Escape Velocity - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how objects break free from gravity and travel into space
What is Escape Velocity?

Escape velocity is the minimum speed needed for an object to break free from the gravitational pull of a planet or moon without further propulsion. It's like throwing a ball upward—if you throw it too slowly, it will fall back down, but if you throw it fast enough, it will escape Earth's gravity completely.
Every celestial body has its own escape velocity based on its mass and size. For Earth, this speed is approximately 11.2 kilometers per second (about 25,000 miles per hour)! That's more than 30 times faster than a commercial jet airplane.
Space Fact!
Escape velocity doesn't actually mean you need to maintain that speed the whole way—it's just the initial speed needed to eventually escape gravity without additional thrust.
How Escape Velocity Works
Escape velocity depends on two main factors: the mass of the celestial body and its radius. The mathematical formula for escape velocity is:
v = √(2GM/R)
Where:
• v = escape velocity
• G = gravitational constant
• M = mass of the planet/moon
• R = radius of the planet/moon
This means larger, more massive planets have higher escape velocities, while smaller bodies like moons have lower escape velocities.
Gravity's Pull
All objects with mass exert gravitational force
Energy Needed
To escape, an object needs enough kinetic energy to overcome gravitational potential energy
Critical Speed
Escape velocity is the speed where kinetic energy equals gravitational potential energy
Breaking Free
At this speed, an object can escape gravity without additional propulsion
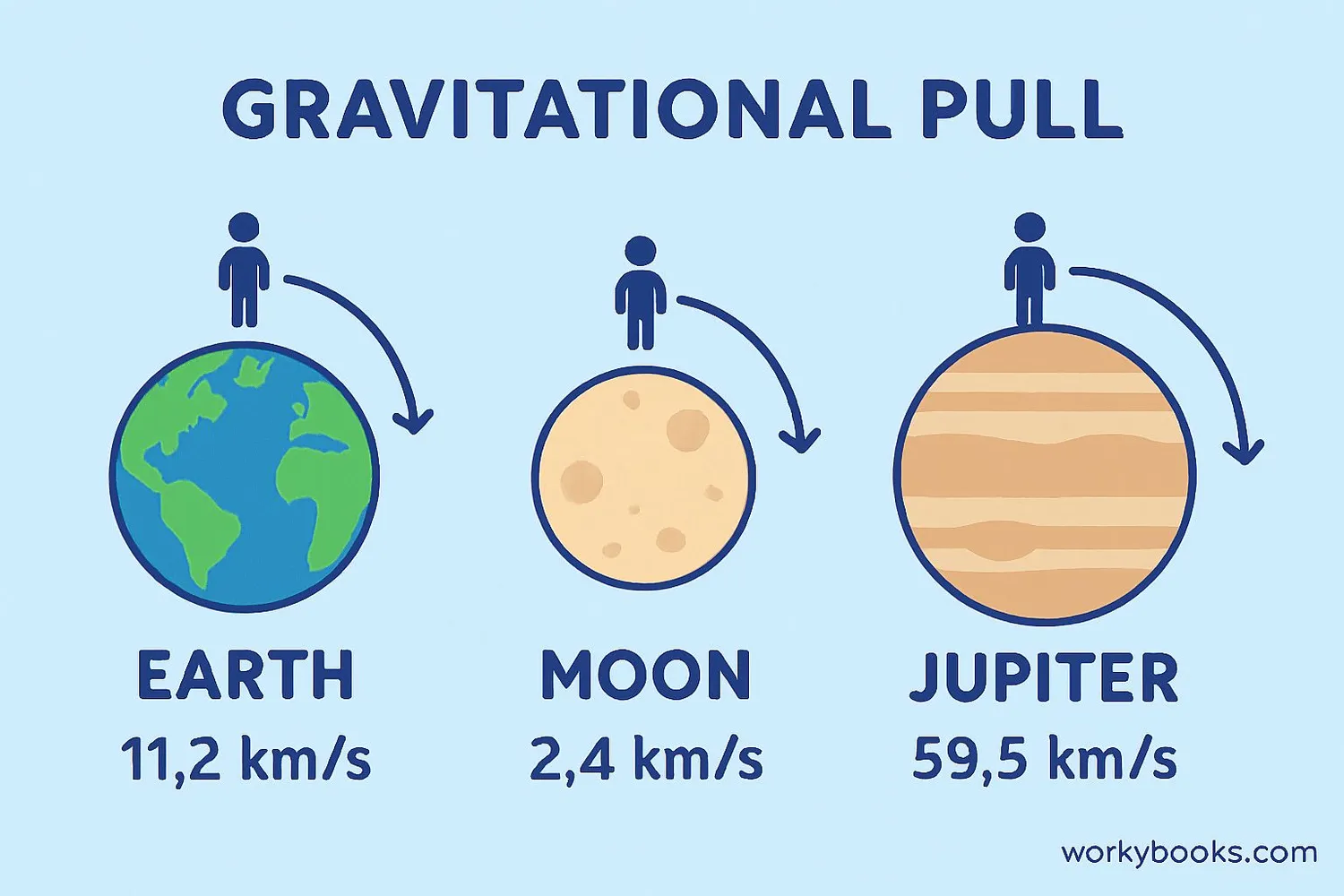
Celestial Comparison
Here's how escape velocity differs across our solar system:
| Celestial Body | Escape Velocity (km/s) | Compared to Earth |
|---|---|---|
| Mercury | 4.3 | 38% of Earth's |
| Venus | 10.4 | 93% of Earth's |
| Earth | 11.2 | 100% (baseline) |
| Moon | 2.4 | 21% of Earth's |
| Mars | 5.0 | 45% of Earth's |
| Jupiter | 59.5 | 531% of Earth's |
| Sun | 617.5 | 5,514% of Earth's |
Why Escape Velocity is Important
Understanding escape velocity is crucial for space exploration and many other scientific applications:
Space Exploration
Rockets must reach escape velocity to leave Earth's orbit and explore other celestial bodies
Satellite Deployment
Different orbits require different velocities, with some needing escape velocity to leave Earth entirely
Understanding Universe
Helps explain why some planets have atmospheres while others don't
Without understanding escape velocity, we couldn't:
• Launch satellites into specific orbits
• Send spacecraft to other planets
• Understand atmospheric retention on planets
• Plan efficient space missions
The concept also helps explain why smaller celestial bodies like our Moon have no atmosphere—their escape velocity is too low to hold onto gases.
Real World Example
The Voyager spacecraft, launched in 1977, achieved escape velocity from our solar system and is now traveling in interstellar space—the first human-made object to do so!
Escape Velocity Quiz
Test your knowledge about escape velocity with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about escape velocity:
Fun Escape Velocity Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about escape velocity!
Human Achievement
The Apollo missions to the Moon required reaching escape velocity—about 11.2 km/s (25,000 mph). The astronauts experienced forces up to 4G during this acceleration!
Solar System Escape
To completely leave our solar system, a spacecraft needs to reach the Sun's escape velocity at Earth's distance from the Sun—about 42 km/s (94,000 mph)!
Atmospheric Escape
Earth loses about 90 tonnes of atmospheric hydrogen daily because some molecules reach speeds exceeding escape velocity due to thermal energy in the upper atmosphere.
Not Exactly 11.2 km/s
Earth's escape velocity is typically stated as 11.2 km/s, but this value changes slightly depending on altitude and latitude due to Earth's rotation and oblate shape.





