Neutralization Reactions - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how acids and bases interact to form salt and water!
What is Neutralization?
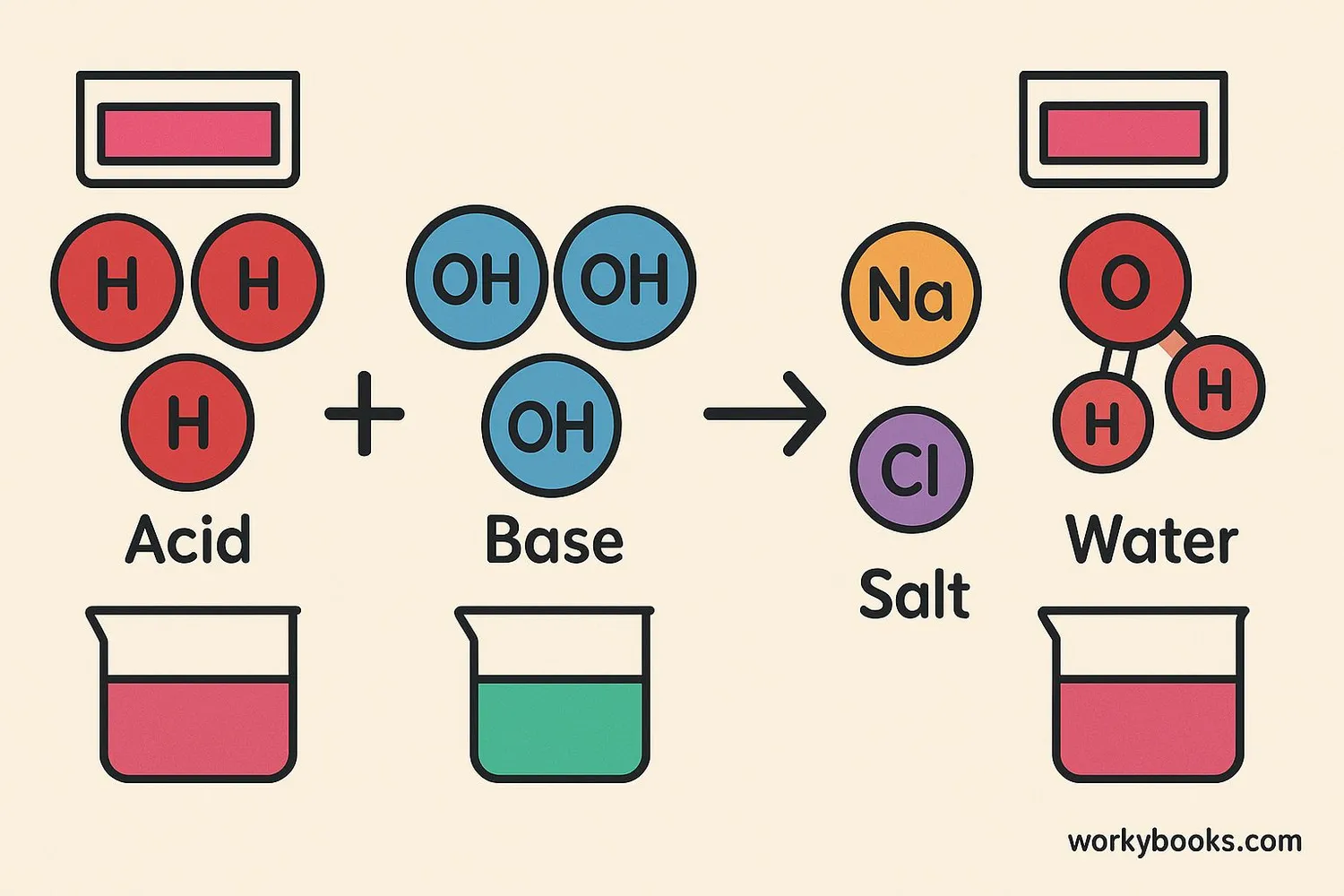
Neutralization is a special chemical reaction that happens when an acid and a base mix together. When they combine, they create two new substances: salt and water.
Think of acids and bases as opposites that balance each other out! Acids have a sour taste (like lemon juice) and bases have a bitter taste (like baking soda). When they meet, they cancel each other's properties and become neutral - not too acidic and not too basic.
Chemistry Fact!
The word "neutralization" comes from "neutral," meaning balanced or in the middle of the pH scale.
