Acceleration Due to Gravity - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how gravity pulls objects toward Earth and makes them accelerate
What is Acceleration Due to Gravity?
Acceleration due to gravity is the rate at which objects speed up as they fall toward Earth. On our planet, this acceleration is approximately 9.8 meters per second squared (m/s²).
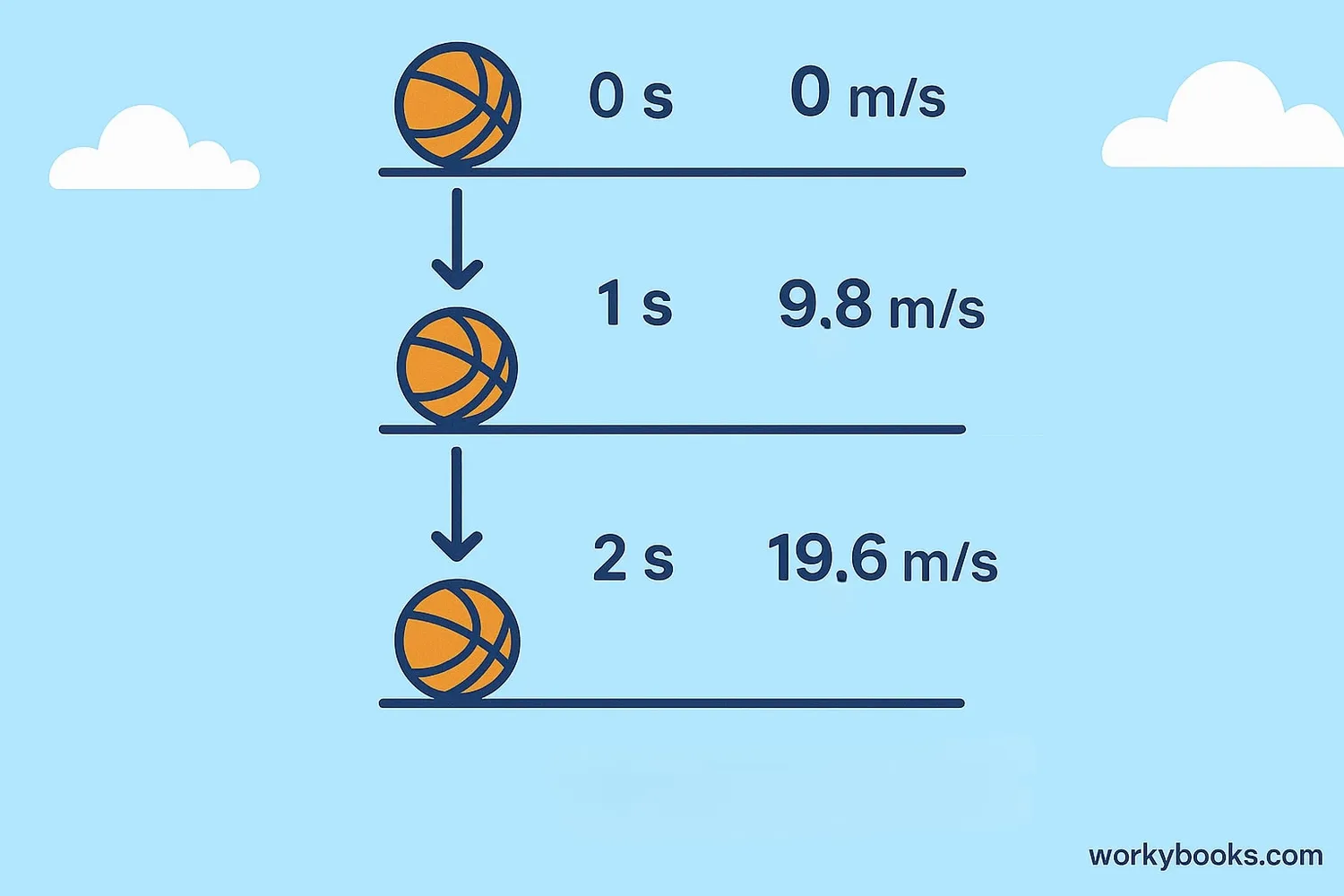
This means that every second an object is falling, its speed increases by 9.8 m/s. So after 1 second, it's falling at 9.8 m/s; after 2 seconds, 19.6 m/s; and so on. This acceleration happens because of Earth's gravitational pull.
Important Gravity Fact!
Acceleration due to gravity is the same for all objects, regardless of their mass! A feather and a bowling ball would fall at the same rate if there were no air resistance.
Gravitational Force
Earth pulls objects toward its center
Constant Acceleration
Objects accelerate at 9.8 m/s² downward
Free Fall
When only gravity acts on an object
How Gravity Acceleration Works
The acceleration due to gravity is calculated using this formula:
Where:
g = acceleration due to gravity
G = gravitational constant (6.67430 × 10⁻¹¹ m³ kg⁻¹ s⁻²)
MEarth = mass of Earth (5.972 × 10²⁴ kg)
REarth = radius of Earth (6,371,000 m)
Real-World Example
If you drop a ball from a tall building, after 3 seconds of free fall:
Velocity = g × time = 9.8 m/s² × 3s = 29.4 m/s (about 65 mph!)
Distance fallen = ½ × g × time² = 0.5 × 9.8 × 9 = 44.1 meters
Why Gravity Acceleration Matters

Understanding acceleration due to gravity helps explain many phenomena:
Keeps Us Grounded
Gravity prevents us from floating away into space
Water Flow
Causes rivers to flow downhill to the oceans
Orbital Motion
Keeps satellites and the Moon in orbit around Earth
Without gravity acceleration:
• Objects wouldn't fall to the ground
• Water wouldn't flow in rivers
• Planets wouldn't orbit the Sun
• Our atmosphere would escape into space
This fundamental physics principle is essential for life as we know it!
Gravity Acceleration Quiz
Test your understanding with this gravity quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about gravity acceleration:
Gravity Acceleration Trivia
Discover fascinating facts about gravity:
Weight vs. Mass
Your mass stays the same throughout the universe, but your weight changes! On Jupiter you'd weigh 2.5 times more than on Earth, while on Mars you'd weigh just 38% of your Earth weight.
Space Adaptation
Astronauts can grow up to 2 inches taller in space! Without gravity compressing their spines, the vertebrae expand. But they return to normal height after coming back to Earth.
Precision Measurement
The most accurate measurement of gravity to date was made in 2023 using atomic interferometry, measuring g with uncertainty of just 7 parts per billion!
Animal Gravity Sense
Some animals have special gravity-sensing organs! Fish have otoliths in their inner ears - tiny crystals that move when they change position, helping them sense up and down.





