Parasitism - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how some organisms live by taking from others
What is Parasitism?
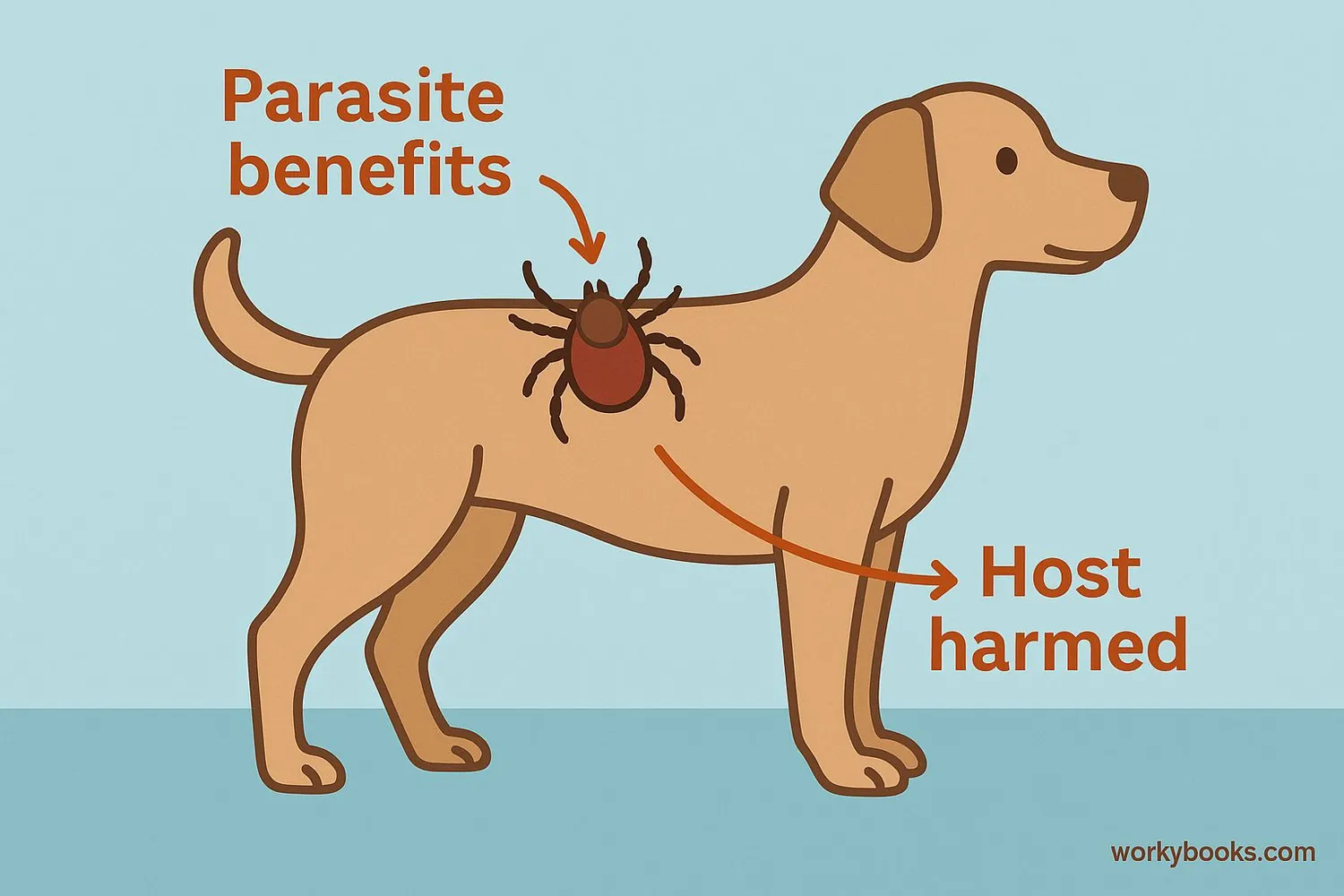
Parasitism is a special relationship between two different kinds of living things where one benefits while the other is harmed. The organism that benefits is called the parasite, and the one that is harmed is called the host.
Think of it like this: if you had a friend who always ate your lunch but never brought any food to share, and sometimes even made you feel sick—that would be a parasitic relationship! The parasite gets food and a place to live from its host, while the host loses nutrients and may become sick or weak.
Key Point
In parasitism, one organism benefits (the parasite) while the other is harmed (the host), but the host is typically not killed immediately.
