Autotrophs - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how plants and other organisms make their own food!
What are Autotrophs?
Autotrophs are living organisms that can make their own food! The word "autotroph" comes from Greek words meaning "self-feeder." Unlike animals that need to eat other organisms for energy, autotrophs produce their own nourishment.
Most autotrophs use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to create glucose (sugar) through a process called photosynthesis. This glucose gives them energy to grow and survive. Plants are the most common autotrophs, but there are other types too!
Did You Know?
Autotrophs form the base of nearly every food chain on Earth! Without them, most other living things wouldn't have a food source.
Types of Autotrophs
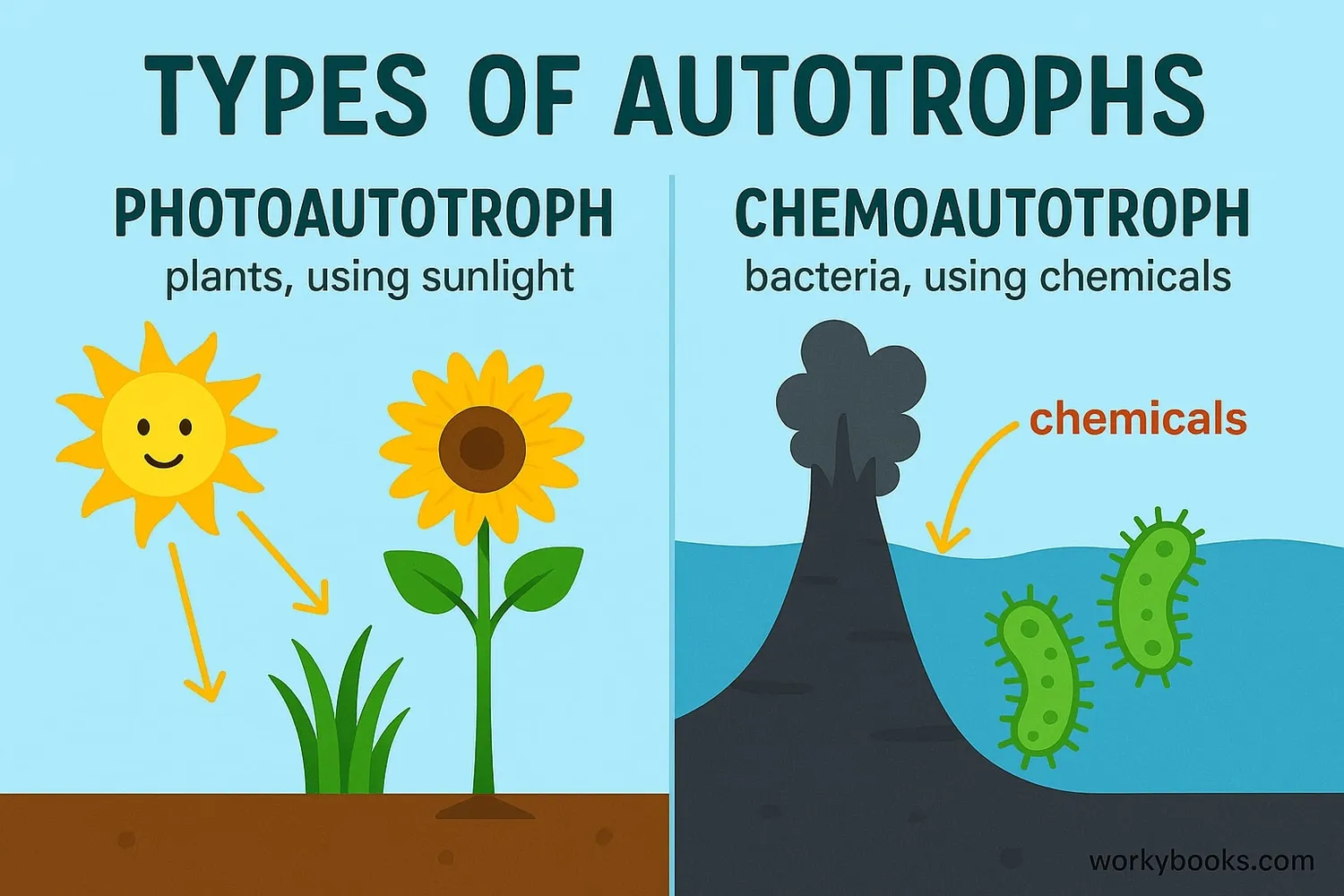
There are two main types of autotrophs, classified by how they get energy to make food:
Photoautotrophs
Use sunlight energy through photosynthesis. Examples: plants, algae, cyanobacteria.
Chemoautotrophs
Use chemical energy from inorganic compounds. Examples: bacteria in deep sea vents, sulfur bacteria.
Photoautotrophs are the most common type. They contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that captures sunlight energy. This energy converts carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
Chemoautotrophs are less common but equally fascinating! They live in extreme environments like deep ocean hydrothermal vents or hot springs. Instead of using sunlight, they get energy from chemicals like hydrogen sulfide.
