Alleles - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how tiny differences in your DNA create your unique traits!
What Are Alleles?
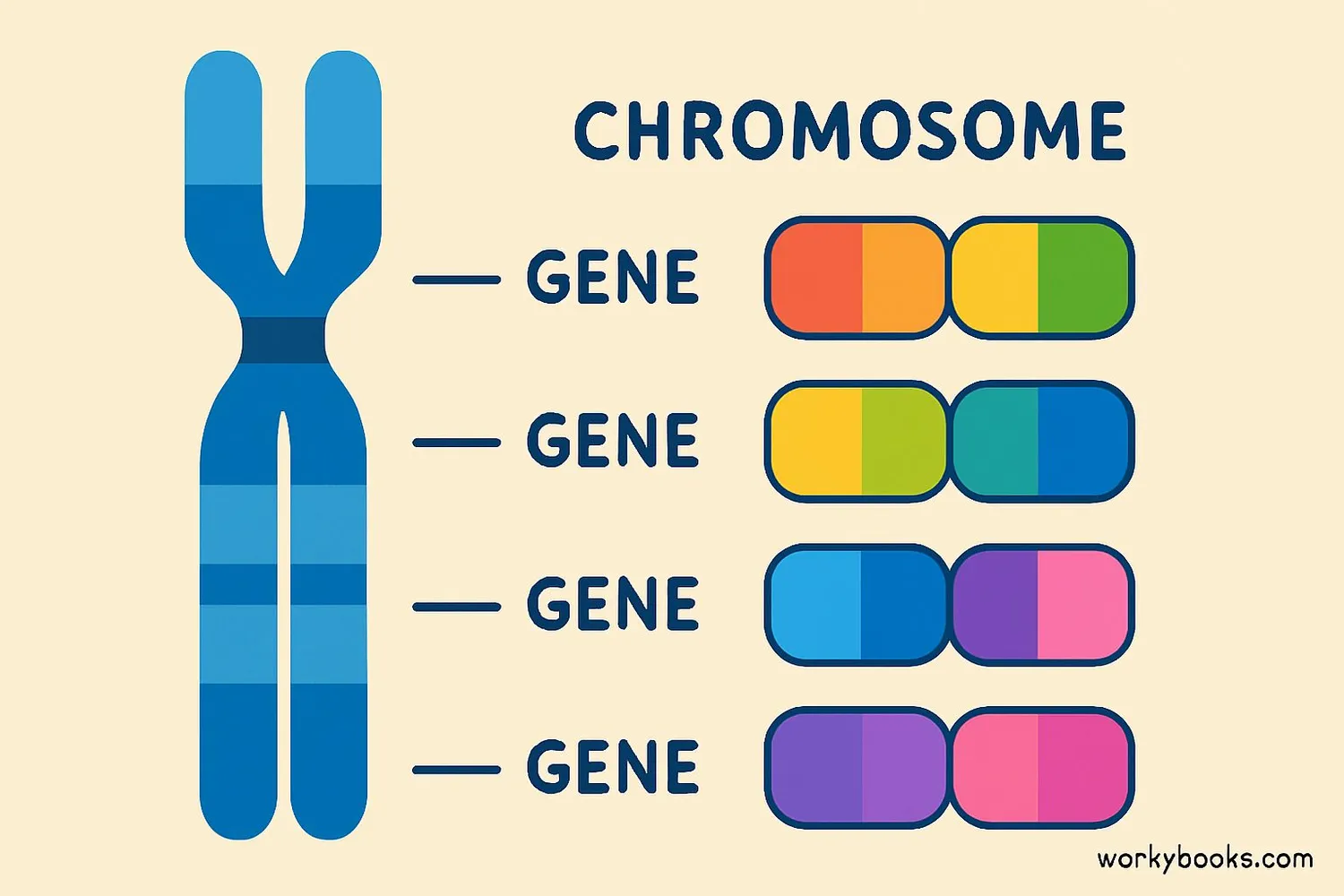
Alleles are different versions of the same gene. Think of genes as recipes in a cookbook (your DNA), and alleles as slightly different versions of those recipes.
Every person has two copies of each gene - one from their mother and one from their father. These two copies might be identical or different versions (alleles). For example, the gene for eye color has alleles for blue, brown, green, and other colors!
Here are some key terms:
• Gene: A section of DNA that codes for a specific trait
• Allele: A specific version of a gene
• Locus: The specific location of a gene on a chromosome
• Chromosome: Thread-like structures that carry your genes
Genetics Fact!
Humans have about 20,000-25,000 genes, and most genes have multiple possible alleles!
