Polar Covalent Bonds - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how atoms share electrons unequally to create special bonds!
What Are Polar Covalent Bonds?
Polar covalent bonds are special chemical bonds where atoms share electrons unequally. Unlike regular covalent bonds where electrons are shared equally, polar bonds happen when one atom pulls the shared electrons closer to itself.
This happens because different atoms have different abilities to attract electrons, called electronegativity. When two atoms with different electronegativity form a bond, the electrons spend more time around the atom with higher electronegativity.
Electronegativity
An atom's ability to attract electrons
Electron Sharing
Atoms share electrons unequally
Partial Charges
One end becomes slightly negative, the other slightly positive
Key Fact!
Water is the most important example of polar covalent bonding. Its polarity makes it the "universal solvent" that can dissolve many substances!
How Polar Covalent Bonds Work
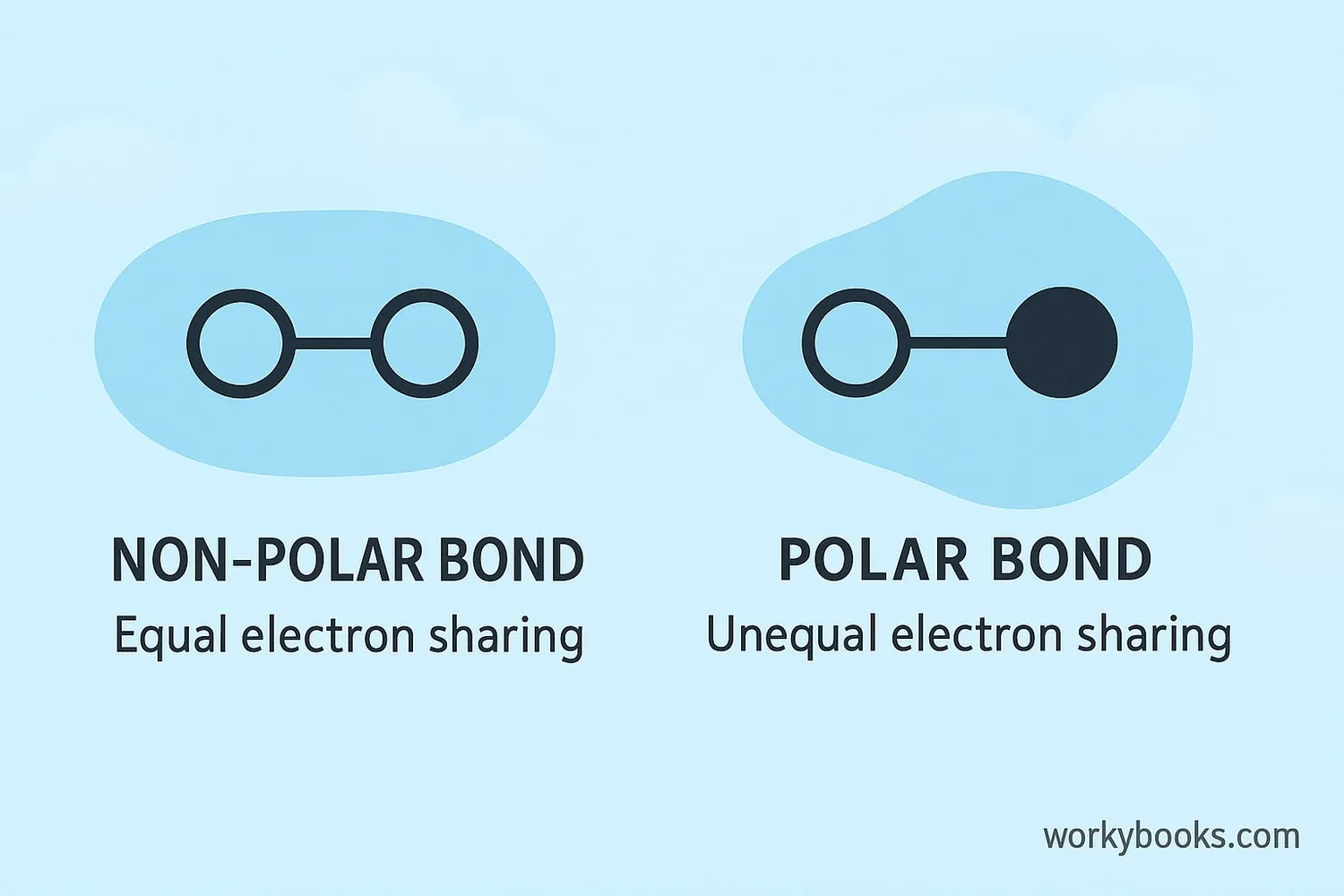
Polar covalent bonds form when two different atoms with different electronegativity values bond together. The atom with higher electronegativity pulls the shared electrons closer to itself, creating partial charges:
Electronegativity Difference
Atoms must have different "electron-pulling" power
Electron Cloud Shift
Electron cloud shifts toward more electronegative atom
Partial Charges
Creates δ+ (partial positive) and δ- (partial negative) ends
The polarity of a bond can be measured by the difference in electronegativity between the two atoms:
• 0.0-0.4: Non-polar covalent bond (equal sharing)
• 0.5-1.7: Polar covalent bond (unequal sharing)
• >1.7: Ionic bond (electron transfer)
Electronegativity Scale!
Fluorine is the most electronegative element (4.0), while cesium is the least (0.7). This difference creates highly polar bonds!
