Bronsted-Lowry Acid - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how acids and bases transfer protons to create chemical reactions!
What is Bronsted-Lowry Theory?
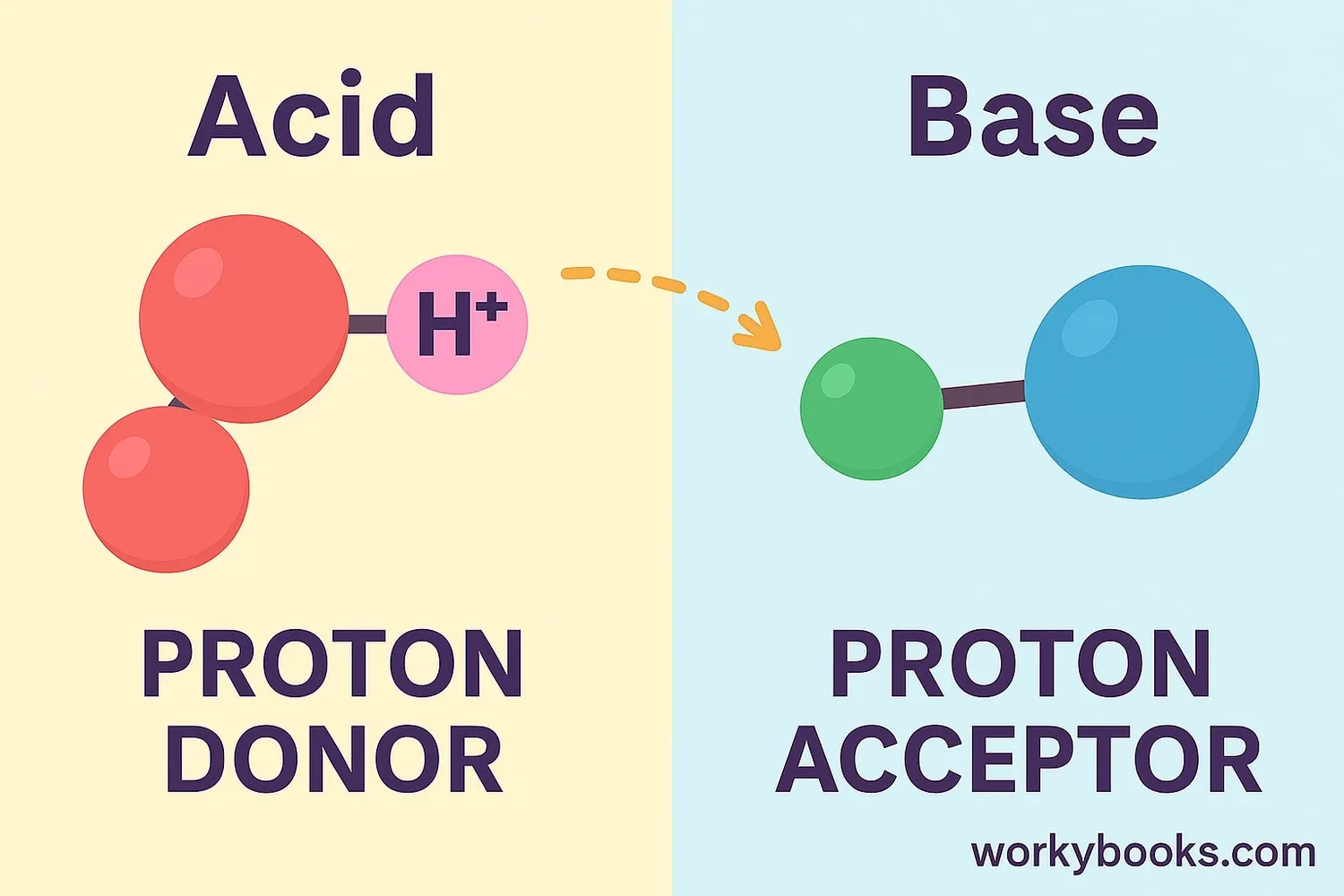
The Bronsted-Lowry theory is a way to understand acids and bases. In this theory:
• An acid is a substance that can donate a proton (H⁺ ion)
• A base is a substance that can accept a proton (H⁺ ion)
Think of it like this: acids are proton "givers" and bases are proton "receivers." This proton transfer is what makes acid-base reactions work!
Bronsted-Lowry Definition:
Base = Proton Acceptor
Chemistry Fact!
The word "proton" comes from the Greek word "protos" meaning "first," because protons are fundamental particles in atoms!
