Stoichiometry - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how chemists measure and balance chemical reactions!
What is Stoichiometry?
Stoichiometry (stoy-kee-OM-uh-tree) is like a recipe for chemistry! It's the part of chemistry that helps us measure and calculate the amounts of substances involved in chemical reactions.
Think of it like baking cookies: if a recipe says you need 2 cups of flour to make 24 cookies, stoichiometry helps you figure out how much flour you'd need for 48 cookies, or how many cookies you could make with 3 cups of flour.
In chemistry, we use stoichiometry to answer questions like: How much oxygen do we need to burn this fuel? How much product will this reaction create? It's all about the ratios between chemicals in reactions!
Word Origin
The word "stoichiometry" comes from Greek words: "stoicheion" (element) and "metron" (measure). So it literally means "measuring elements"!
How Stoichiometry Works
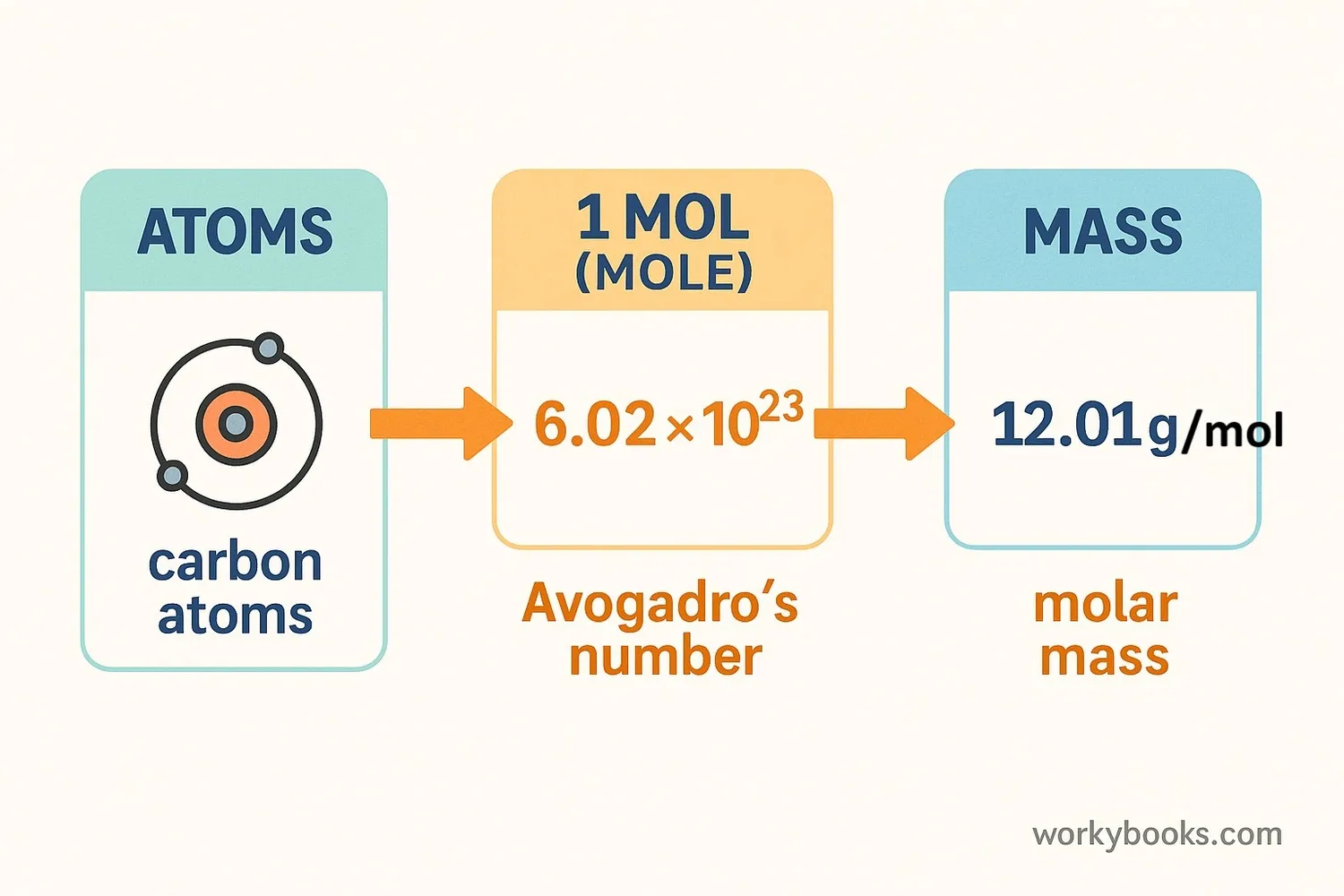
Stoichiometry works using a special chemistry unit called the mole. Don't think of the animal - a mole in chemistry is like a "dozen" but much bigger! While a dozen means 12 of something, a mole means 602,200,000,000,000,000,000,000 of something! (We write this as 6.022 × 10²³ and call it Avogadro's Number).