How Alleles Work
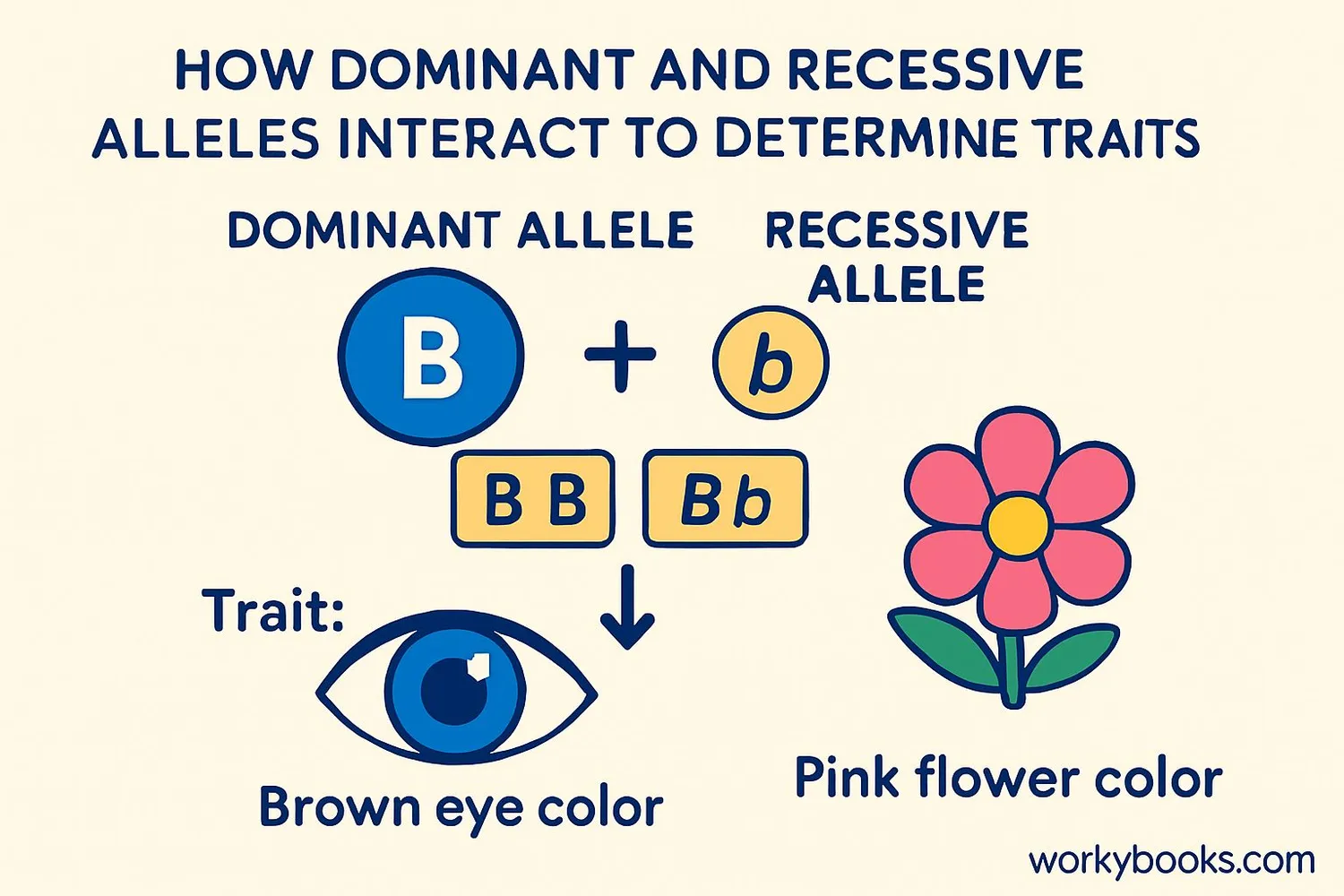
Alleles work together in pairs to determine your traits. How they combine creates your physical characteristics (phenotype), while the actual allele combination is your genotype.
There are two important types of alleles:
• Dominant Alleles: These are stronger and show their trait even if there's only one copy
• Recessive Alleles: These are weaker and only show their trait when there are two copies
Homozygous
When both alleles for a gene are identical (AA or aa)
Heterozygous
When the two alleles are different (Aa)
Phenotype
The physical trait you can see (brown eyes)
Genotype
The actual allele combination (BB, Bb, or bb)
For example, in pea plants:
• B = Dominant allele for purple flowers
• b = Recessive allele for white flowers
• BB = Purple flowers
• Bb = Purple flowers (dominant shows)
• bb = White flowers
Dominance Fact!
Some traits show incomplete dominance where the heterozygous phenotype is a blend (like pink flowers from red and white alleles).