Types of Parasitism
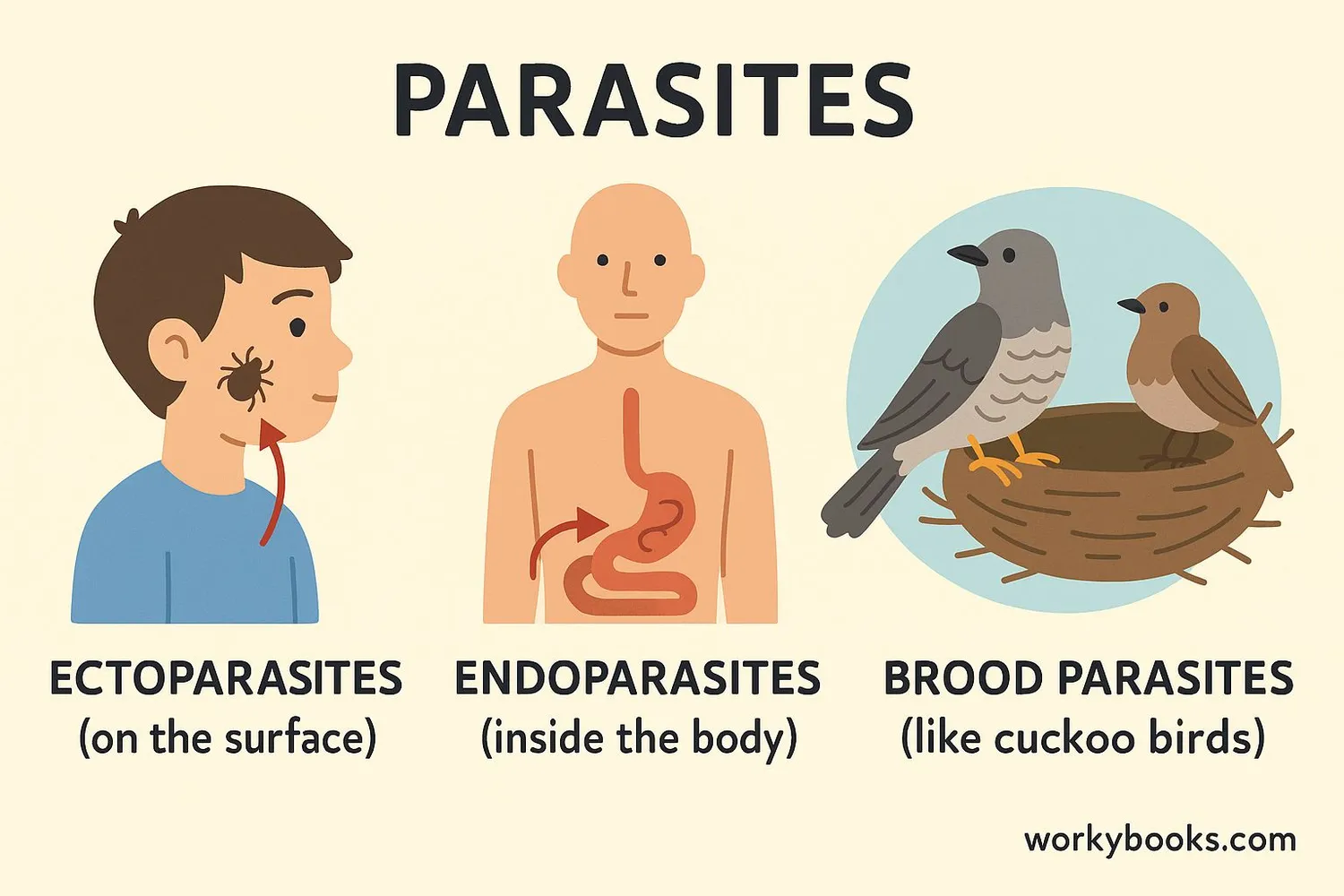
Parasites come in many different forms. Scientists categorize them based on where they live and how they interact with their hosts:
Ectoparasites
Live on the outside of the host's body
Endoparasites
Live inside the host's body
Brood Parasites
Trick other species into raising their young
Ectoparasites include creatures like ticks, fleas, and lice that live on the skin or fur of animals. Endoparasites live inside the host's body, like tapeworms in intestines or malaria parasites in blood. Brood parasites are different—they don't feed directly on the host but trick other animals into raising their young, like cuckoo birds that lay eggs in other birds' nests.
