Free Fall - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how gravity affects falling objects and learn about motion principles
What is Free Fall?
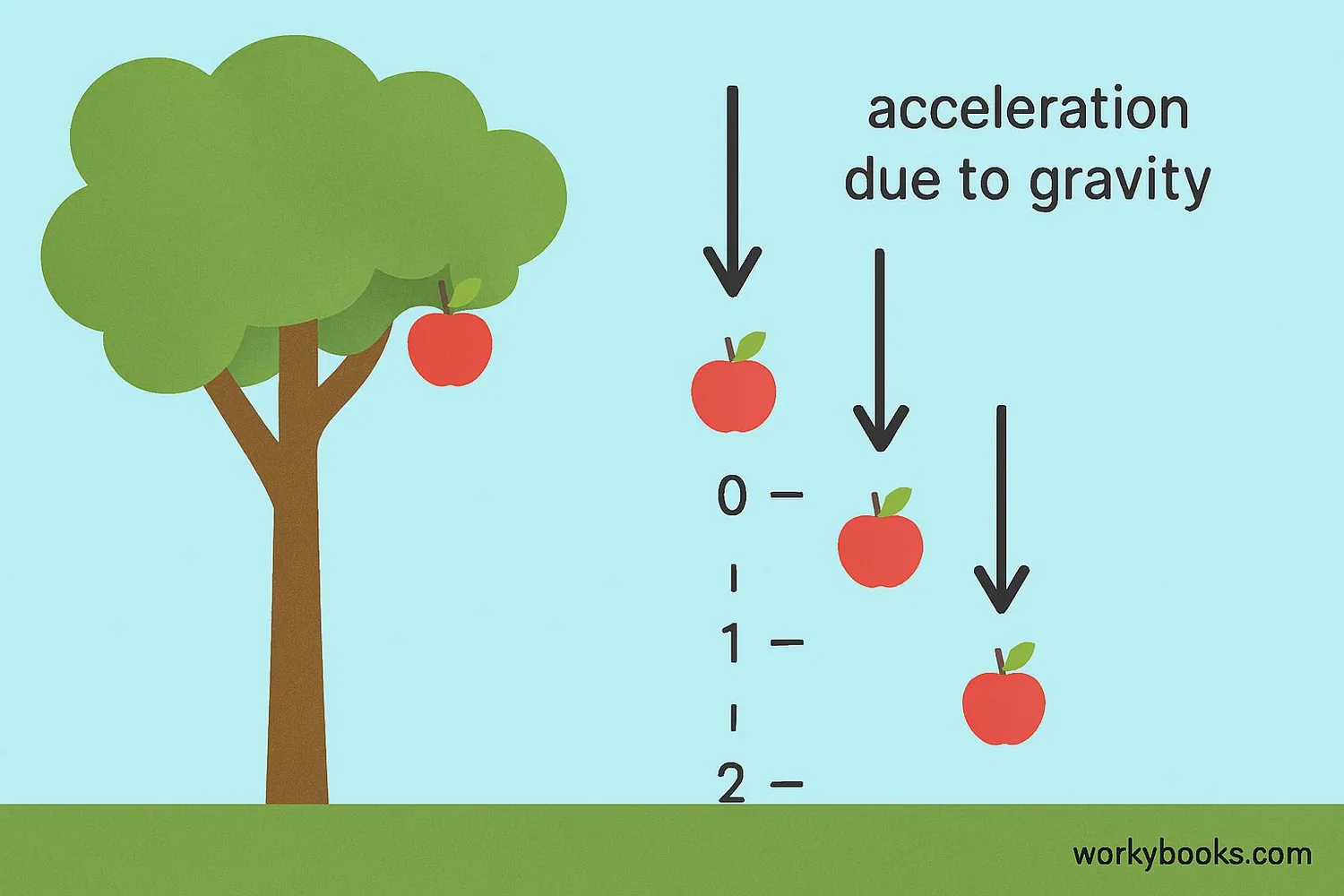
Free fall is the motion of an object falling solely under the influence of gravity. When something is in free fall, gravity is the only force acting upon it, causing it to accelerate downward.
Imagine dropping a ball from your hand. The moment you release it, the ball begins to accelerate toward the ground. This acceleration happens because Earth's gravity pulls objects toward its center. In a vacuum (where there's no air), all objects fall at the same rate regardless of their weight!
Did You Know?
Galileo Galilei famously demonstrated that objects of different masses fall at the same rate when air resistance is negligible. He may have dropped balls from the Leaning Tower of Pisa!
