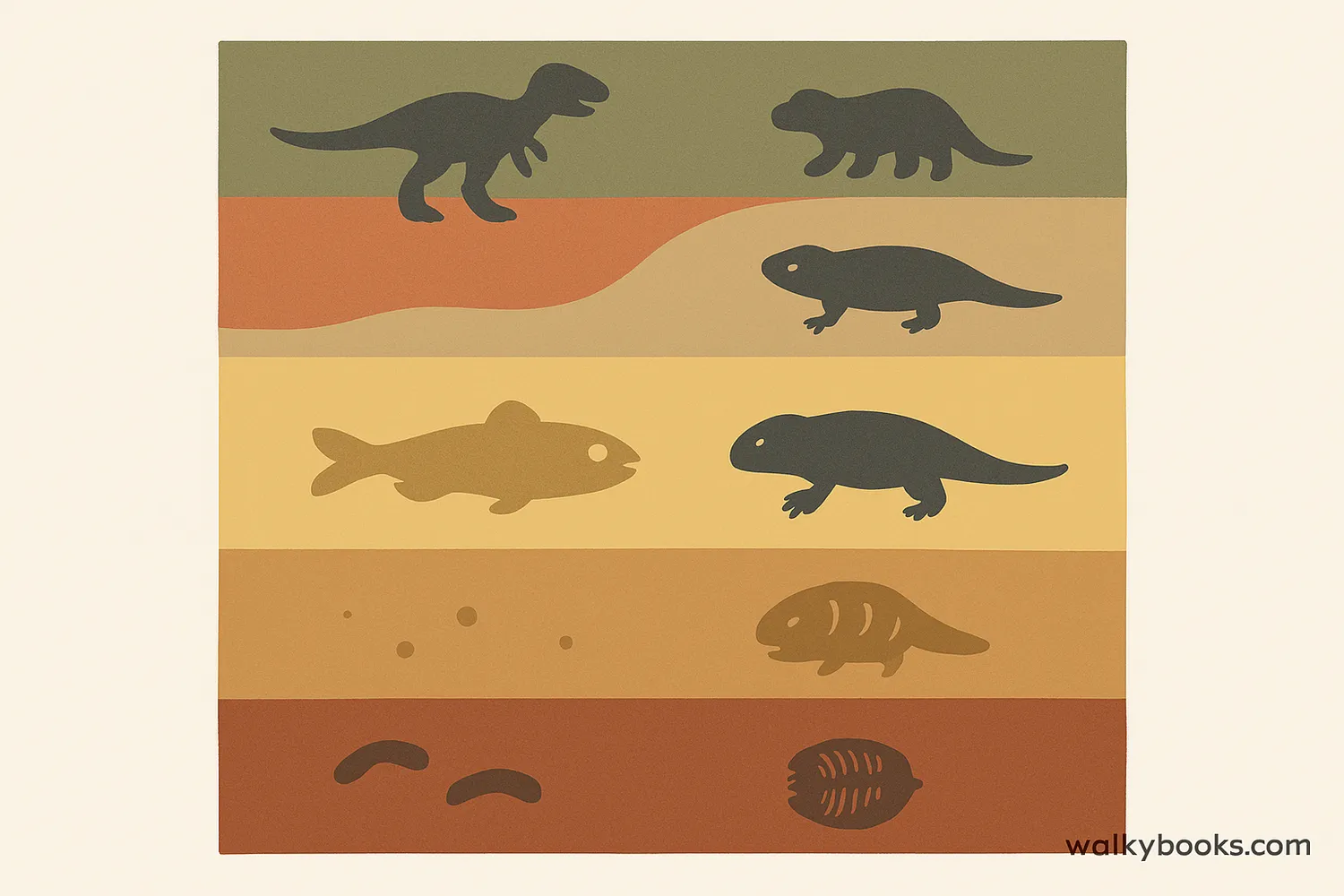

The fossil record is all the fossils that have been discovered and the information they provide about the history of life on Earth. It's like a giant picture book of Earth's history, with each fossil being a page that tells us about life from long ago.
The fossil record shows us that life on Earth has changed dramatically over time. Simple life forms appeared first, with more complex organisms developing later. This record helps scientists understand evolution and how species are related.
