Newton's First Law - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how objects behave when forces act on them!
What is Newton's First Law?
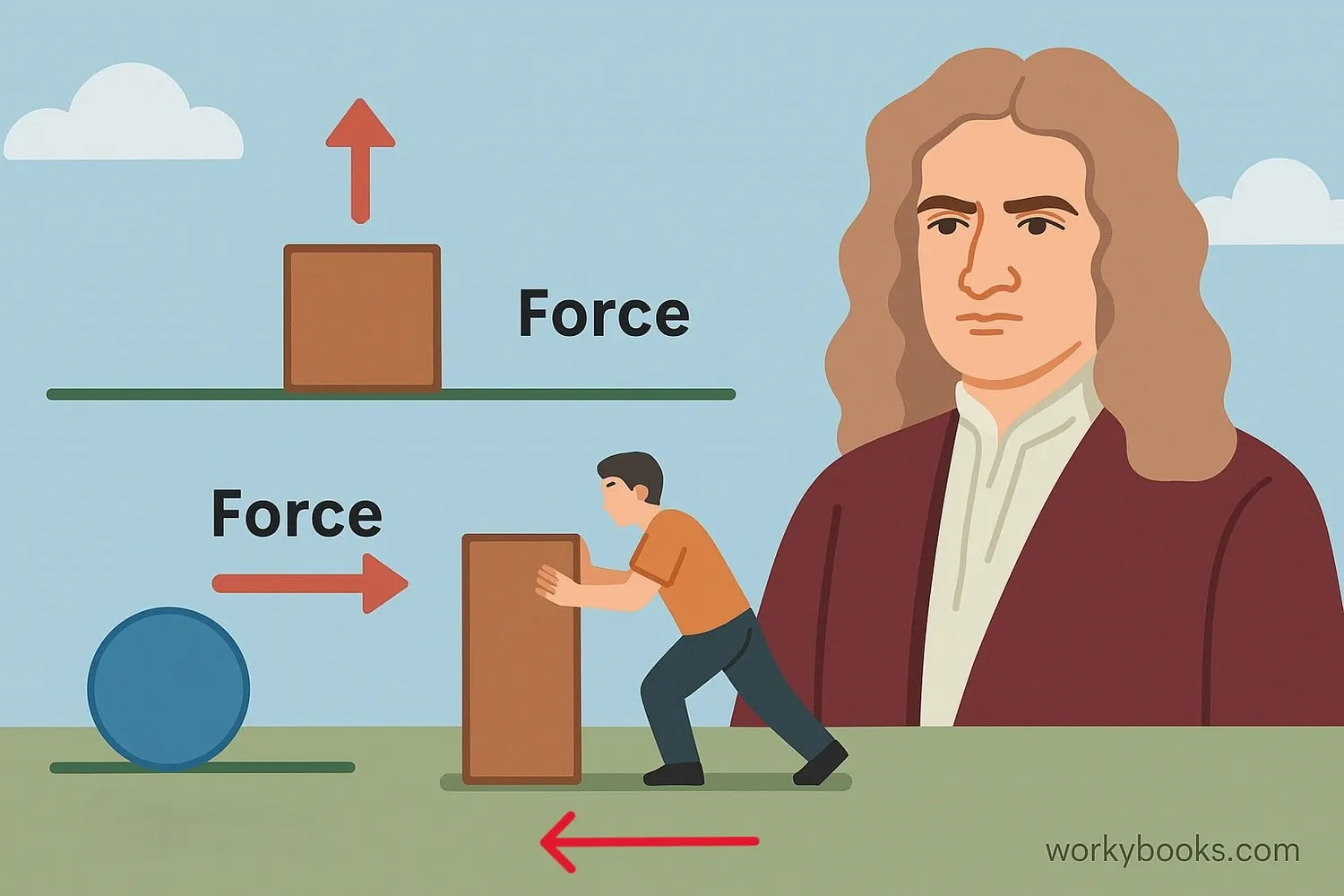
Newton's First Law of Motion, also called the Law of Inertia, states that:
"An object at rest stays at rest, and an object in motion stays in motion at constant speed and in a straight line unless acted upon by an unbalanced force."
This means that objects will keep doing what they're already doing unless something changes their motion. If an object is sitting still, it will stay still. If it's moving, it will keep moving at the same speed and in the same direction.
Sir Isaac Newton described this law in 1687, building on ideas from Galileo Galilei. This law helps us understand why we need seatbelts in cars and why it's hard to stop a heavy object once it's moving!
Key Definition
An unbalanced force is a force that changes an object's motion by making it start moving, stop moving, or change direction.