Gravity & Acceleration
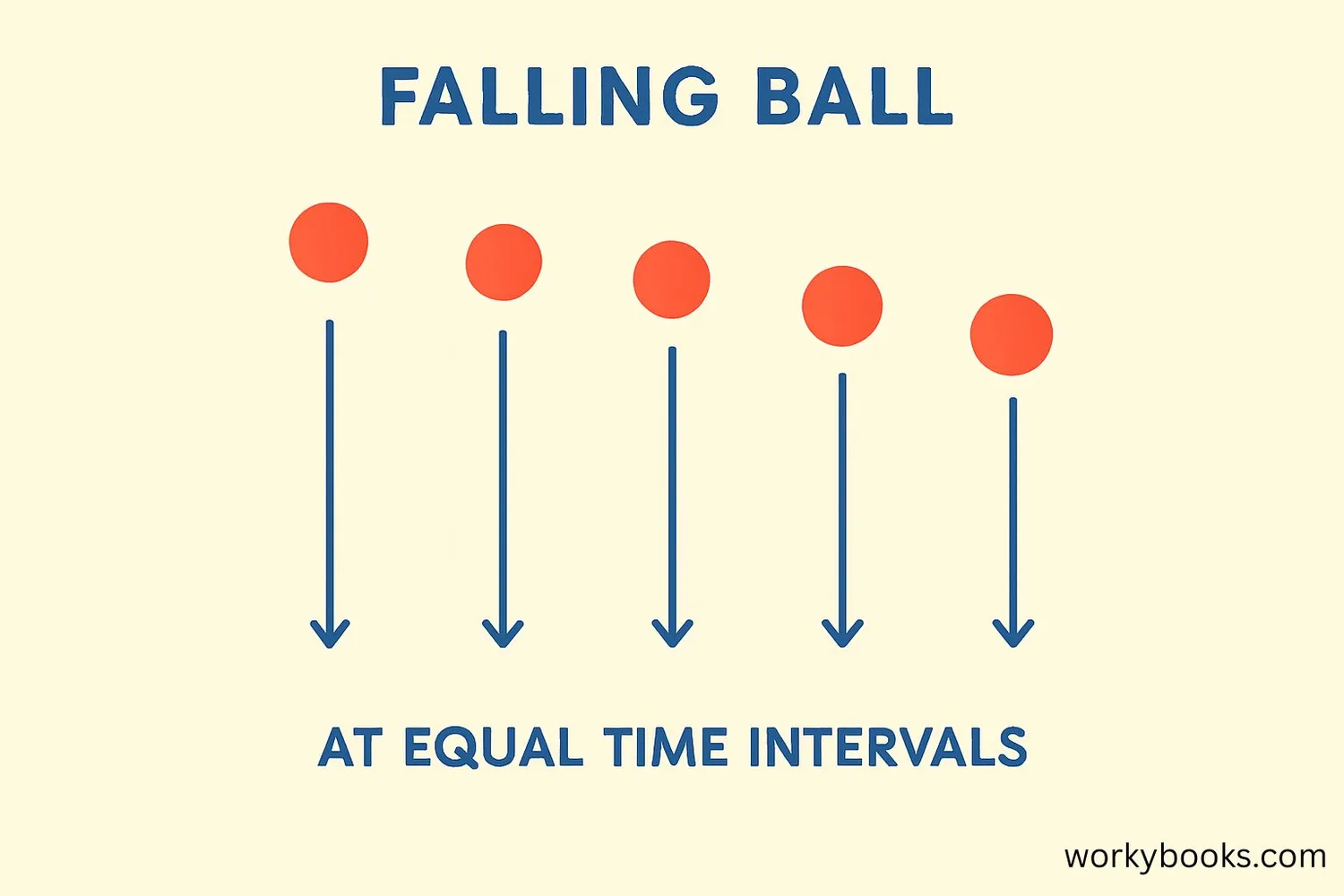
The acceleration due to gravity on Earth is approximately 9.8 m/s². This means that for every second an object is in free fall, its velocity increases by 9.8 meters per second.
Here's what happens during free fall:
Initial Drop
When first released, the object has zero velocity
After 1 Second
Velocity = 9.8 m/s downward
After 2 Seconds
Velocity = 19.6 m/s downward
After 3 Seconds
Velocity = 29.4 m/s downward
The distance an object falls can be calculated using the equation:
d = ½ × g × t²
Where d is distance, g is acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s²), and t is time in seconds.
Real World Example
When skydivers jump from a plane, they're initially in free fall until they open their parachutes. They accelerate until air resistance balances gravity.