Relative Dating
Determining the age of fossils by their position in rock layers
Absolute Dating
Using radioactive elements to determine exact ages of fossils
Comparison
Comparing fossils to understand evolutionary relationships
Dinosaurs
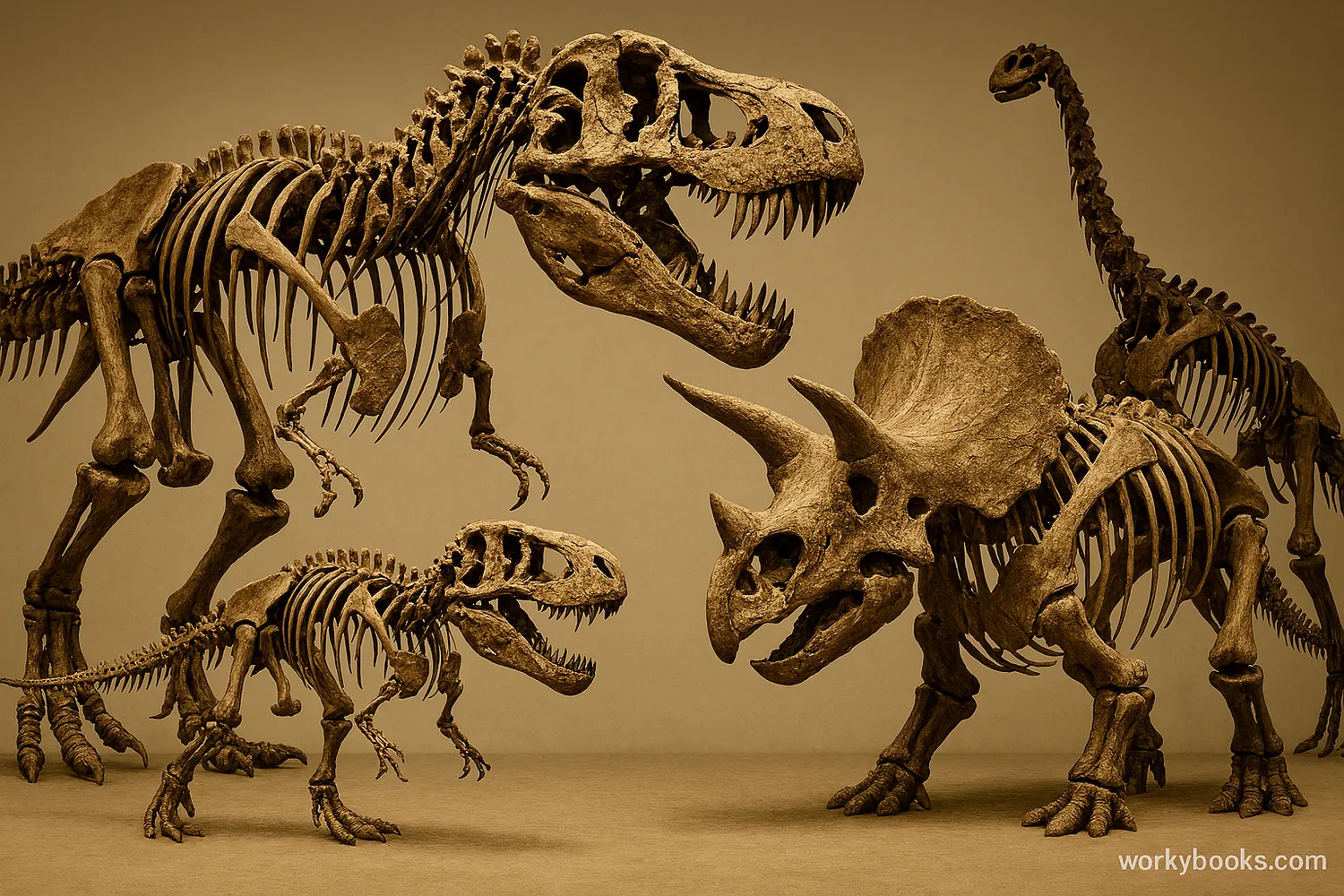

Dinosaurs were a diverse group of reptiles that first appeared about 230 million years ago. They dominated life on land for over 150 million years before most went extinct about 65 million years ago. The word "dinosaur" means "terrible lizard," but dinosaurs weren't actually lizards - they were a special group of reptiles with unique features.
Did You Know?
Birds are actually living dinosaurs! They evolved from small feathered dinosaurs millions of years ago.
There were many different types of dinosaurs. Some were enormous like Argentinosaurus, which was as long as three school buses! Others were small, like the chicken-sized Compsognathus. Some ate plants, while others were fierce predators.