Understanding Inertia
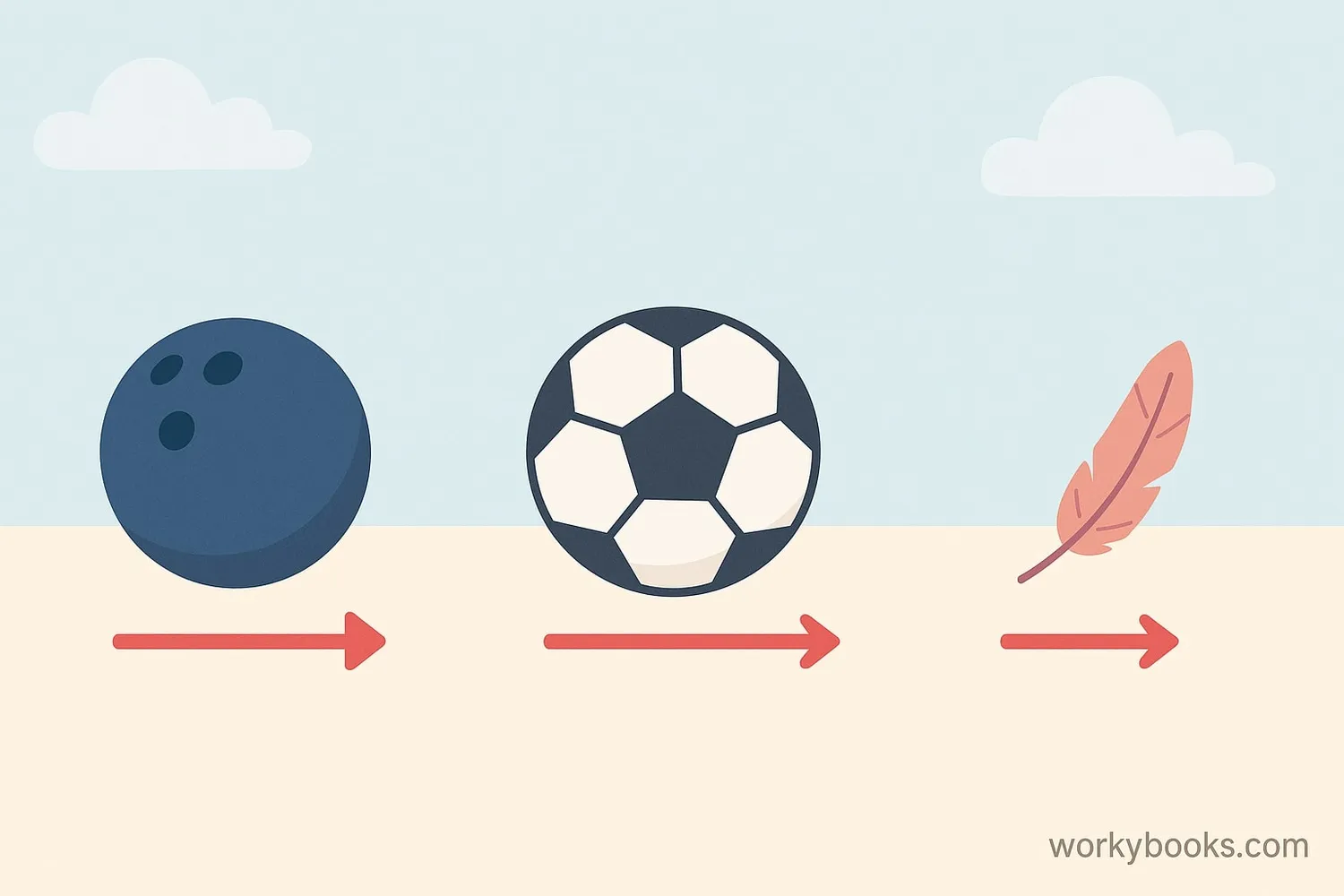
Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist changes to its motion. It's the reason why:
• A bowling ball is harder to move than a soccer ball
• A moving truck is harder to stop than a bicycle
• You feel pushed back in your seat when a car accelerates
Inertia comes from an object's mass. The more mass something has, the more inertia it has. This means heavier objects are harder to start moving and harder to stop once they're moving.
Mass Matters
Objects with more mass have more inertia
Resistance to Change
Inertia resists changes to motion
All Objects
Everything has inertia - from atoms to planets
Inertia Insight
When you're in a moving car and it stops suddenly, your body wants to keep moving forward because of inertia. That's why seatbelts are so important!