We use moles because atoms and molecules are too tiny to count individually. With stoichiometry, we can:
Balance Equations
Make sure atoms are conserved in reactions
Use Ratios
Find proportions between reactants and products
Convert Units
Move between grams, moles, and molecules
The most important rule in stoichiometry is the law of conservation of mass: matter cannot be created or destroyed. So in chemical reactions, all the atoms we start with must end up in the products - they just get rearranged!
In this formula, the lowercase letters (a, b, c, d) are the coefficients that tell us the ratios of the chemicals (A, B, C, D) in the reaction.
Stoichiometry Examples
Let's look at some examples to understand how stoichiometry works in real chemical reactions:
Example 1: Making Water
The reaction: 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O
This tells us that 2 molecules of hydrogen gas react with 1 molecule of oxygen gas to make 2 molecules of water.
So the ratios are: 2 H₂ : 1 O₂ : 2 H₂O
Example 2: Rust Formation
The reaction: 4Fe + 3O₂ → 2Fe₂O₃
This tells us that 4 atoms of iron react with 3 molecules of oxygen to make 2 molecules of rust (iron oxide).
So the ratios are: 4 Fe : 3 O₂ : 2 Fe₂O₃
Example 3: Baking Soda and Vinegar
The reaction: NaHCO₃ + CH₃COOH → CO₂ + H₂O + CH₃COONa
This tells us that 1 molecule of baking soda reacts with 1 molecule of vinegar to produce 1 molecule of carbon dioxide gas, 1 molecule of water, and 1 molecule of sodium acetate.
So the ratios are: 1:1:1:1:1
With stoichiometry, we can use these ratios to calculate how much of each substance we need or how much product we'll get. It's like using the coefficients in the chemical equation as a conversion factor!
Why Stoichiometry is Important
Stoichiometry isn't just something chemists study - it has important uses in our everyday lives and many industries:
Medicine
Calculating precise drug dosages and formulations
Manufacturing
Making products efficiently without waste
Environment
Calculating pollution levels and treatment needs
Without stoichiometry, we would:
• Waste valuable resources in manufacturing
• Have difficulty creating effective medicines
• Struggle to understand environmental processes
• Be unable to predict reaction outcomes accurately
Stoichiometry helps scientists and engineers create the right amounts of products, reduce waste, and understand how chemicals interact in our world!
Real-world Connection
Car manufacturers use stoichiometry to design catalytic converters that change harmful exhaust gases into less harmful substances!
Stoichiometry Quiz
Test your stoichiometry knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about stoichiometry:
Fun Stoichiometry Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about stoichiometry!
Historical Origins
Stoichiometry principles were first established by Jeremias Benjamin Richter, a German chemist, in 1792. He was the first to show that chemicals combine in fixed proportions!
Rocket Science
NASA engineers use stoichiometry to calculate exactly how much fuel rockets need! Too little fuel and the rocket won't reach space; too much and it's too heavy to launch efficiently.
Environmental Protection
Stoichiometry helps environmental scientists calculate how to neutralize acid rain. They determine exactly how much base (like limestone) is needed to counteract the acid in lakes and soils.
Culinary Chemistry
When you follow a recipe, you're doing practical stoichiometry! Doubling a recipe requires exactly twice each ingredient, just like scaling up a chemical reaction.