How Proton Transfer Works
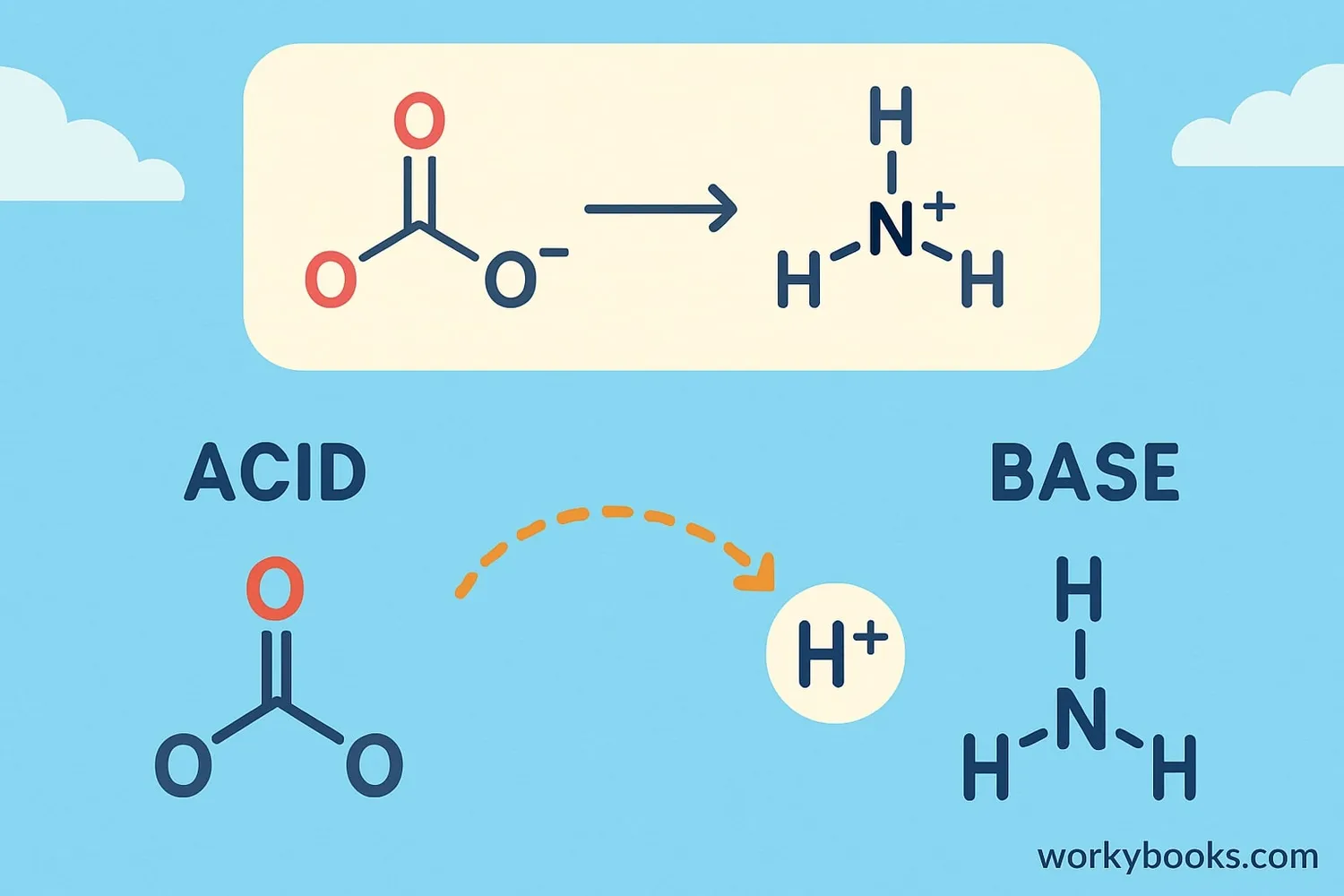
In Bronsted-Lowry theory, acids and bases always work together. When an acid donates a proton, it needs a base to accept it. This creates a chemical reaction!
Here's what happens during proton transfer:
Acid Donates
An acid molecule gives away a hydrogen ion (H⁺)
Base Accepts
A base molecule receives the H⁺ ion
New Substances
The acid becomes a conjugate base
Reaction Complete
The base becomes a conjugate acid
This transfer can be shown in a simple equation:
Where HA is the acid, B is the base, A⁻ is the conjugate base, and HB⁺ is the conjugate acid.
Proton Power!
Protons are incredibly small - about 100,000 times smaller than an atom! Yet they power all acid-base reactions.