Examples of Parasitism
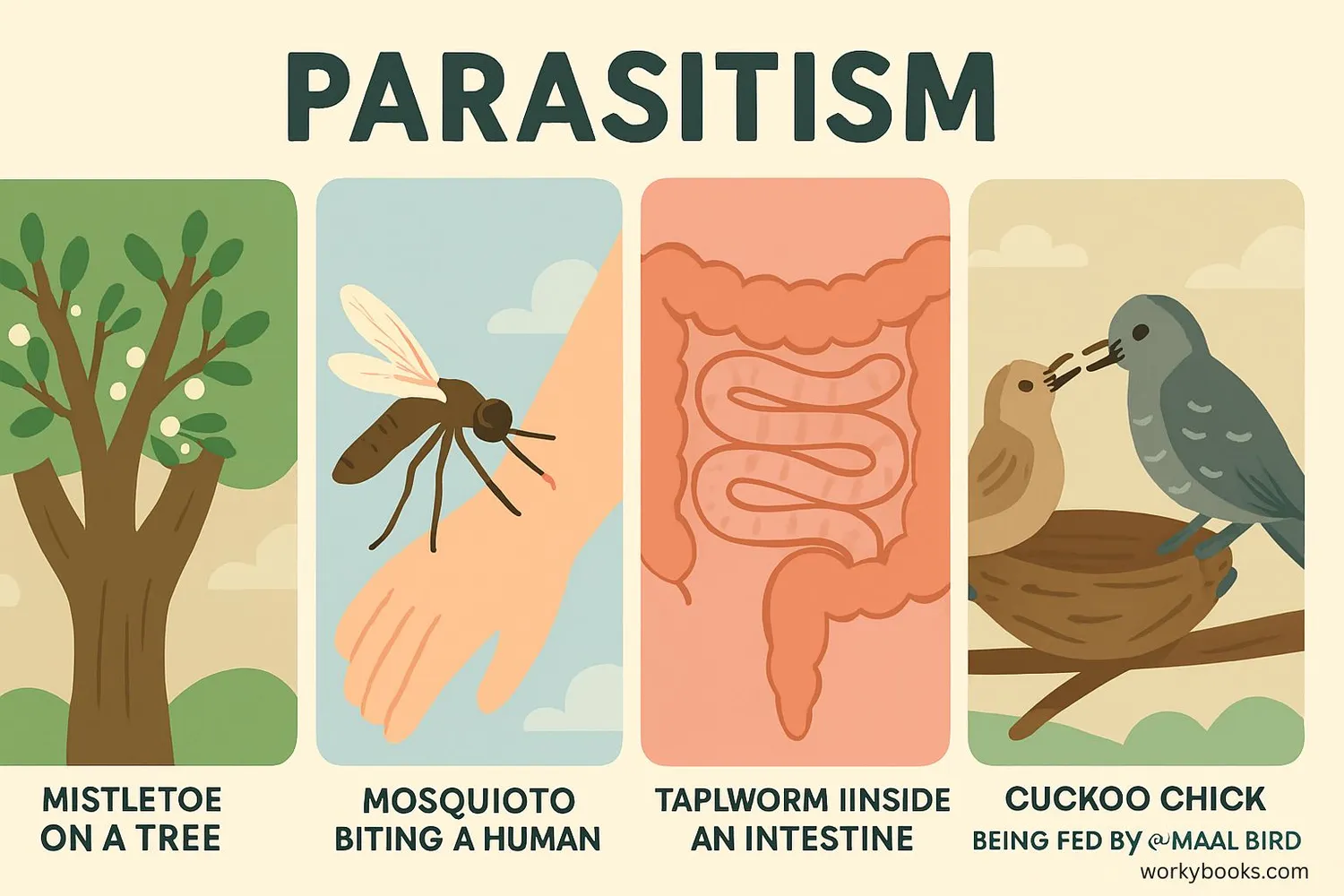
Parasitism exists all around us in nature. Here are some common examples:
Mosquitoes
Feed on blood from animals and humans, potentially transmitting diseases
Mistletoe
A plant that grows on trees and takes water and nutrients from them
Tapeworms
Live inside animal intestines and consume digested food
Other examples include fleas on dogs, ticks on deer, and certain fungi that grow on plants. Even some birds like cowbirds are brood parasites—they lay their eggs in other birds' nests so those birds will raise the young cowbirds instead of their own babies.