Types of Alleles
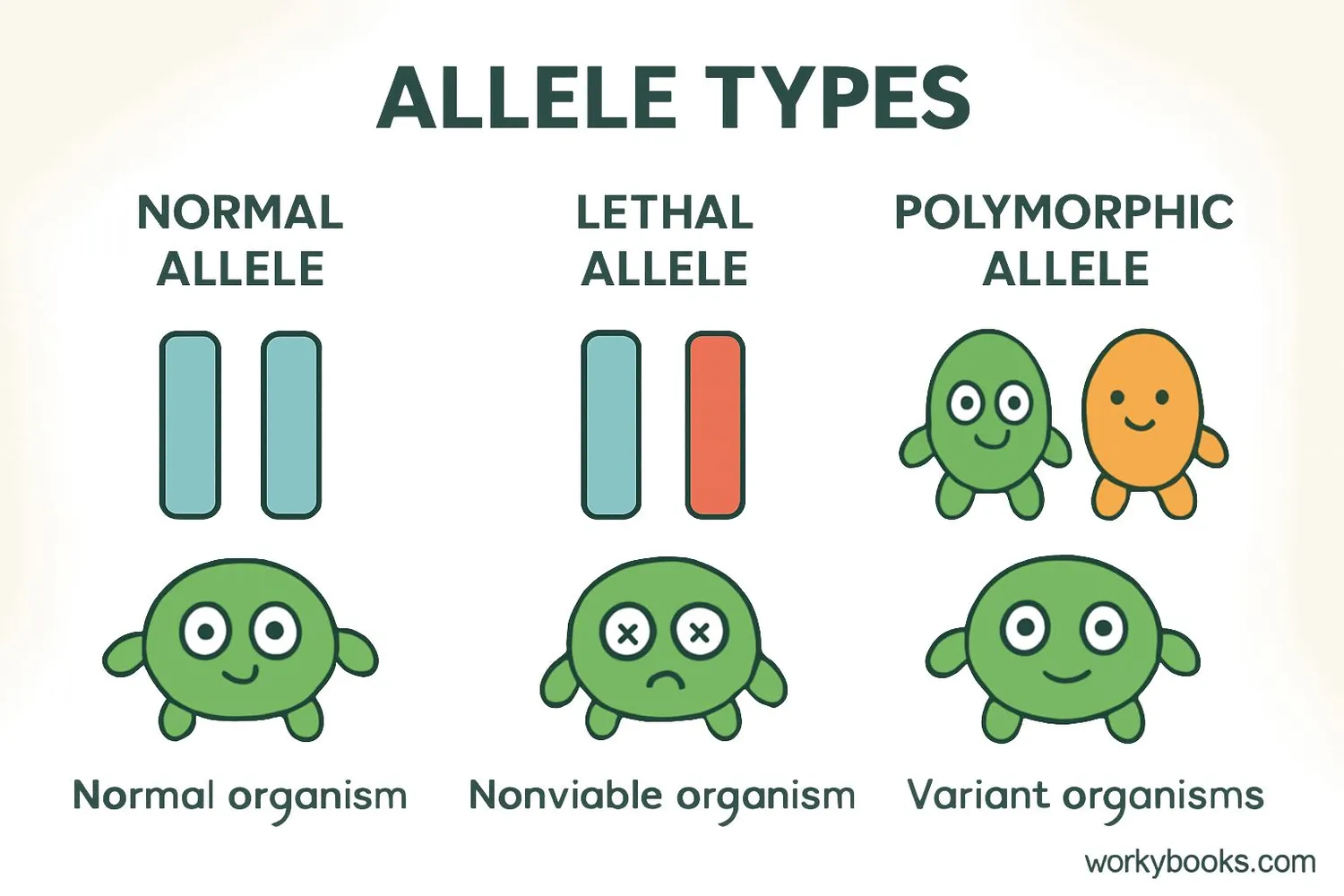
Not all alleles are created equal! There are several special types that have unique effects:
Lethal Alleles
Alleles that cause death when present in homozygous form
Polymorphisms
When multiple alleles exist in a population (like blood types)
Allele Frequency
How common an allele is in a population
Scientists study alleles to understand:
• Population Genetics: How alleles change in populations over time
• Natural Selection: How some alleles become more common because they help survival
• Hardy-Weinberg Law: A principle that explains how allele frequencies stay the same without evolutionary forces
• Mutations: Changes in DNA that create new alleles
Special types of alleles include:
• SNPs (Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms): Tiny differences in single DNA letters
• mtDNA (Mitochondrial DNA): Special DNA passed only from mother to child
Alleles Quiz
Test your genetics knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about alleles:
Fun Genetics Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about alleles and genetics!
DNA Length
If you uncoiled all the DNA in your body's cells, it would stretch to the sun and back about 600 times! That's about 10 billion miles of DNA in one person.
Identical Twins
Identical twins have exactly the same DNA, but as they grow, they develop different mutations and epigenetic changes, making them genetically different over time!
Banana Similarity
Humans share about 60% of their DNA with bananas! We share many basic genes for cellular functions with all living things.
Mutation Rate
Every time your cells divide, you get about 3 new mutations in your DNA. Most don't affect you, but they create new alleles in the population!