Air Resistance & Terminal Velocity
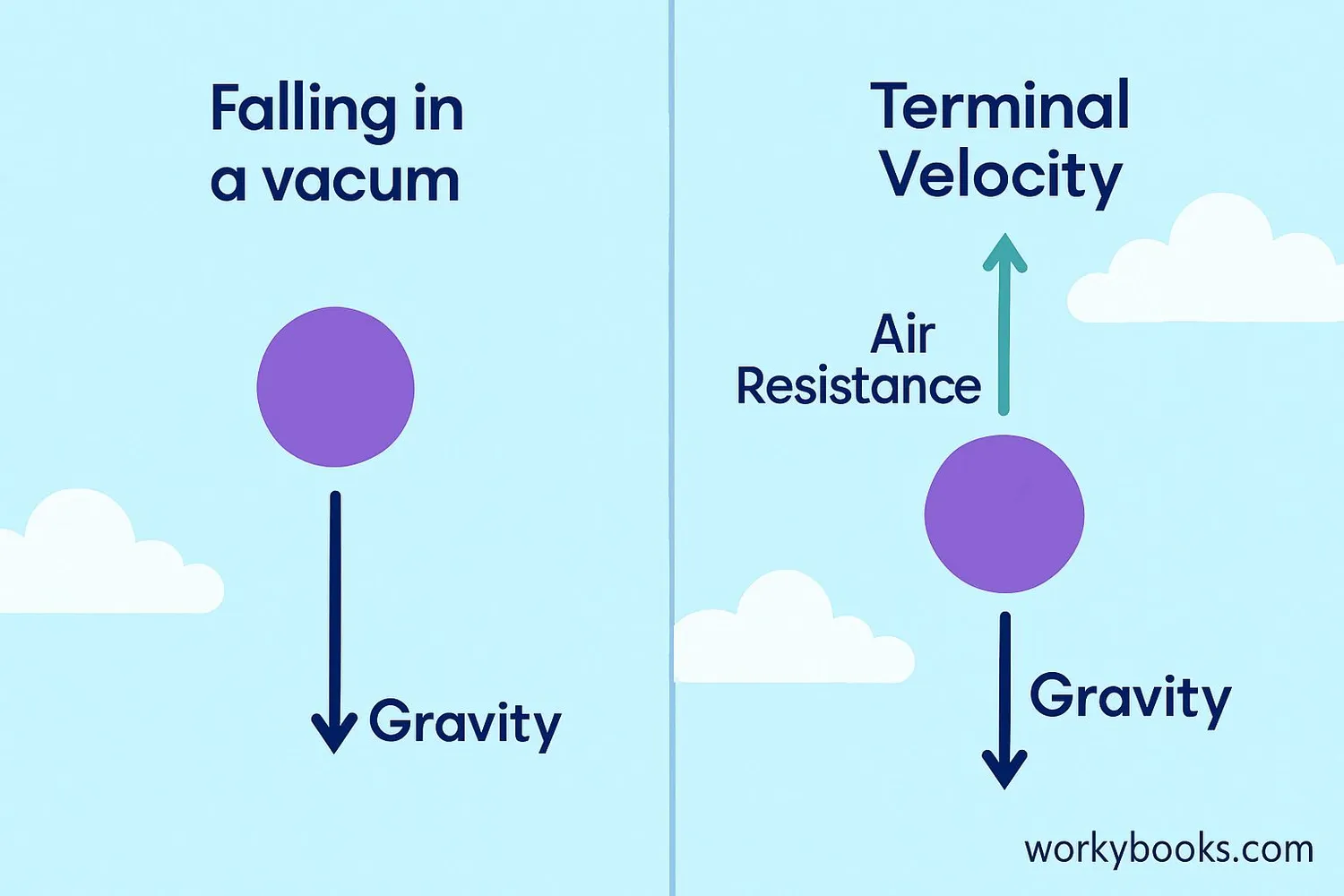
In the real world, air resistance affects falling objects. Air resistance is a force that pushes against objects moving through air. The amount of air resistance depends on the object's speed, size, and shape.
When an object first starts falling, gravity is stronger than air resistance, so the object accelerates. As the object falls faster, air resistance increases. Eventually, air resistance becomes equal to the force of gravity. When this happens, the object stops accelerating and falls at a constant speed called terminal velocity.
Light Objects
Feathers and paper have low terminal velocity due to high air resistance
Dense Objects
Baseballs have higher terminal velocity than feathers
Parachutes
Increase air resistance to reduce terminal velocity for safe landing
For a skydiver in a belly-down position, terminal velocity is about 200 km/h (124 mph). When the parachute opens, the increased air resistance dramatically reduces terminal velocity to about 18 km/h (11 mph), allowing for a safe landing.
Free Fall Physics Quiz
Test your knowledge of free fall physics with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about free fall:
Free Fall Science Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about free fall and gravity!
Moon Gravity
The acceleration due to gravity on the Moon is only 1.6 m/s²—about one-sixth of Earth's gravity. This is why astronauts can jump higher and objects fall more slowly there.
Speed Record
In 2012, Felix Baumgartner set a record by jumping from a balloon 39 km above Earth. He reached a maximum speed of 1,357.6 km/h (843.6 mph)—faster than the speed of sound!
Animal Free Fall
The peregrine falcon is the fastest animal in free fall. When diving for prey, it can reach speeds over 320 km/h (200 mph) by tucking its wings to minimize air resistance.
Weightless Feeling
Astronauts train for weightlessness in aircraft nicknamed "vomit comets" that fly parabolic arcs. During these arcs, everyone inside experiences about 25 seconds of free fall.





