Heterotrophs - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how living things get energy by consuming other organisms!
What is a Heterotroph?

A heterotroph is a living thing that cannot make its own food. Instead, it gets energy by eating other organisms. The word "heterotroph" comes from Greek words meaning "other feeder."
Think of yourself - you can't make food from sunlight like plants do. You need to eat plants, animals, or both to get energy. That makes you a heterotroph! Most animals, fungi, and many microorganisms are heterotrophs.
Did You Know?
All animals are heterotrophs! From tiny ants to giant whales, every animal gets its energy by consuming other living things.
Types of Heterotrophs
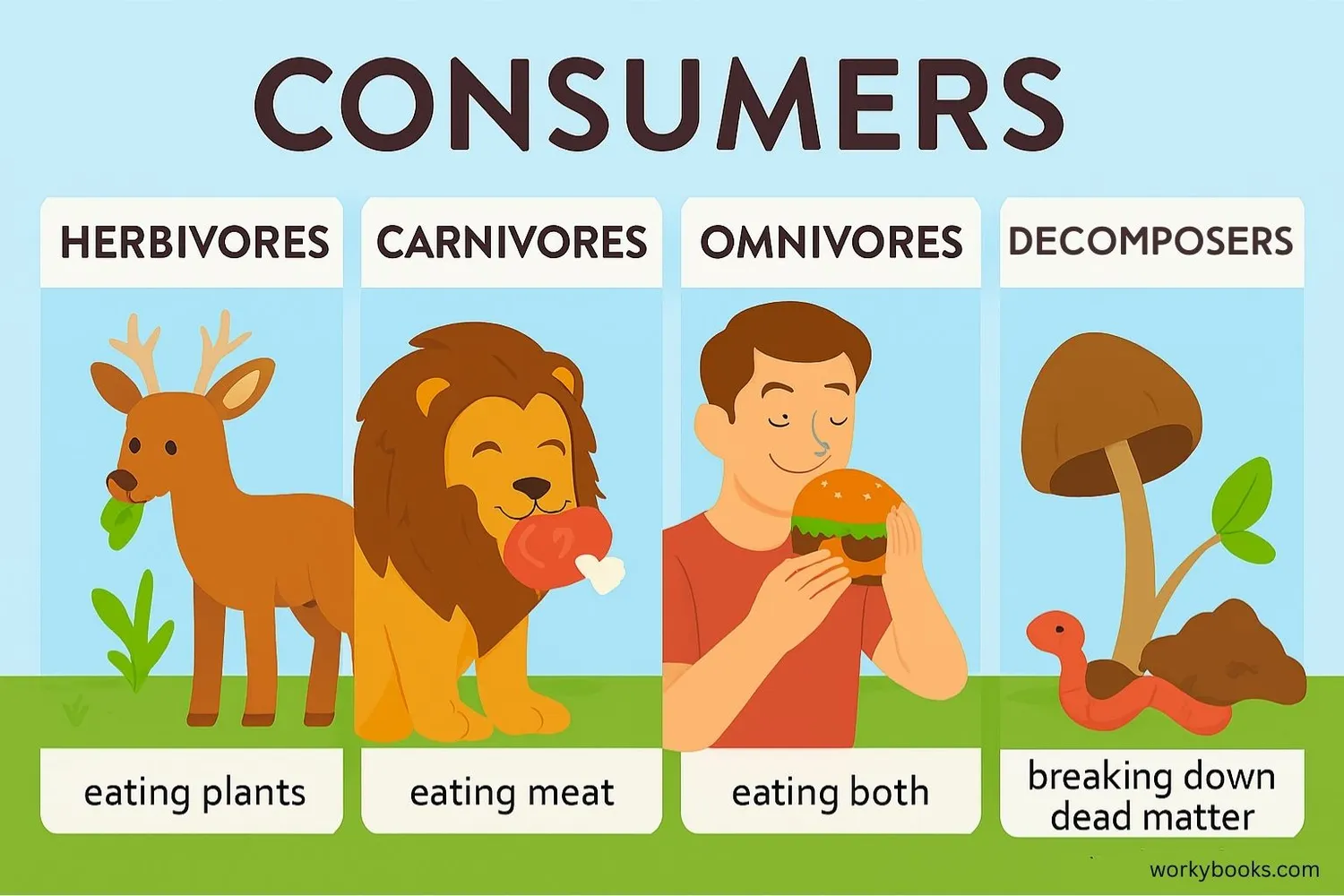
Heterotrophs can be classified into different groups based on what they eat:
Herbivores
Eat only plants (e.g., deer, rabbits, cows)
Carnivores
Eat only other animals (e.g., lions, hawks, sharks)
Omnivores
Eat both plants and animals (e.g., humans, bears, raccoons)
Decomposers
Break down dead organisms (e.g., fungi, bacteria, worms)
Each type of heterotroph plays an important role in the food chain. Herbivores eat plants, carnivores eat herbivores, and decomposers break down waste and dead organisms, returning nutrients to the soil for plants to use again.
Decomposers: Nature's Recyclers
Without decomposers, our planet would be covered in dead plants and animals! Decomposers break down dead matter and return nutrients to the soil.