Extreme Life!
Chemoautotrophs can survive in complete darkness at the bottom of the ocean, where no sunlight reaches!
Autotroph vs Heterotroph
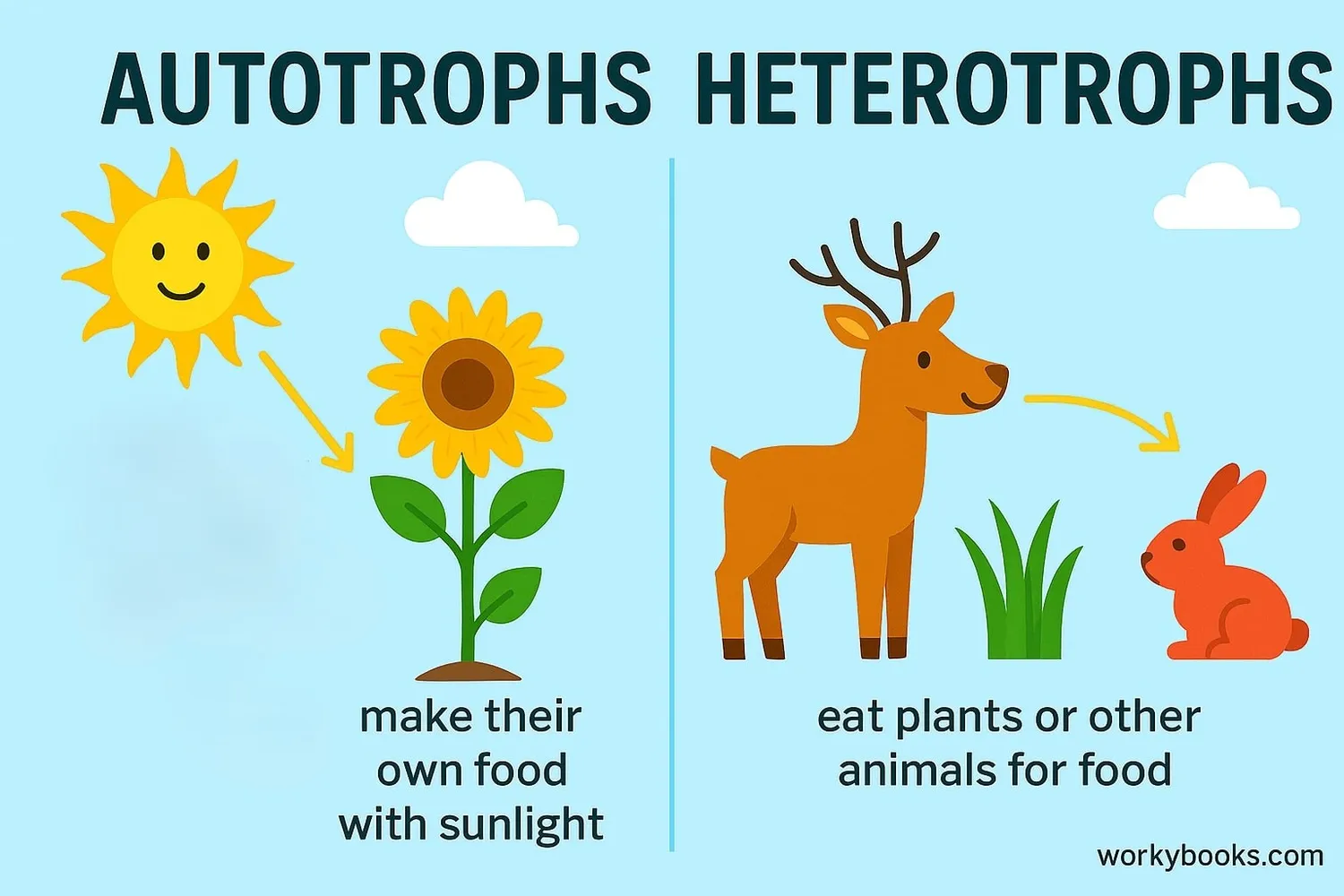
All living things need energy, but they obtain it in different ways. The main difference between autotrophs and heterotrophs is their food source:
| Feature | Autotrophs | Heterotrophs |
|---|---|---|
| Food Source | Make their own food | Eat other organisms |
| Energy Source | Sunlight or chemicals | Consuming autotrophs or other heterotrophs |
| Examples | Plants, algae, some bacteria | Animals, fungi, most bacteria |
| Role in Food Chain | Producers (first level) | Consumers (higher levels) |
While autotrophs are producers that form the base of food chains, heterotrophs are consumers that rely on autotrophs for energy. Even carnivores that eat other animals ultimately depend on autotrophs, since the animals they eat consumed plants or plant-eating animals.