Symbiosis Comparisons
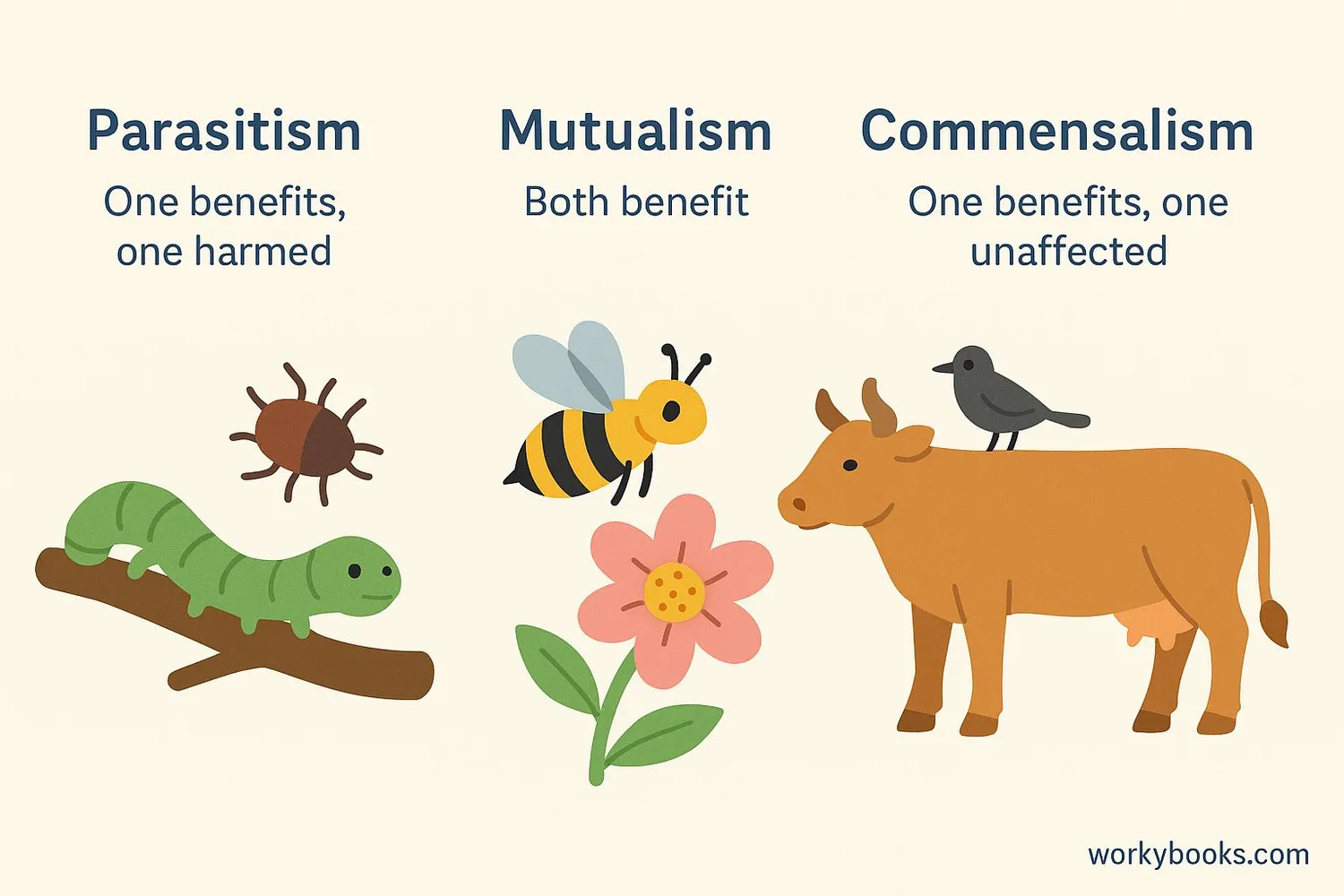
Parasitism is one type of symbiotic relationship between organisms. Symbiosis means "living together," and there are different kinds:
| Relationship Type | Organism A | Organism B | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parasitism | Benefits | Harmed | Tick on a dog |
| Mutualism | Benefits | Benefits | Bees and flowers |
| Commensalism | Benefits | Unaffected | Barnacles on whales |
As you can see, parasitism is different from mutualism (where both organisms benefit) and commensalism (where one benefits and the other isn't affected). Understanding these differences helps scientists classify how organisms interact in ecosystems.
Parasitism Quiz
Test your knowledge about parasitism with this quiz. Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about parasitism:
Interesting Facts About Parasitism
Discover some fascinating facts about parasitism:
Ancient Relationship
Parasitism is an ancient relationship—scientists have found evidence of parasites in fossilized dinosaur feces that is over 200 million years old!
Tongue-Eating Parasite
The tongue-eating louse is a parasite that enters fish through their gills, attaches to the tongue, and eventually replaces the tongue by becoming a functioning tongue itself!
Zombie Ants
Some fungi can infect ants and take control of their behavior, forcing them to climb to high positions before the fungus grows out of their heads to spread its spores.
Medical Use
Some parasites are being studied for medical benefits. For example, hookworms might help treat autoimmune diseases by calming overactive immune systems.





