Fahrenheit to Kelvin (F to K) - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn to convert between Fahrenheit and Kelvin temperature scales with easy explanations and practice activities
What is Temperature Conversion?
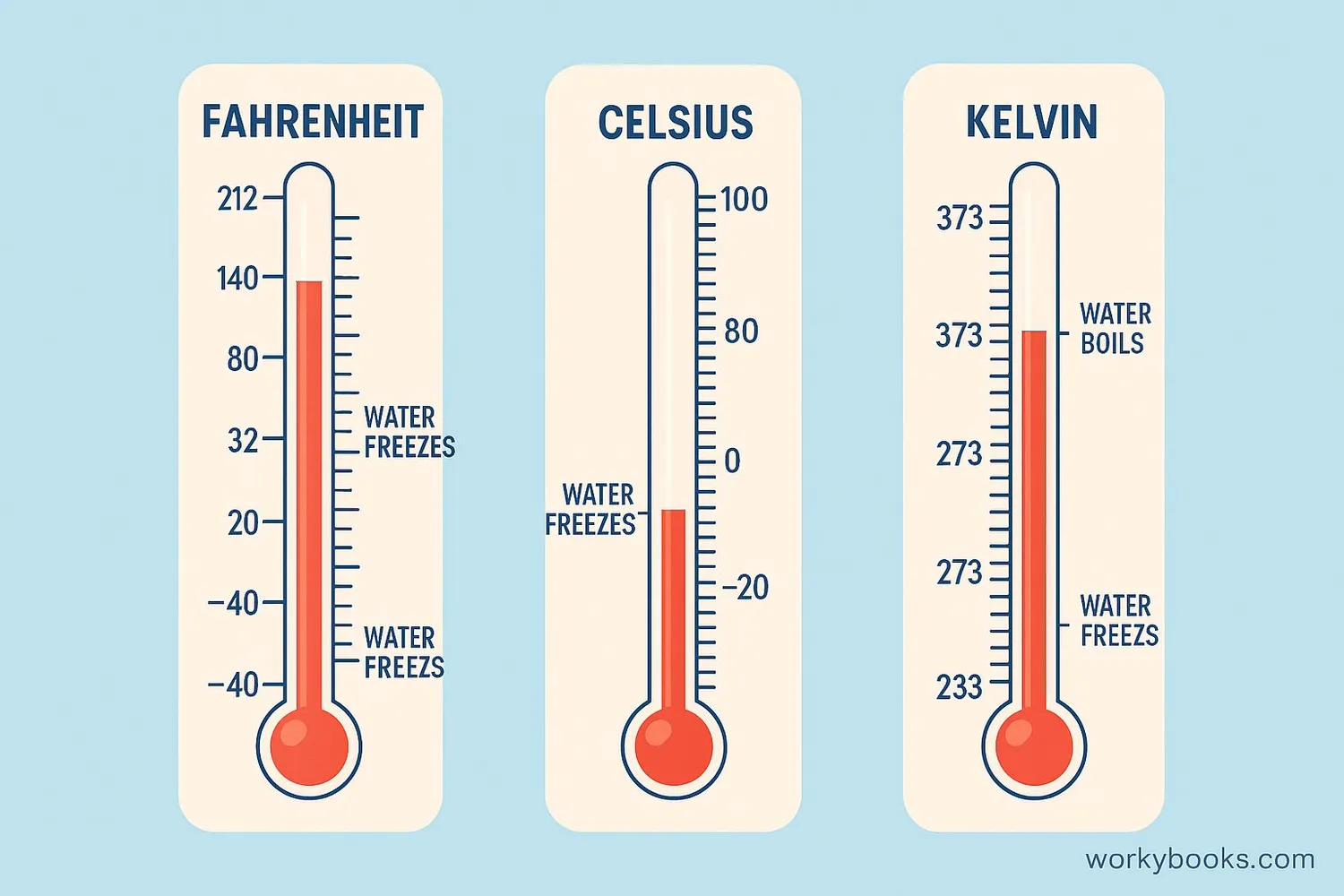
Temperature conversion means changing a temperature measurement from one scale to another. In this lesson, we're learning how to convert between Fahrenheit (used mainly in the United States) and Kelvin (used in scientific measurements).