Heterotroph vs Autotroph
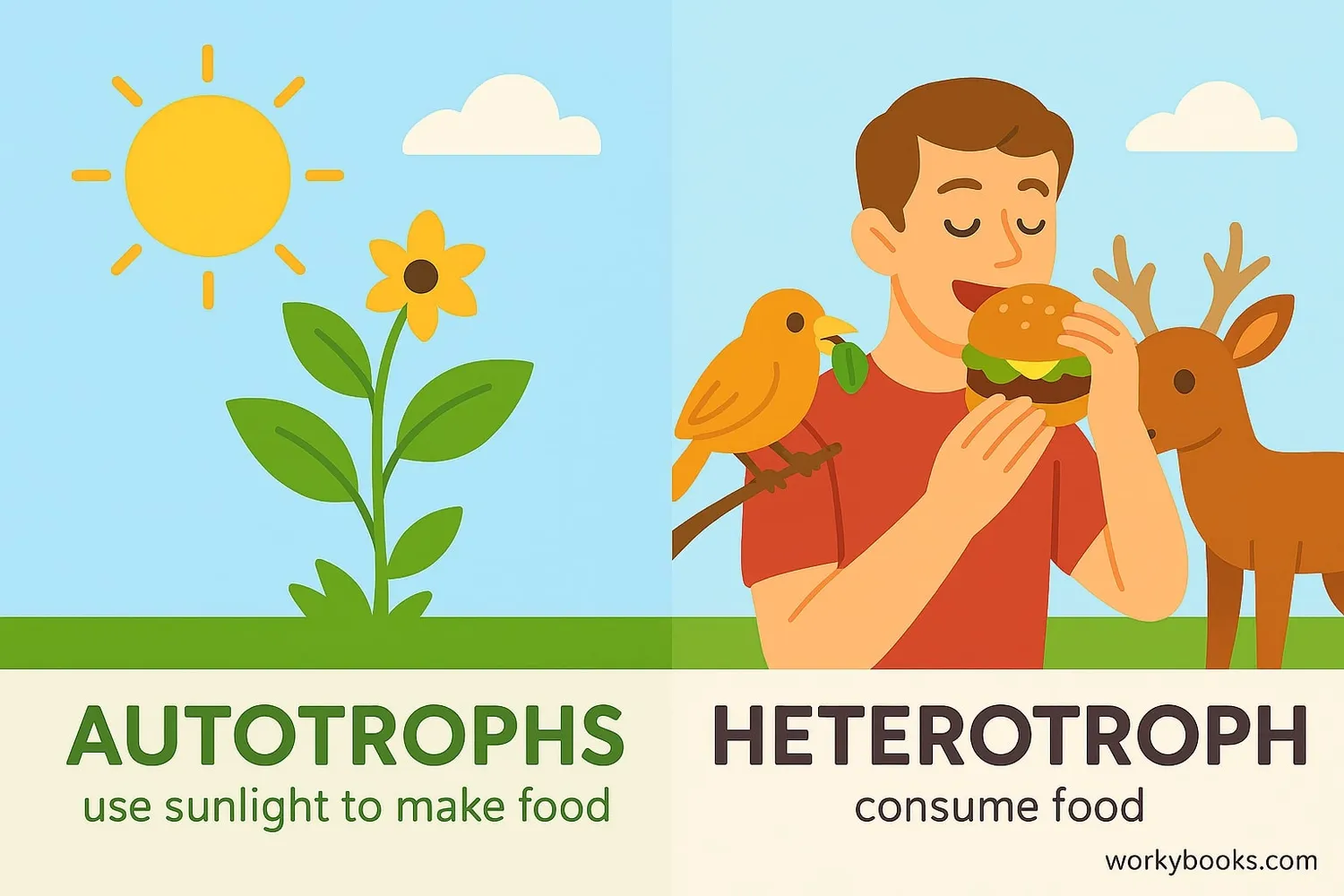
The main difference between heterotrophs and autotrophs is how they get energy:
Heterotrophs
• Get energy by consuming other organisms
• Cannot make their own food
• Examples: animals, fungi, most bacteria
Autotrophs
• Make their own food using sunlight or chemicals
• Are producers in the food chain
• Examples: plants, algae, some bacteria
Autotrophs are like nature's chefs - they can prepare their own food from basic ingredients like sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide. Heterotrophs are like restaurant customers - they need to eat food that someone else has prepared.
Most ecosystems depend on both autotrophs and heterotrophs. Autotrophs create the energy (through photosynthesis), and heterotrophs consume and transfer that energy through the food chain.