Acid-Base Pairs
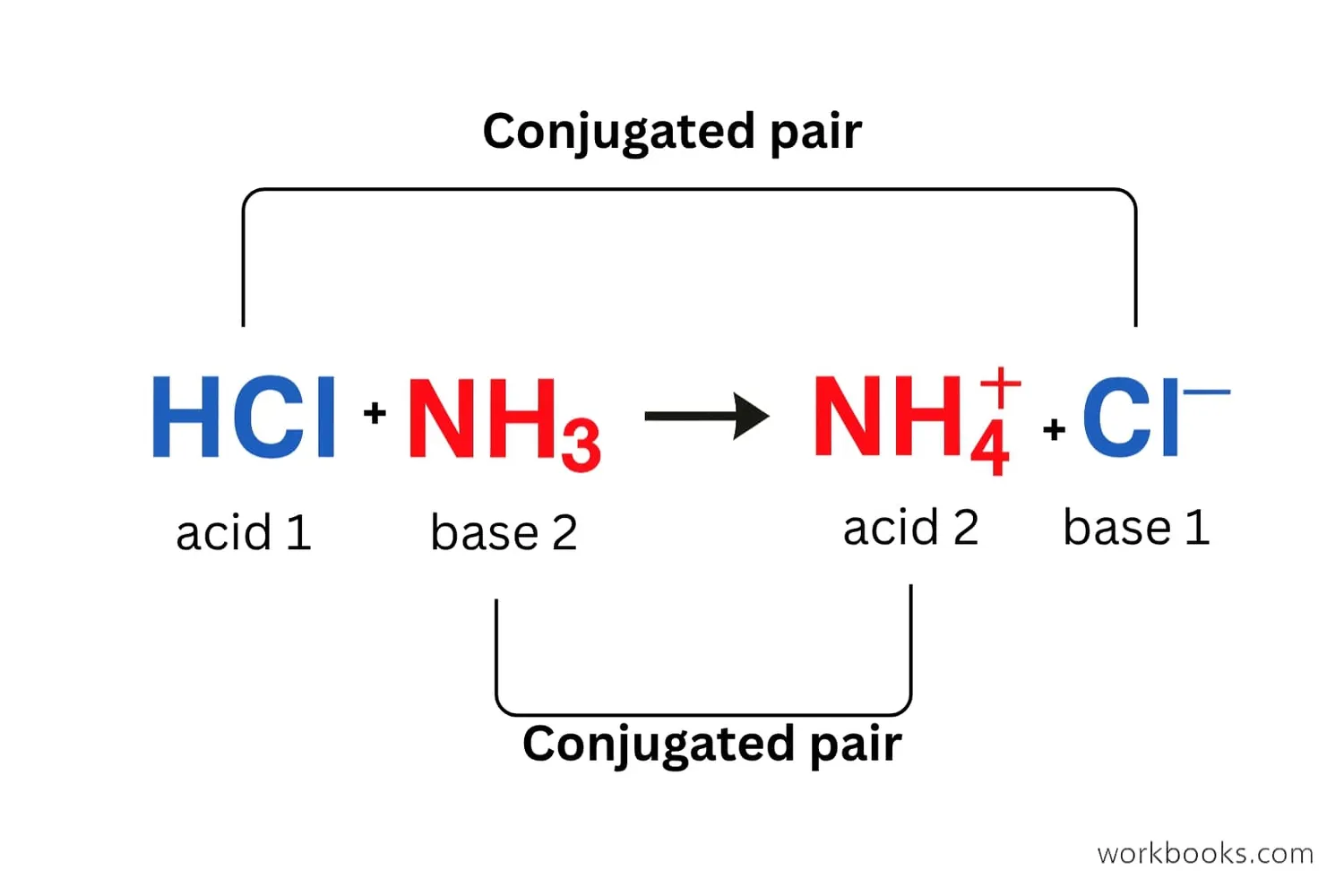
Every acid has a matching base, and every base has a matching acid. We call these conjugate pairs.
• When an acid donates its proton, it becomes a conjugate base
• When a base accepts a proton, it becomes a conjugate acid
Here are some examples of conjugate acid-base pairs:
Acetic Acid
CH₃COOH (acid) and CH₃COO⁻ (conjugate base)
Ammonia
NH₃ (base) and NH₄⁺ (conjugate acid)
Water
H₂O can act as both acid and base!
These pairs always differ by just one proton (H⁺). Understanding conjugate pairs helps us predict how acids and bases will behave in chemical reactions.