Why do we need to convert? Different situations use different temperature scales. Weather forecasts in the US use Fahrenheit, while scientists use Kelvin for experiments. Understanding how to convert between these scales helps us communicate measurements accurately.
The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale where 0 K represents absolute zero, the coldest possible temperature. The Fahrenheit scale sets water's freezing point at 32°F and boiling point at 212°F.
Key Concept
Absolute zero (0 K) is -459.67°F. This is the foundation for understanding the relationship between Fahrenheit and Kelvin.
How to Convert Fahrenheit to Kelvin
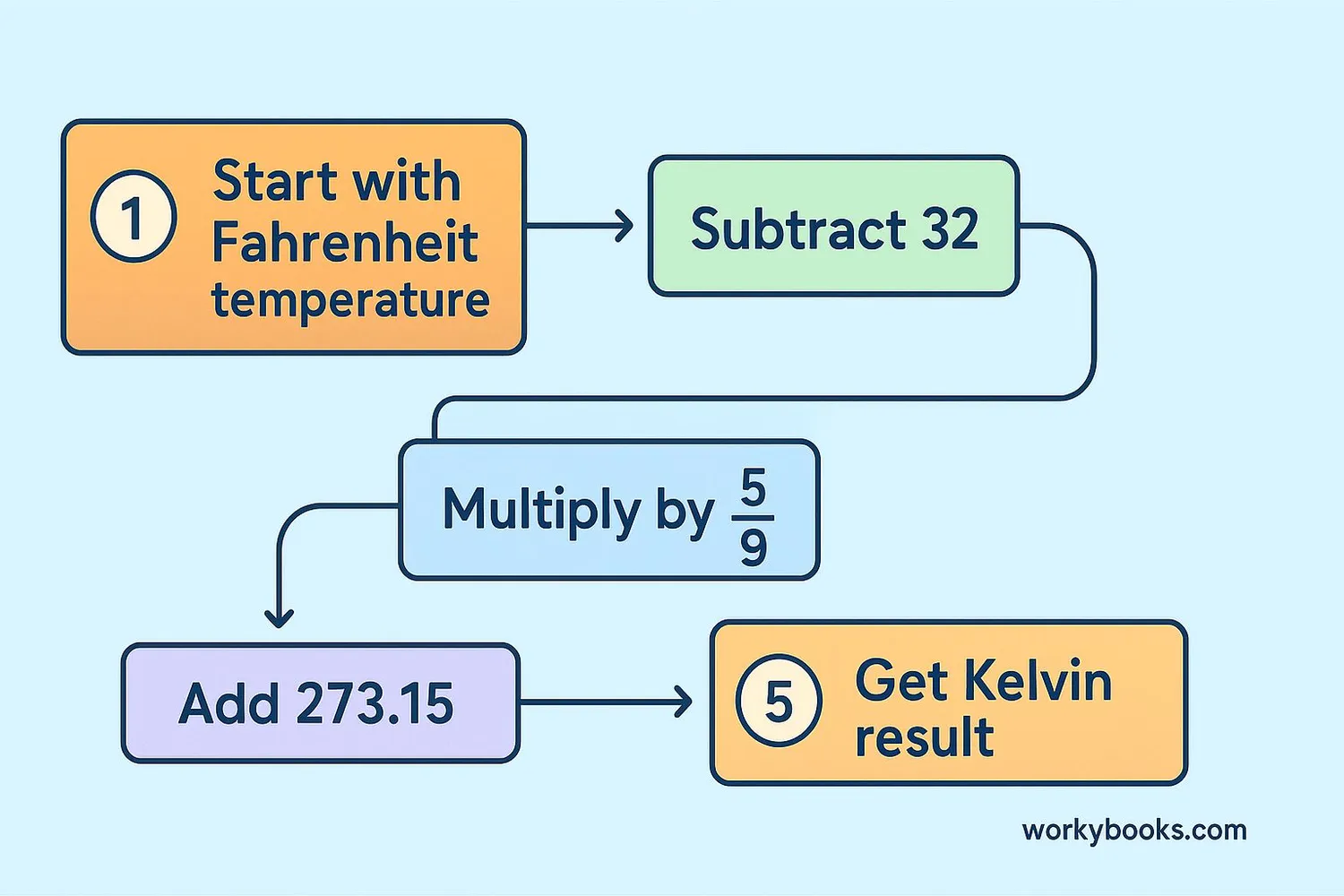
Converting Fahrenheit to Kelvin requires two steps. First, we convert Fahrenheit to Celsius, then Celsius to Kelvin:
Conversion Formula
To convert any temperature in Fahrenheit to Kelvin, subtract 32, multiply by 5/9, then add 273.15.