Importance of Autotrophs
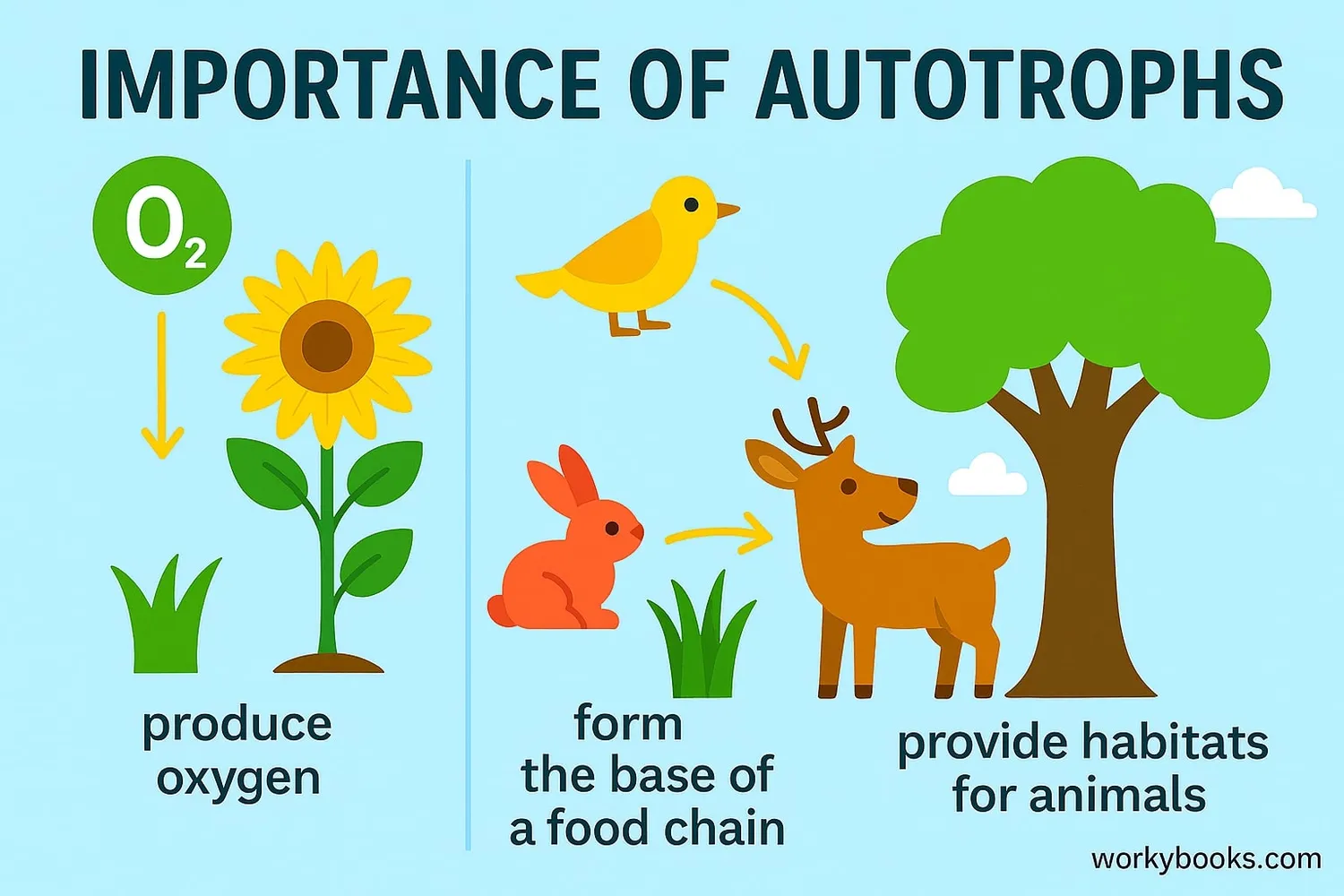
Autotrophs are incredibly important to life on Earth! Here's why we couldn't live without them:
Oxygen Production
Through photosynthesis, plants release oxygen that animals breathe
Food Source
They provide food for herbivores and ultimately all animals
Habitats
Plants provide shelter and homes for countless animals
Without autotrophs, Earth would be very different:
• No oxygen to breathe
• No food for animals
• No forests, grasslands, or coral reefs
• No fossil fuels (which come from ancient plants)
Autotrophs also help regulate Earth's climate by absorbing carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas. They truly are the foundation of life on our planet!
Autotroph Quiz
Test your knowledge about autotrophs with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about autotrophs:
Fun Autotroph Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about autotrophs!
Oxygen Producers
Scientists estimate that phytoplankton in the ocean produce between 50-85% of the oxygen in Earth's atmosphere! That's more than all land plants combined.
Size Range
Autotrophs come in all sizes! From tiny cyanobacteria less than 1 micrometer wide to giant sequoia trees that can grow over 300 feet tall!
Deep Sea Life
Chemoautotrophs were discovered near hydrothermal vents in 1977. These amazing organisms support entire ecosystems in complete darkness miles below the ocean surface!
Ancient Autotrophs
The earliest evidence of autotrophs dates back about 3.5 billion years! These ancient cyanobacteria began producing oxygen that eventually changed Earth's atmosphere.





