Synapses - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how brain cells communicate through special connections
What is a Synapse?
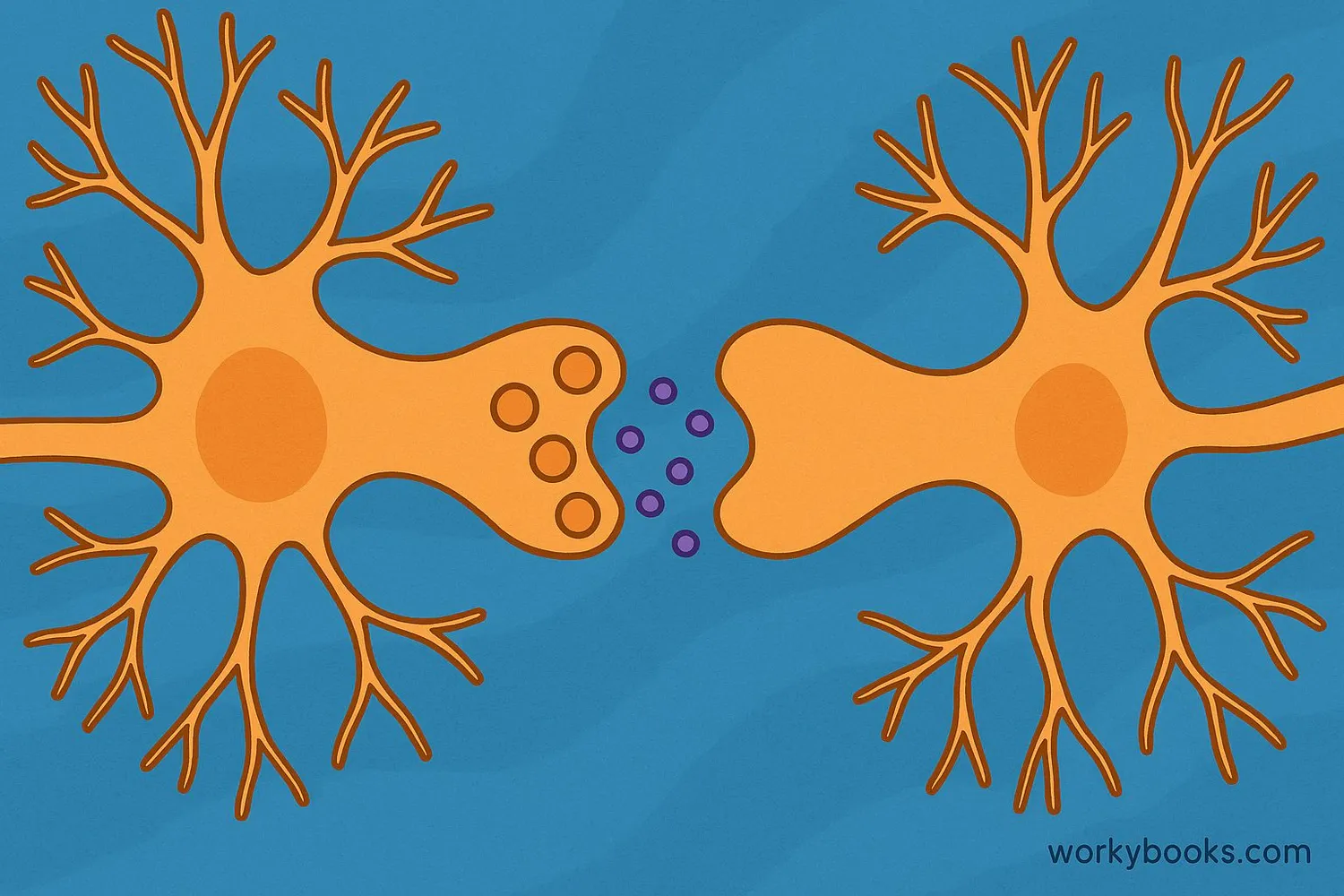
A synapse is a tiny gap between nerve cells (neurons) where communication happens in your brain and nervous system. It's like a microscopic messaging station that allows brain cells to talk to each other!
Think of neurons as friends playing telephone. The synapse is the space between them where the message gets passed along. When one neuron wants to send a message to another, it releases special chemicals called neurotransmitters that float across the synapse and deliver the message.
Synapse Fact!
Your brain has about 100 billion neurons and each can form thousands of synaptic connections - that's trillions of synapses in your brain!