Example: Convert 68°F to Kelvin
Step 1: Subtract 32 → 68 - 32 = 36
Step 2: Multiply by 5/9 → 36 × 5/9 = 20
Step 3: Add 273.15 → 20 + 273.15 = 293.15 K
So 68°F equals 293.15 K. Room temperature is about 293 K!
Remember
Kelvin temperatures don't use the degree symbol (°). We just write "K" after the number, like 300 K.
Fahrenheit to Kelvin Conversion Charts
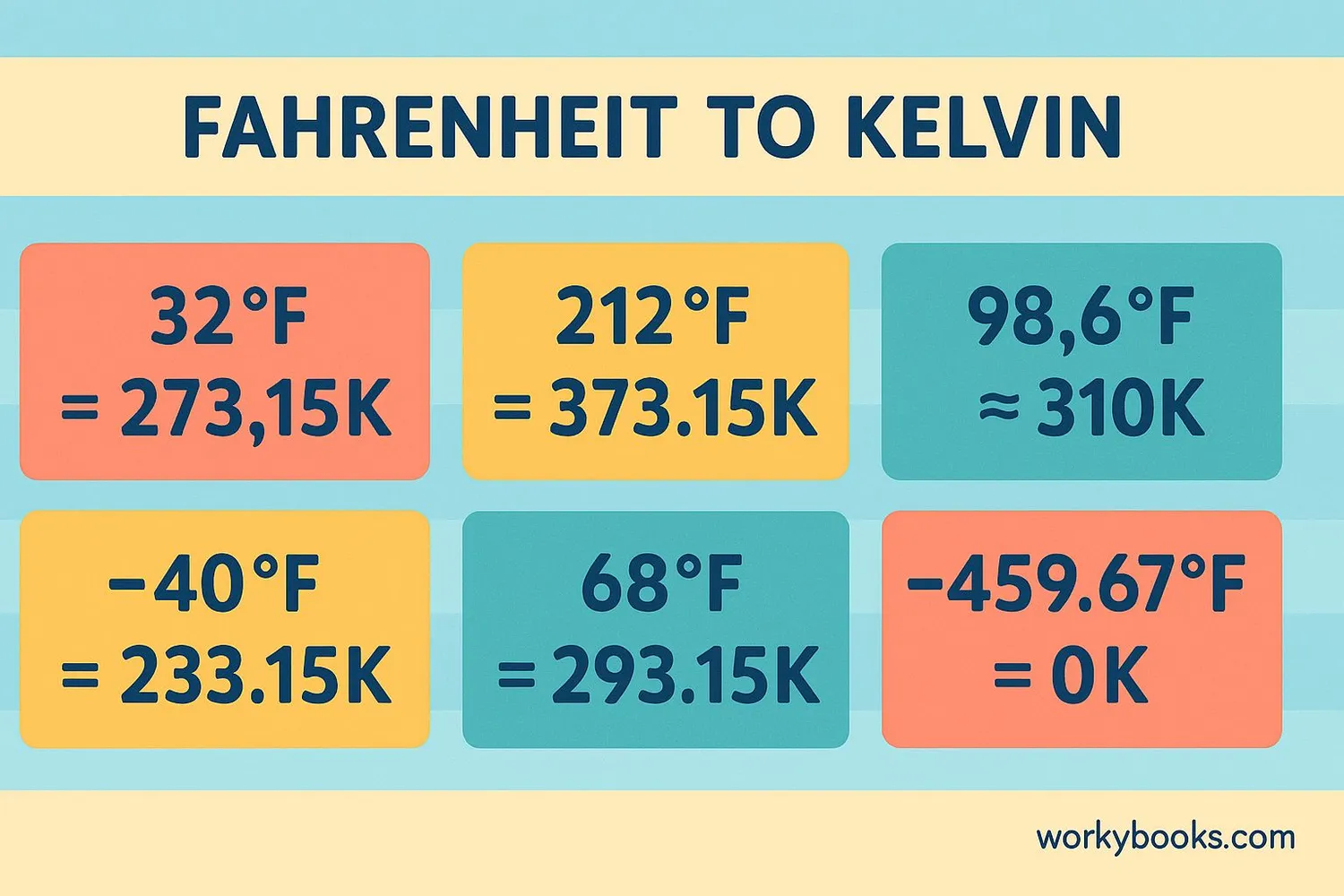
Conversion charts help us quickly find equivalent temperatures without calculating each time. Here are useful charts for converting Fahrenheit to Kelvin:
Fahrenheit to Kelvin Temperature Conversion Chart
| Fahrenheit (°F) | Kelvin (K) |
|---|---|
| -459.67°F | 0 K |
| -40°F | 233.15 K |
| 0°F | 255.37 K |
| 32°F | 273.15 K |
| 68°F | 293.15 K |
| 98.6°F | 310.15 K |
| 212°F | 373.15 K |
| 300°F | 422.04 K |
| 400°F | 477.59 K |
| 500°F | 533.15 K |
Common Temperature Reference Points
| Description | Fahrenheit | Kelvin |
|---|---|---|
| Absolute Zero | -459.67°F | 0 K |
| Water Freezes | 32°F | 273.15 K |
| Room Temperature | 68°F | 293.15 K |
| Human Body Temperature | 98.6°F | 310.15 K |
| Water Boils | 212°F | 373.15 K |
Chart Tip
Notice how Fahrenheit and Kelvin both increase as temperature gets hotter, but they increase at different rates.
Real-World Examples
Let's practice conversion with some real-world examples:
Example 1: On a cold winter day, the temperature is 14°F. What is this in Kelvin?
Solution: K = (14 - 32) × 5/9 + 273.15 = (-18) × 5/9 + 273.15 = -10 + 273.15 = 263.15 K
Example 2: A pizza oven needs to be 475°F to cook properly. Convert this to Kelvin.
Solution: K = (475 - 32) × 5/9 + 273.15 = 443 × 5/9 + 273.15 ≈ 246.11 + 273.15 = 519.26 K
Example 3: The surface of the Sun is about 9,941°F. What is this in Kelvin?