How Newton's First Law Works
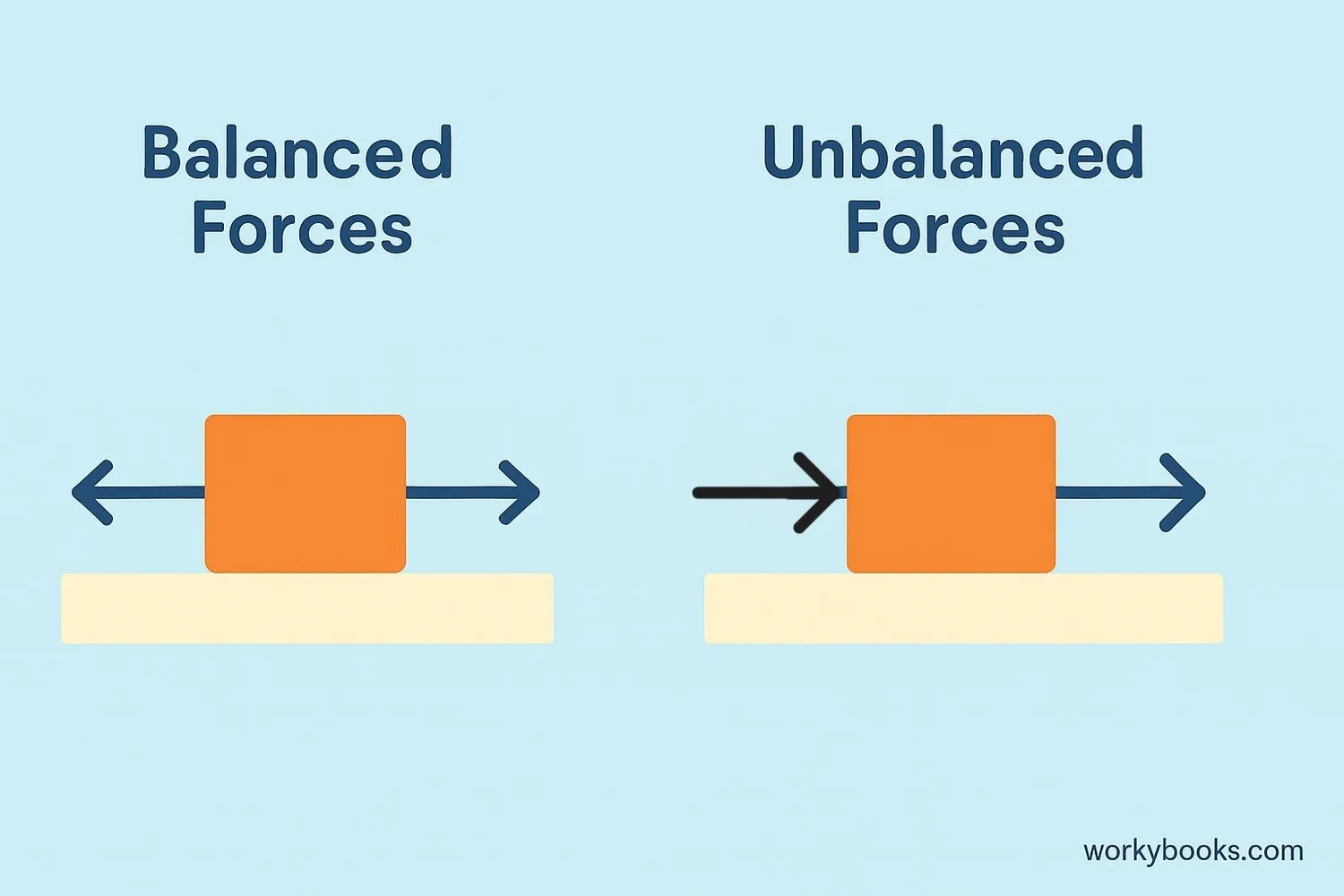
Newton's First Law works through the balance of forces:
1. Objects at Rest: When an object is sitting still, all the forces acting on it are balanced. For example, a book on a table has gravity pulling it down and the table pushing it up with equal force.
2. Objects in Motion: When an object is moving at constant velocity (constant speed in a straight line), the forces acting on it are balanced too. For example, a spaceship in deep space far from any planets will keep moving forever because there are no forces to change its motion.
3. Changing Motion: When forces become unbalanced, the object's motion changes. This could mean starting to move, stopping, speeding up, slowing down, or changing direction.
Constant Velocity
Constant velocity means moving at the same speed in a straight line. When forces are balanced, objects either stay at rest or maintain constant velocity.
Real-World Examples

We see Newton's First Law in action every day:
Car Safety
Seatbelts stop passengers from continuing forward when a car stops suddenly
Sports
A soccer ball stays still until kicked, and keeps moving until friction stops it
Everyday Objects
Books stay on shelves until you move them because forces are balanced
More examples of Newton's First Law:
• When you slide a book across a table, it eventually stops because of friction
• Astronauts float in space because there's no force to stop their motion
• Dusting a rug makes dust particles fly off because they resist changes to motion
• Your body keeps moving forward when a bus suddenly stops
Newton's First Law Quiz
Test your understanding with this quiz! Choose the best answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about Newton's First Law:
Fun Physics Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about Newton's First Law and inertia!
Space Travel
Voyager 1 spacecraft, launched in 1977, is still traveling through space at about 38,000 mph. It will continue moving indefinitely until it hits something, thanks to Newton's First Law!
Sports Physics
In ice hockey, the puck slides much farther than on other surfaces because ice has very low friction. This is a great example of Newton's First Law in sports!
Earth's Motion
Earth is constantly moving through space at about 67,000 mph around the Sun. We don't feel this motion because we're moving at constant velocity along with everything around us.
Newton's Apple
The famous story of Newton discovering gravity when an apple fell on his head? It was actually thinking about why the apple fell straight down that helped him develop his laws of motion.





