Fahrenheit to Celsius (F to C) - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius temperature measurements with easy explanations and practice activities
What is Temperature Conversion?
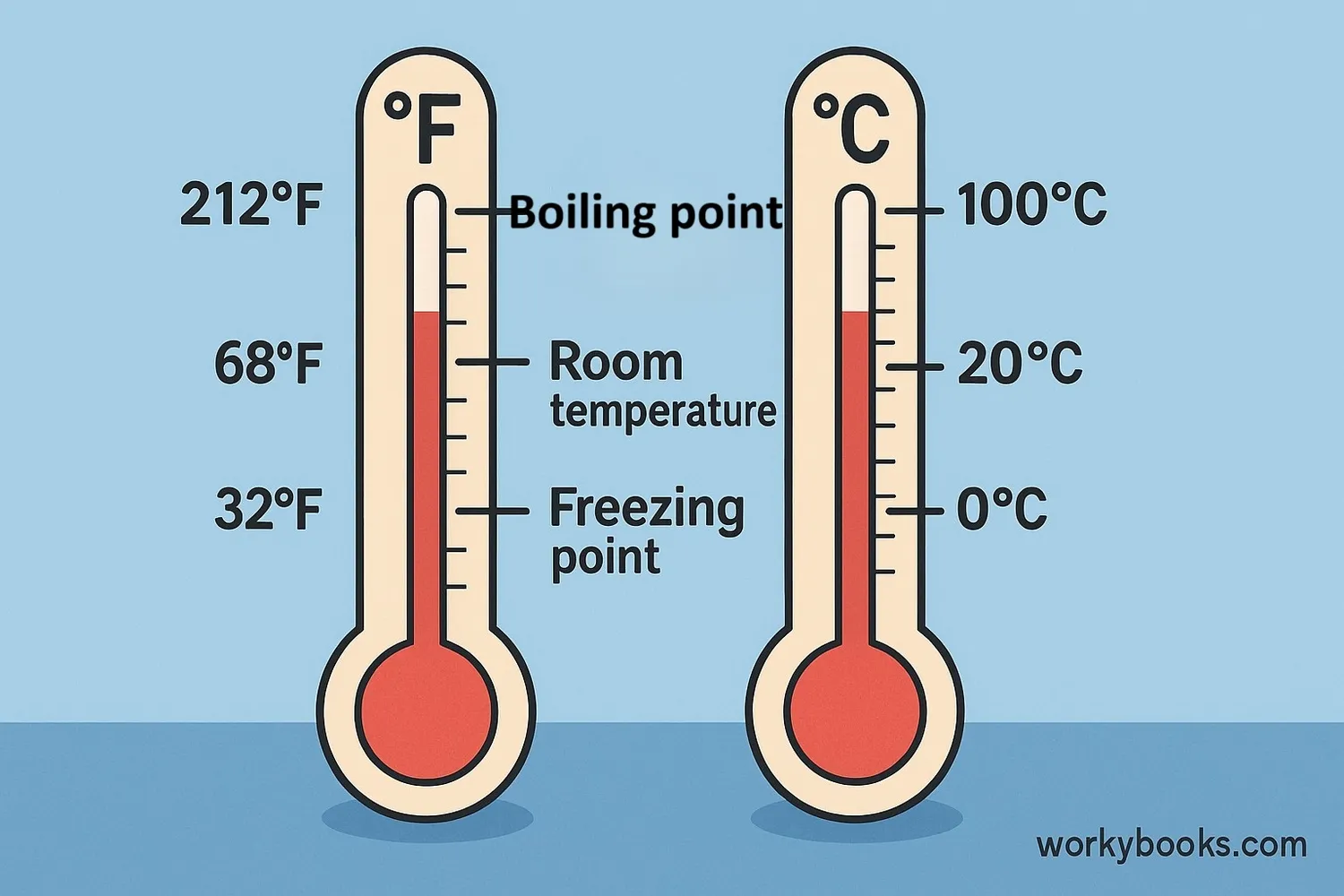
Temperature conversion means changing a temperature measurement from one unit to another. In this lesson, we're learning how to convert between Fahrenheit (used mainly in the US) and Celsius (used in most other countries and in science).