Solution: K = (9941 - 32) × 5/9 + 273.15 = 9909 × 5/9 + 273.15 = 5505 + 273.15 = 5778.15 K
Example 4: Liquid nitrogen boils at 77 K. What is this in Fahrenheit?
Solution: To convert Kelvin to Fahrenheit, first convert to Celsius: C = K - 273.15 = 77 - 273.15 = -196.15°C
Then convert to Fahrenheit: F = (-196.15 × 9/5) + 32 = -353.07 + 32 = -321.07°F
Practice converting temperatures you encounter in daily life - the weather, cooking temperatures, or scientific measurements!
Conversion Tip
To convert Kelvin back to Fahrenheit, use the formula: °F = (K - 273.15) × 9/5 + 32
Conversion Practice Quiz
Test your conversion skills with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about Fahrenheit and Kelvin conversion:
Temperature Trivia
Discover interesting facts about temperature measurement:
Origin of Fahrenheit
The Fahrenheit scale was developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in 1724. He originally set 0°F as the temperature of a ice-salt mixture and 96°F as human body temperature (later adjusted to 98.6°F).
Lord Kelvin's Contribution
The Kelvin scale is named after Belfast-born British physicist William Thomson, also known as Lord Kelvin. He developed the concept of an absolute temperature scale in 1848 based on the laws of thermodynamics.
Space Temperatures
The temperature in outer space is about 2.7 K (-455°F), which is the temperature of cosmic microwave background radiation left over from the Big Bang. This is just slightly above absolute zero.
Hottest Temperature
The highest temperature ever created by humans was 5.5 trillion K (9.9 trillion°F) at the Large Hadron Collider in 2012. This is about 366,000 times hotter than the center of the Sun!