Evolution and Paleontology
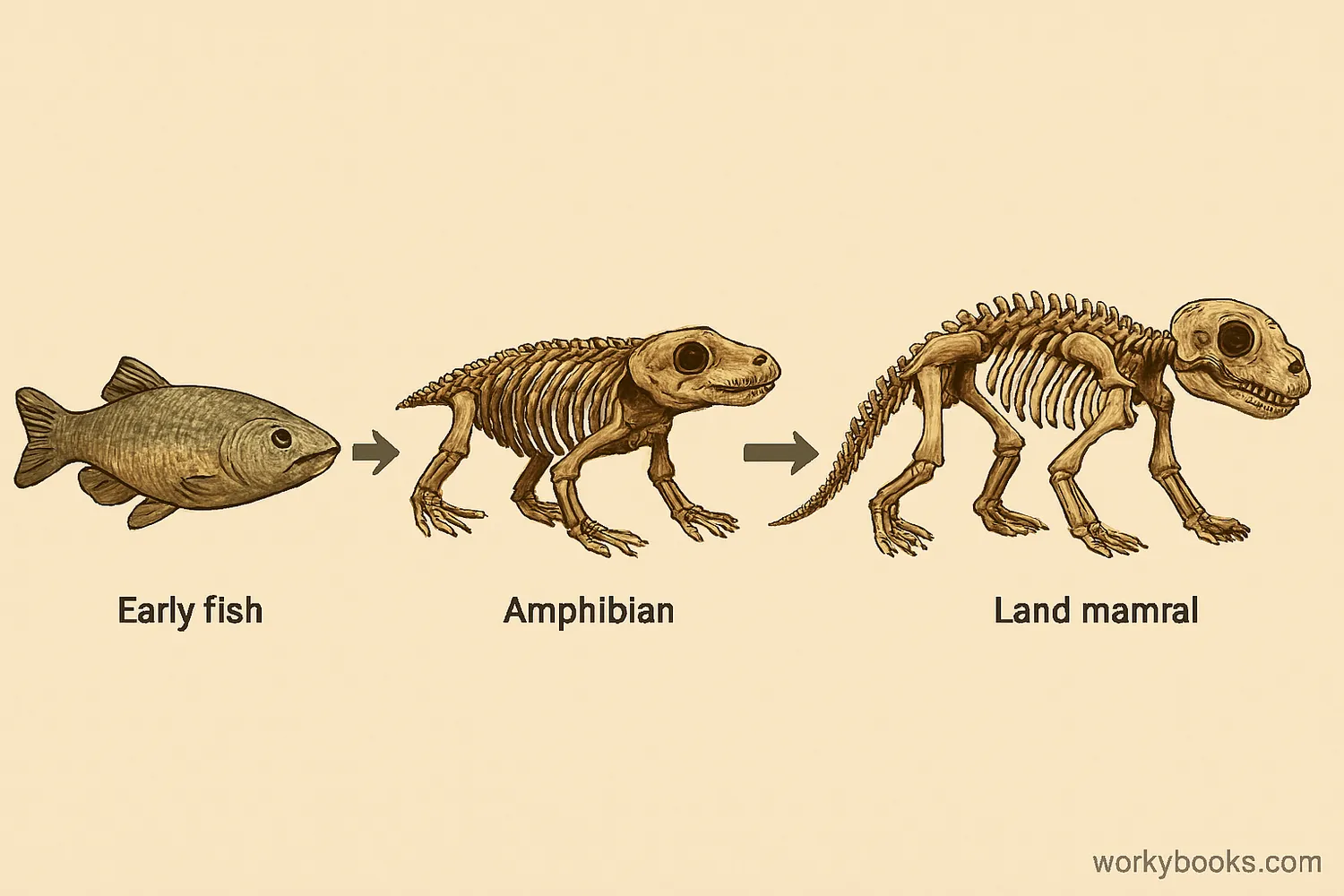
Paleontology provides important evidence for evolution - the process by which living things change over generations. Fossils show us how species have changed over millions of years and how different groups are related.
One famous example is the evolution of whales. Fossil evidence shows that whales evolved from land mammals that gradually adapted to life in the water. Paleontologists have found many transitional fossils that show each step in this amazing transformation.
Transitional Fossils
Fossils that show intermediate forms between different groups
Stratigraphic Evidence
How fossils appear in rock layers shows the sequence of evolution
Comparative Anatomy
Similarities in fossil structures show evolutionary relationships
Extinction Events

Throughout Earth's history, there have been times when large numbers of species died out in a relatively short period. These are called mass extinction events. The most famous is the extinction that killed the dinosaurs 65 million years ago.
Scientists believe this extinction was caused by a massive asteroid impact that threw so much dust into the atmosphere that it blocked sunlight, causing plants to die and disrupting food chains worldwide.
The Big Five
Earth has experienced five major mass extinction events. The most severe was 250 million years ago when about 96% of marine species went extinct.