Why Bronsted-Lowry Theory Matters
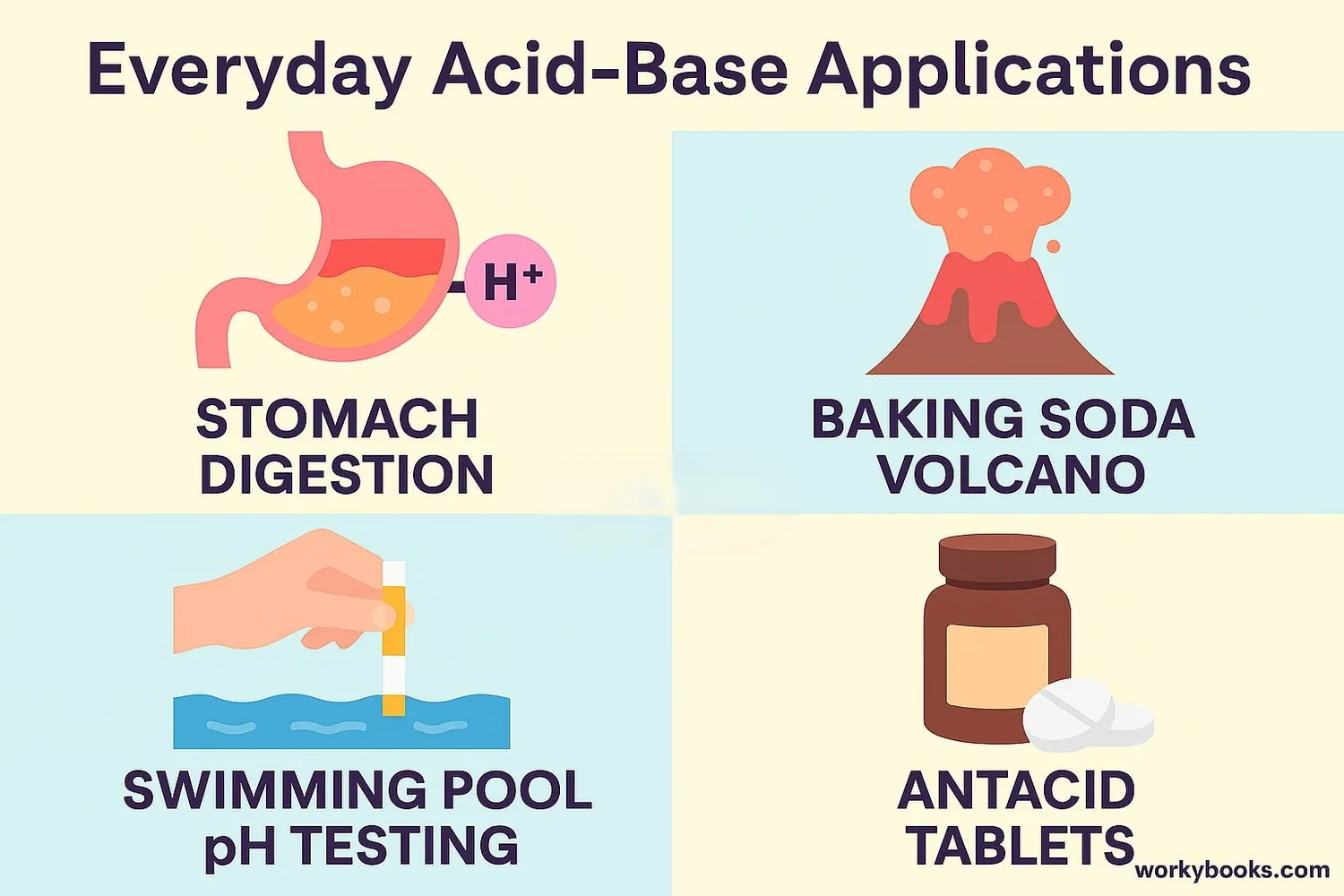
The Bronsted-Lowry theory helps us understand many important chemical processes:
Digestion
Stomach acid breaks down food using proton transfer
Water Treatment
pH balance is maintained using acid-base chemistry
Medicines
Antacids neutralize excess stomach acid
The Bronsted-Lowry theory is important because:
• It works for reactions in any solvent, not just water
• It explains why some substances can act as both acids and bases
• It helps us understand chemical equilibrium
• It's fundamental to biochemistry and life processes
Acid-Base Quiz
Test your knowledge of Bronsted-Lowry theory with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about Bronsted-Lowry theory:
Chemistry Trivia
Discover fascinating facts about acids, bases, and chemical reactions:
Historical Discovery
The Bronsted-Lowry theory was proposed independently by Johannes Nicolaus Bronsted and Thomas Martin Lowry in 1923 - the same year Gilbert Lewis proposed his electron-pair theory!
Biological Importance
Proton transfer is essential for life! Your cells use proton gradients to produce energy in mitochondria through cellular respiration.
pH Scale Origin
The pH scale was invented in 1909 by Søren Sørensen. The "p" stands for "potenz" (German for power) and H is for hydrogen, so pH means "power of hydrogen!"
Super Acids
Fluoroantimonic acid is the strongest superacid known - it's 10 quadrillion times stronger than sulfuric acid! It can even protonate hydrocarbons.