Heterotrophic Nutrition
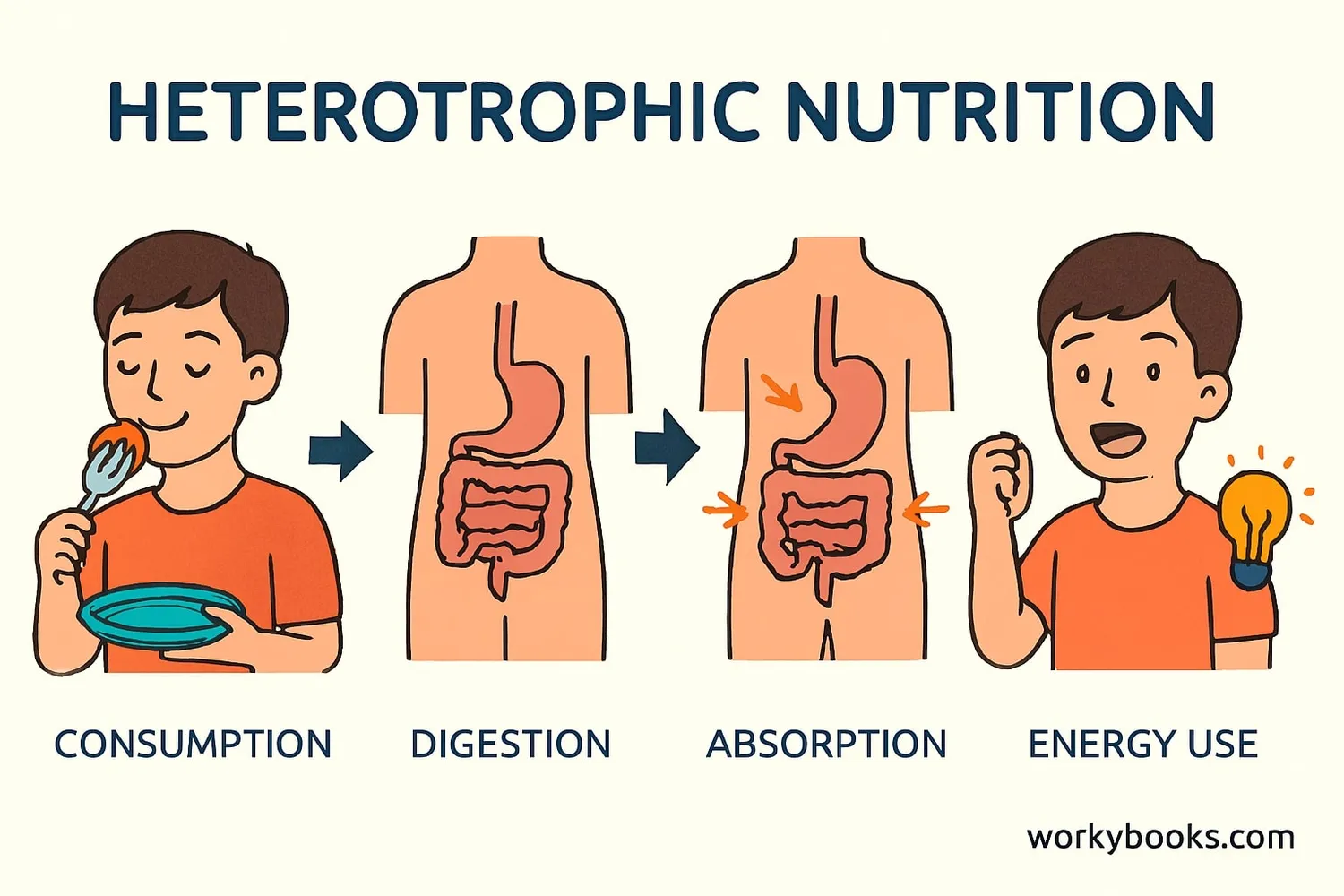
Heterotrophic nutrition is the process by which heterotrophs obtain and use nutrients from other organisms. This process involves:
Ingestion
Taking in food through eating or absorption
Digestion
Breaking down food into smaller molecules
Absorption
Taking in nutrients into cells
Assimilation
Using nutrients for growth and energy
Egestion
Removing undigested waste
Different heterotrophs have different ways of obtaining nutrition:
• Holozoic nutrition: Animals that eat solid food (herbivores, carnivores, omnivores)
• Saprophytic nutrition: Organisms that feed on dead matter (fungi, bacteria)
• Parasitic nutrition: Organisms that live on or in another organism and obtain nutrients from it (ticks, tapeworms)
Energy Transfer
When a deer eats grass, it gets only about 10% of the energy that was in the grass. This is why food chains usually have only 3-4 levels!
Heterotroph Knowledge Check
Test what you've learned about heterotrophs with this quiz. Answer all 5 questions to check your understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about heterotrophs:
Interesting Heterotroph Facts
Discover some amazing facts about heterotrophs and their role in ecosystems!
Nature's Recyclers
Without decomposer heterotrophs like fungi and bacteria, Earth would be covered in dead plants and animals! These organisms break down dead matter and return nutrients to the soil.
Energy Pyramid
Only about 10% of energy transfers from one trophic level to the next. This means if a herbivore eats 100 calories of plants, a carnivore eating that herbivore gets only about 10 calories!
Human Heterotrophs
The average person will eat about 35 tons of food in their lifetime! That's about the weight of 7 adult elephants.
Diverse Diets
Some heterotrophs have very specialized diets. For example, koalas only eat eucalyptus leaves, and pandas primarily eat bamboo. These animals have adapted to digest these specific plants.