Why Polar Covalent Bonds Are Important
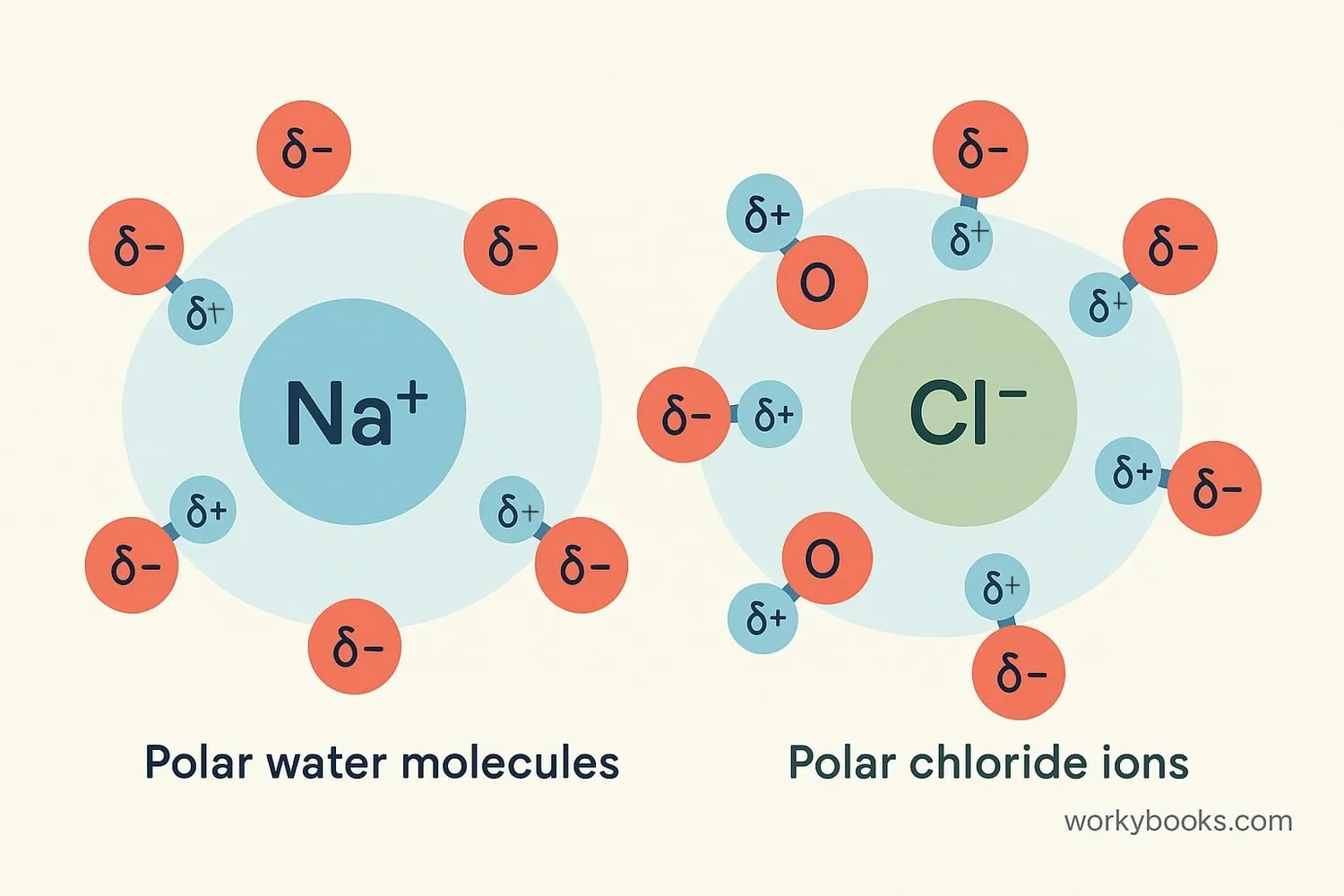
Polar covalent bonds are essential for life and many natural processes. Their importance comes from the special properties they give to molecules:
Water Properties
Polarity gives water high surface tension and capillary action
Solvent Ability
Polar solvents dissolve other polar substances
Biological Functions
Essential for DNA structure and protein folding
Without polar covalent bonds, we wouldn't have:
• Water as we know it (no surface tension, boiling at different temperatures)
• Ability to dissolve salts and sugars in water
• Cell membranes that control what enters and exits cells
• Many medicines that work by binding to specific molecules
Polar covalent bonds create molecules with "positive" and "negative" ends that can attract other molecules in special ways!
Polar Bonds Quiz
Test your knowledge about polar covalent bonds with this quiz!
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about polar covalent bonds:
Chemistry Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about polar covalent bonds and chemistry!
Water's Special Properties
Water is the only substance on Earth that naturally exists in all three states (solid, liquid, gas) at normal temperatures. This is possible because of its polar bonds!
Human Body Chemistry
Your body is about 60% water. The polar nature of water allows it to dissolve nutrients, carry them through your bloodstream, and help chemical reactions happen in cells.
DNA Structure
The double helix structure of DNA is held together by hydrogen bonds between polar molecules. These bonds are strong enough to maintain structure but weak enough to allow DNA to "unzip" for replication.
Electronegativity Scale
The electronegativity scale was developed by Nobel Prize winner Linus Pauling. Fluorine is the most electronegative element (4.0), while cesium is the least (0.7).