Why do we need to convert? Different countries use different temperature scales. Understanding both helps us communicate about weather, cooking, and science experiments. The freezing point of water is 32°F (0°C) and the boiling point is 212°F (100°C).
To convert Fahrenheit to Celsius, we use this formula:
C = (F - 32) × 5/9. This formula helps us understand how the two temperature scales relate to each other.
Key Concept
Water freezes at 32°F (0°C) and boils at 212°F (100°C). This relationship is the foundation for all temperature conversions.
How to Convert Fahrenheit to Celsius
Converting Fahrenheit to Celsius is straightforward when you follow these steps:
Conversion Formula
To convert any Fahrenheit temperature to Celsius, subtract 32, then multiply by 5/9.
Example: Convert 100°F to Celsius
Step 1: Start with the temperature in Fahrenheit → 100°F
Step 2: Subtract 32 → 100 - 32 = 68
Step 3: Multiply by 5/9 → 68 × 5/9 ≈ 37.78
Step 4: The result → 100°F is about 37.8°C
This is why we say "100°F is hot like a summer day" - it's nearly 38°C!
Remember
When converting Fahrenheit to Celsius, the Celsius number will always be smaller than the Fahrenheit number because Celsius degrees are larger.
Fahrenheit to Celsius Conversion Charts
Conversion charts help us quickly find equivalent temperatures without calculating each time. Here are useful charts for converting Fahrenheit to Celsius:
Common Temperature Conversion Chart
| Fahrenheit (°F) | Celsius (°C) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| -40°F | -40°C | Extremely cold (same in both scales) |
| 0°F | -17.8°C | Very cold winter day |
| 32°F | 0°C | Freezing point of water |
| 50°F | 10°C | Cool autumn day |
| 68°F | 20°C | Room temperature |
| 86°F | 30°C | Warm summer day |
| 98.6°F | 37°C | Normal body temperature |
| 100°F | 37.8°C | Hot summer day |
| 212°F | 100°C | Boiling point of water |
Quick Reference Conversion Chart
| Fahrenheit (°F) | Celsius (°C) |
|---|---|
| 0°F | -17.8°C |
| 10°F | -12.2°C |
| 20°F | -6.7°C |
| 30°F | -1.1°C |
| 40°F | 4.4°C |
| 50°F | 10.0°C |
| 60°F | 15.6°C |
| 70°F | 21.1°C |
| 80°F | 26.7°C |
| 90°F | 32.2°C |
| 100°F | 37.8°C |