How Neutralization Works
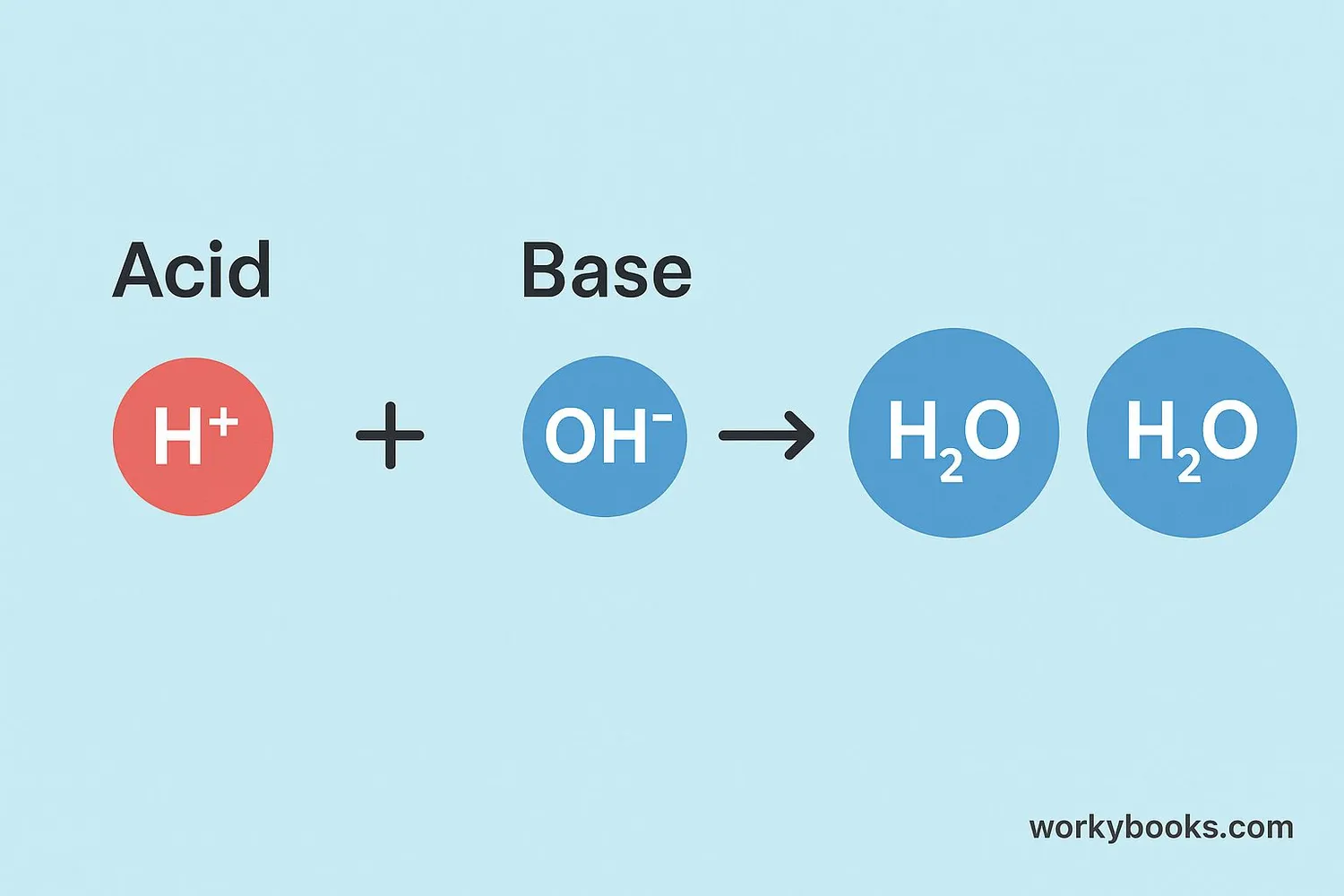
Neutralization works through a special exchange of particles called ions. Acids contain hydrogen ions (H⁺) and bases contain hydroxide ions (OH⁻). When they mix, these ions combine to form water (H₂O). The remaining ions join together to create a salt.
Acid Contribution
Acids provide hydrogen ions (H⁺)
Base Contribution
Bases provide hydroxide ions (OH⁻)
Water Formation
H⁺ and OH⁻ combine to form water (H₂O)
Salt Formation
Remaining ions combine to form salt
pH Balance
The solution becomes neutral (pH 7)
A common example is the reaction between hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH):
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂O
Which means: Hydrochloric acid + Sodium hydroxide → Sodium chloride (table salt) + Water
pH Scale!
The pH scale measures how acidic or basic a substance is. It ranges from 0 (very acidic) to 14 (very basic), with 7 being neutral.