Paleontology Careers
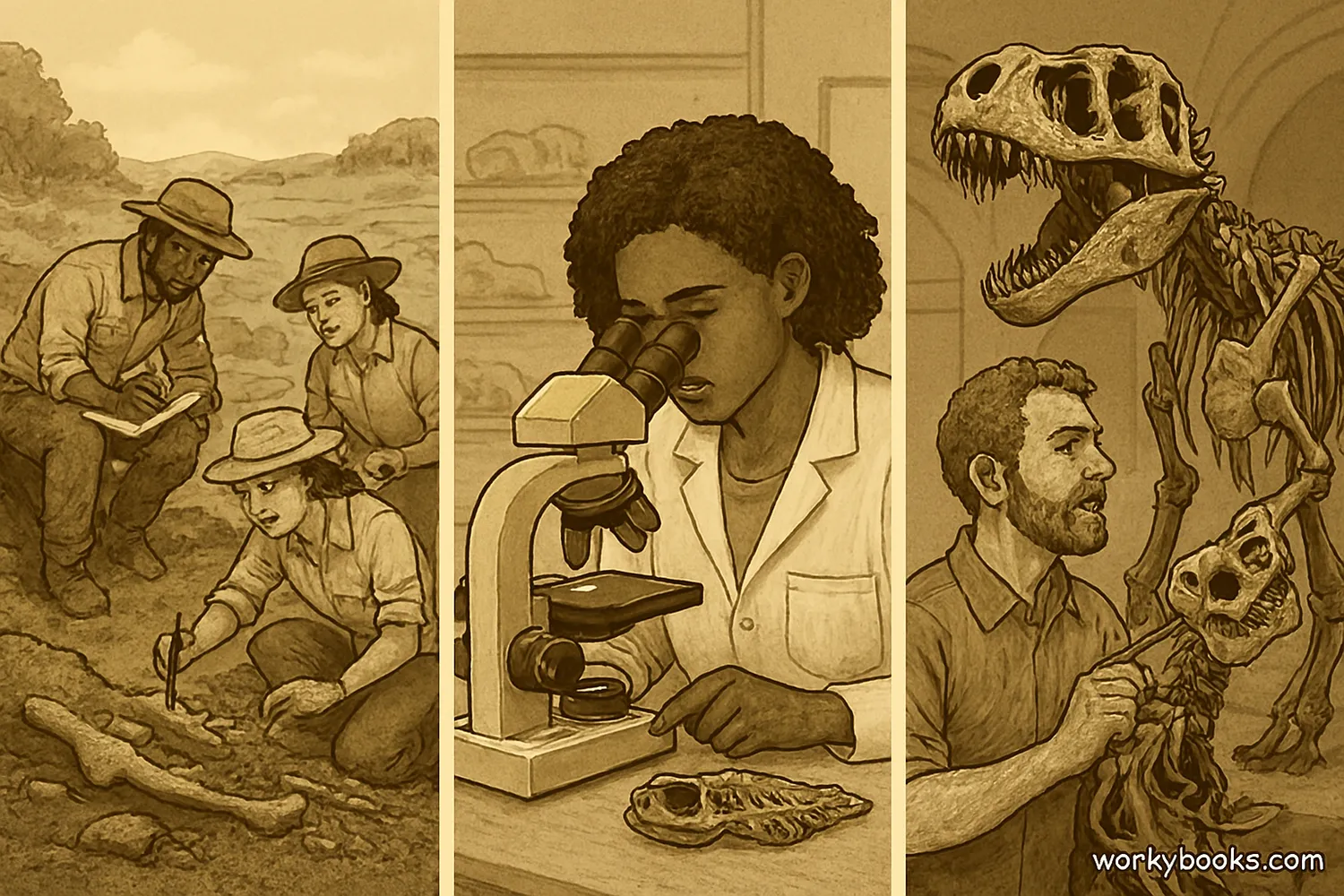

Paleontology offers many exciting career paths for people interested in ancient life. Paleontologists work in museums, universities, government agencies, and even in the petroleum industry.
Field paleontologists travel to dig sites to search for and excavate fossils. Laboratory paleontologists study fossils using microscopes and other scientific equipment. Museum paleontologists prepare fossils for display and educate the public about ancient life.
Education
Most paleontologists have degrees in geology, biology, or paleontology
Field Work
Searching for and carefully excavating fossils at dig sites
Research
Studying fossils to learn about ancient life and environments
Paleontology Quiz
Test your paleontology knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about paleontology:
Science Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about paleontology!
Not All Big Reptiles Were Dinosaurs
Plesiosaurs, pterosaurs, and mosasaurs lived during the time of dinosaurs but were not actually dinosaurs. Dinosaurs had a specific hip structure that these other reptiles didn't have.
Living Fossils
Some organisms have remained virtually unchanged for millions of years. The coelacanth fish was thought to be extinct for 65 million years until one was caught alive in 1938!
Oldest Fossils
The oldest fossils are of microscopic organisms dating back about 3.5 billion years. These ancient life forms were similar to modern bacteria and lived in Earth's early oceans.
Size Extremes
The largest dinosaur was Argentinosaurus, which could reach 115 feet long and weigh up to 100 tons. The smallest dinosaur was Microraptor, about the size of a crow, with feathers on all four limbs.