How Synapses Work
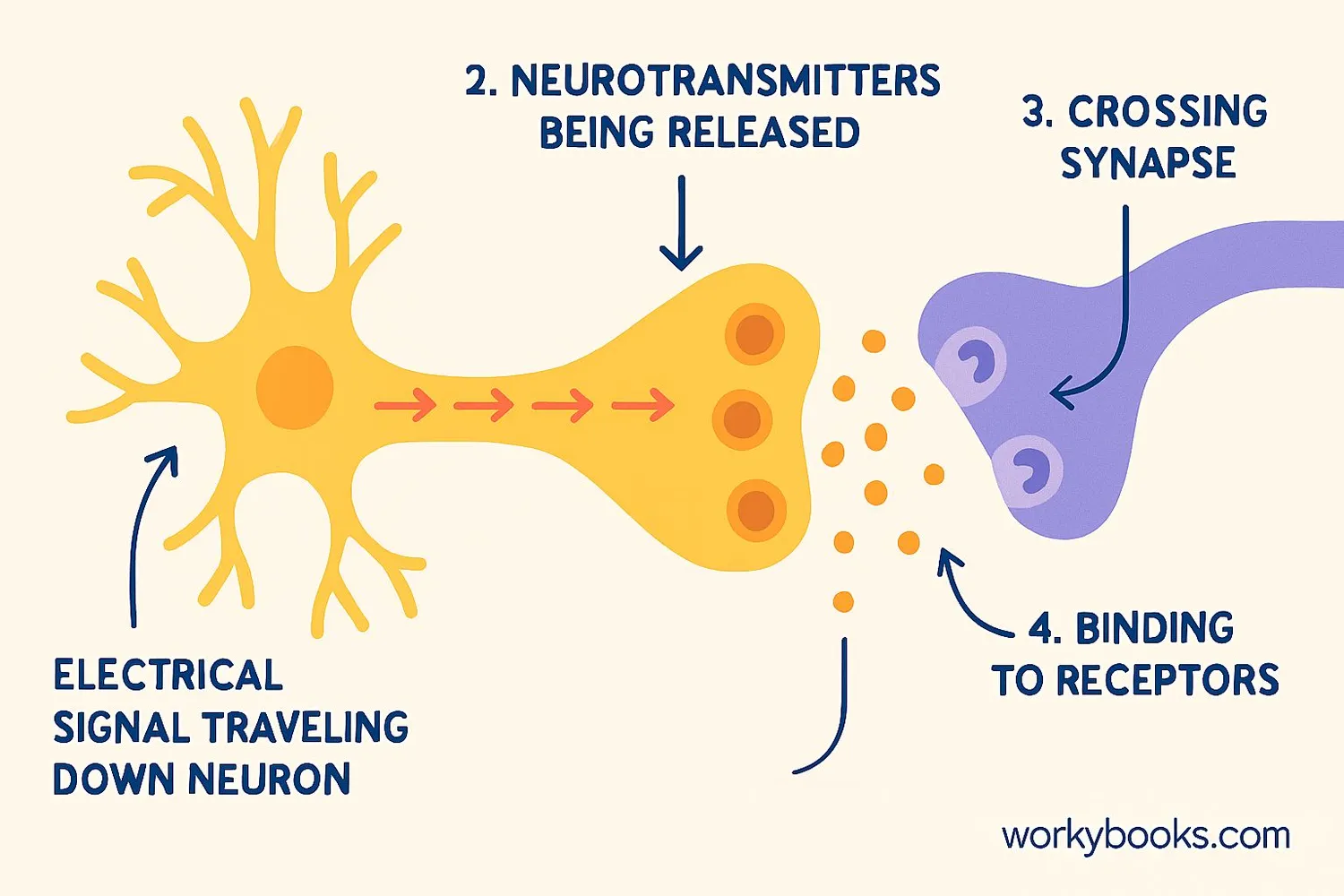
Synapses work through an amazing process called synaptic transmission. Here's how this communication system works:
Electrical Signal
An electrical impulse travels down the sending neuron
Chemical Release
Neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic gap
Crossing the Gap
Chemicals float across the tiny space between neurons
Message Received
Receptors on the receiving neuron detect the chemicals
New Signal
The receiving neuron generates a new electrical signal
The main parts of a synapse are:
• Presynaptic neuron - The sending cell
• Postsynaptic neuron - The receiving cell
• Synaptic cleft - The tiny gap between them
• Neurotransmitters - The chemical messengers
• Receptors - Special proteins that receive the message
Speed of Thought!
Synaptic transmission happens incredibly fast - in just milliseconds! This allows you to react quickly to things you see, hear, or feel.
Why Synapses Matter
Synapses are essential for everything your brain does! Here's why they're so important:
Thinking & Learning
Synapses form the connections that allow you to think, learn, and solve problems
Memory Formation
Memories are stored by strengthening frequently used synaptic connections
Movement Control
Synapses help your brain communicate with muscles to control movement
Without synapses, there would be no:
• Learning or memory formation
• Communication between brain cells
• Ability to move your body intentionally
• Processing of senses like sight, sound, and touch
• Emotions or personality
When you learn something new, your brain actually creates new synaptic connections or strengthens existing ones. This is called neuroplasticity - your brain's amazing ability to change and adapt!
Synapse Quiz
Test your knowledge about synapses with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about synapses:
Amazing Brain Facts
Discover some fascinating facts about synapses and your brain!
Countless Connections
A single neuron can have up to 15,000 synaptic connections with other neurons! Your brain has about 100-500 trillion synapses in total.
Learning Changes Your Brain
When you learn something new, your brain physically changes by forming new synaptic connections. Practice strengthens these pathways, making the knowledge easier to access.
Sleep and Synapses
While you sleep, your brain strengthens important synaptic connections formed during the day and prunes less important ones. This is why sleep is crucial for learning!
Baby Brains
Babies are born with more synapses than adults! Through childhood and adolescence, the brain undergoes "synaptic pruning" - eliminating weaker connections to strengthen important ones.