Why Neutralization is Important
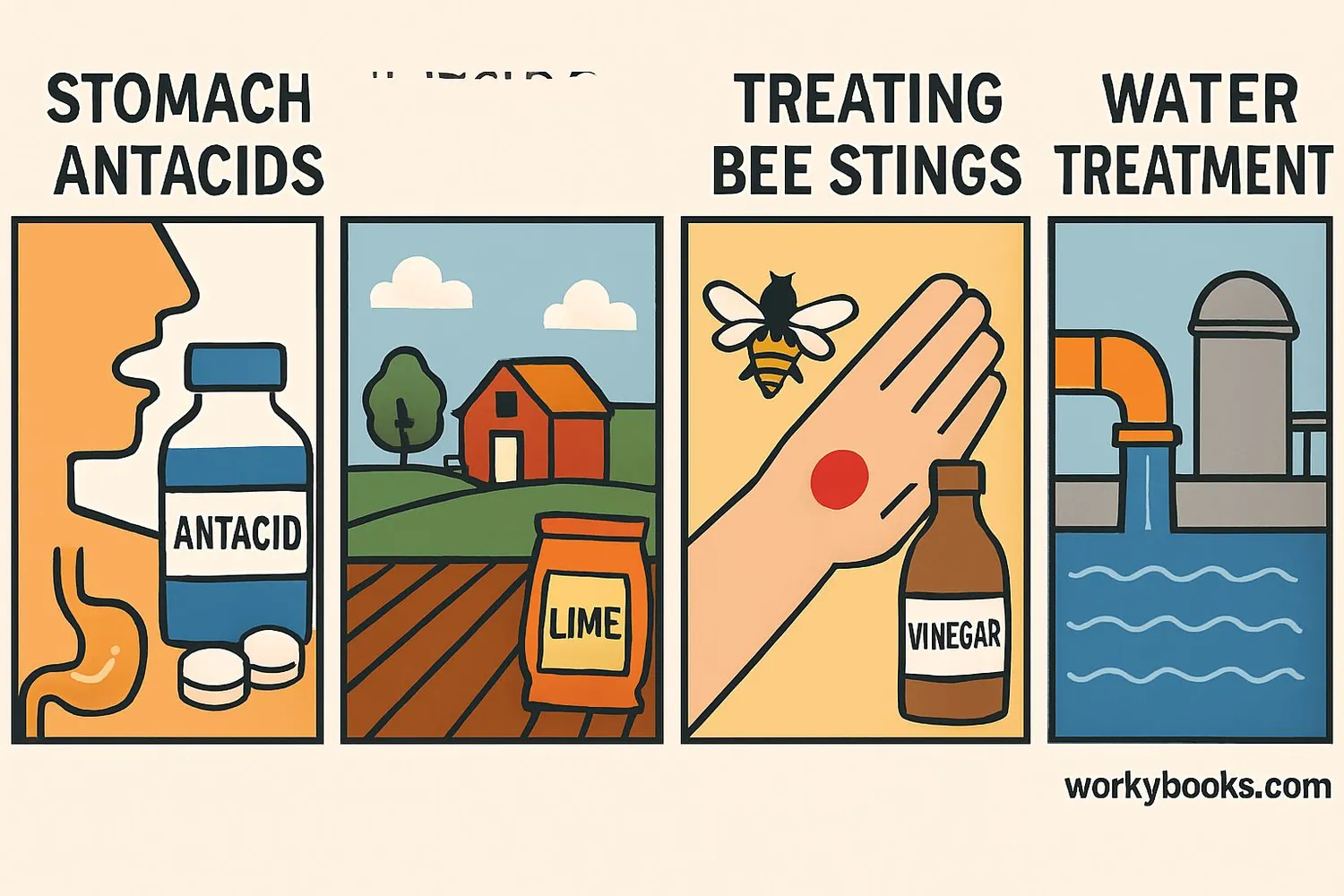
Neutralization reactions are essential in our everyday lives! Here's why they're so important:
Medicine
Antacids neutralize excess stomach acid to relieve indigestion
Agriculture
Farmers use lime (a base) to neutralize acidic soil for better crop growth
Water Treatment
Neutralization adjusts pH levels in water to make it safe for drinking
Other important uses of neutralization include:
• Treating bee stings (acidic) with baking soda (basic)
• Treating wasp stings (basic) with vinegar (acidic)
• Controlling industrial waste before releasing it into the environment
• In chemical manufacturing processes
Neutralization helps keep our bodies and environment in balance!
Neutralization Quiz
Test your knowledge about neutralization reactions with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about neutralization:
Interesting Neutralization Facts
Discover some amazing facts about neutralization reactions!
Ocean Neutralization
The ocean acts as a giant neutralization tank, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and slowly neutralizing it. This helps regulate Earth's climate but is also causing ocean acidification.
Historical Use
Ancient Romans used a form of neutralization by adding calcium carbonate (from seashells) to acidic wine to improve its taste—an early example of pH adjustment in food!
Space Applications
Neutralization reactions are used in spacecraft to remove carbon dioxide from the air astronauts breathe. Lithium hydroxide canisters neutralize CO₂ by forming lithium carbonate and water.
Animal Defense
Some animals use neutralization for defense! Bombardier beetles mix two chemicals in their abdomen that react to produce a hot, irritating spray aimed at predators.