Chart Tip
Notice how every 10°F change is about 5.5°C? You can estimate that each 10°F is approximately 5-6°C.
Real-World Examples
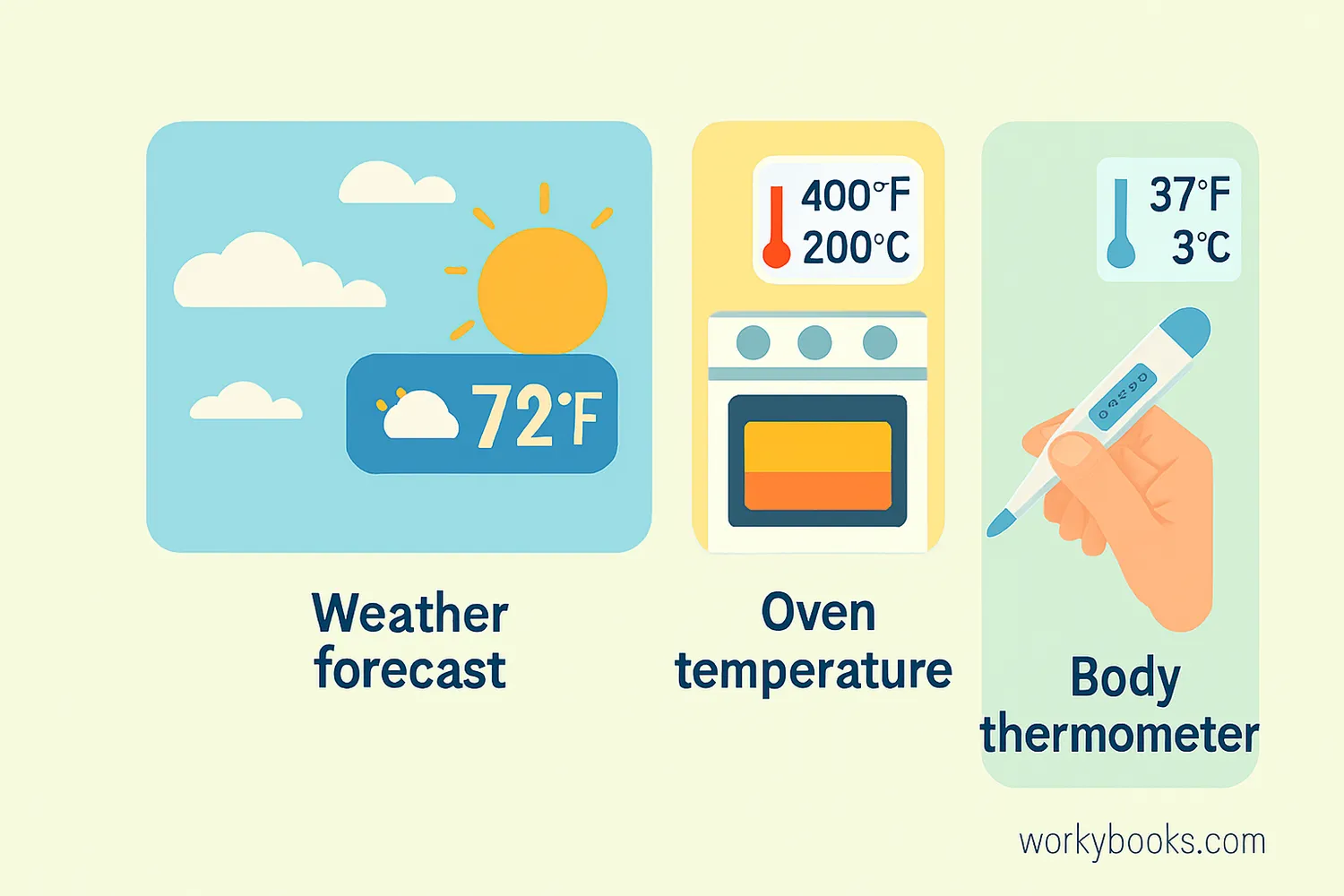
Let's practice conversion with some real-world examples:
Example 1: The weather forecast says it will be 77°F tomorrow. What is this in Celsius?
Solution: C = (77 - 32) × 5/9 = (45) × 5/9 ≈ 25°C
Example 2: Your oven recipe says to bake at 350°F. What Celsius temperature should you set?
Solution: C = (350 - 32) × 5/9 = (318) × 5/9 ≈ 176.7°C (round to 175°C or 180°C)
Example 3: Normal body temperature is 98.6°F. What is this in Celsius?
Solution: C = (98.6 - 32) × 5/9 = (66.6) × 5/9 ≈ 37°C
Example 4: Water freezes at 0°C. What is this in Fahrenheit?
Solution: To convert Celsius to Fahrenheit: F = (C × 9/5) + 32 = (0 × 9/5) + 32 = 32°F
Practice converting temperatures you encounter - the weather, cooking temperatures, or your body temperature!
Conversion Tip
A quick estimate: To convert °F to °C, subtract 30 and divide by 2. This gives an approximate Celsius value that's easy to calculate mentally.
Conversion Practice Quiz
Test your conversion skills with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about Fahrenheit and Celsius conversion:
Temperature Trivia
Discover interesting facts about temperature scales:
Origin of Fahrenheit
The Fahrenheit scale was created in 1724 by Daniel Fahrenheit, a German physicist. He set 0°F as the coldest temperature he could achieve with a mixture of ice, water, and salt.
Celsius Scale Creation
The Celsius scale was developed in 1742 by Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius. Interestingly, he originally set 0° as the boiling point and 100° as the freezing point, which was later reversed.
Space Temperatures
In space, temperatures can vary dramatically. Sunlight can heat objects to 120°C (248°F), while shaded areas can drop to -157°C (-250°F). Space itself has an average temperature of -270°C (-454°F)!
Extreme Temperatures
The highest natural temperature ever recorded on Earth was 56.7°C (134°F) in Death Valley, California. The coldest was -89.2°C (-128.6°F) at Vostok Station in Antarctica.





