Bill of Rights
Discover how the first 10 amendments to the U.S. Constitution protect your rights and freedoms!
What Is the Bill of Rights?
The Bill of Rights is the name given to the first ten amendments to the United States Constitution. These amendments list specific protections for individual liberty and justice and limit the government's power over its citizens.
The Bill of Rights was added to the Constitution in 1791, just a few years after the Constitution itself was written. Many Americans were concerned that the Constitution didn't clearly state the rights of the people, so they insisted on adding these amendments to make sure their freedoms would be protected.
Did You Know?
James Madison, who later became the fourth President of the United States, wrote the Bill of Rights! He originally proposed 12 amendments, but only 10 were approved by the states.
The First Amendment

The First Amendment is perhaps the most famous part of the Bill of Rights. It protects five fundamental freedoms:
Freedom of Speech
The right to express your opinions and ideas without government censorship
Freedom of Religion
The right to practice any religion or no religion at all
Freedom of the Press
The right for newspapers and media to report news without government control
Freedom of Assembly
The right to gather peacefully in groups
Freedom to Petition
The right to complain to the government about problems
These freedoms help ensure that Americans can think for themselves, share ideas, and participate in their government without fear of punishment.
The Second Amendment
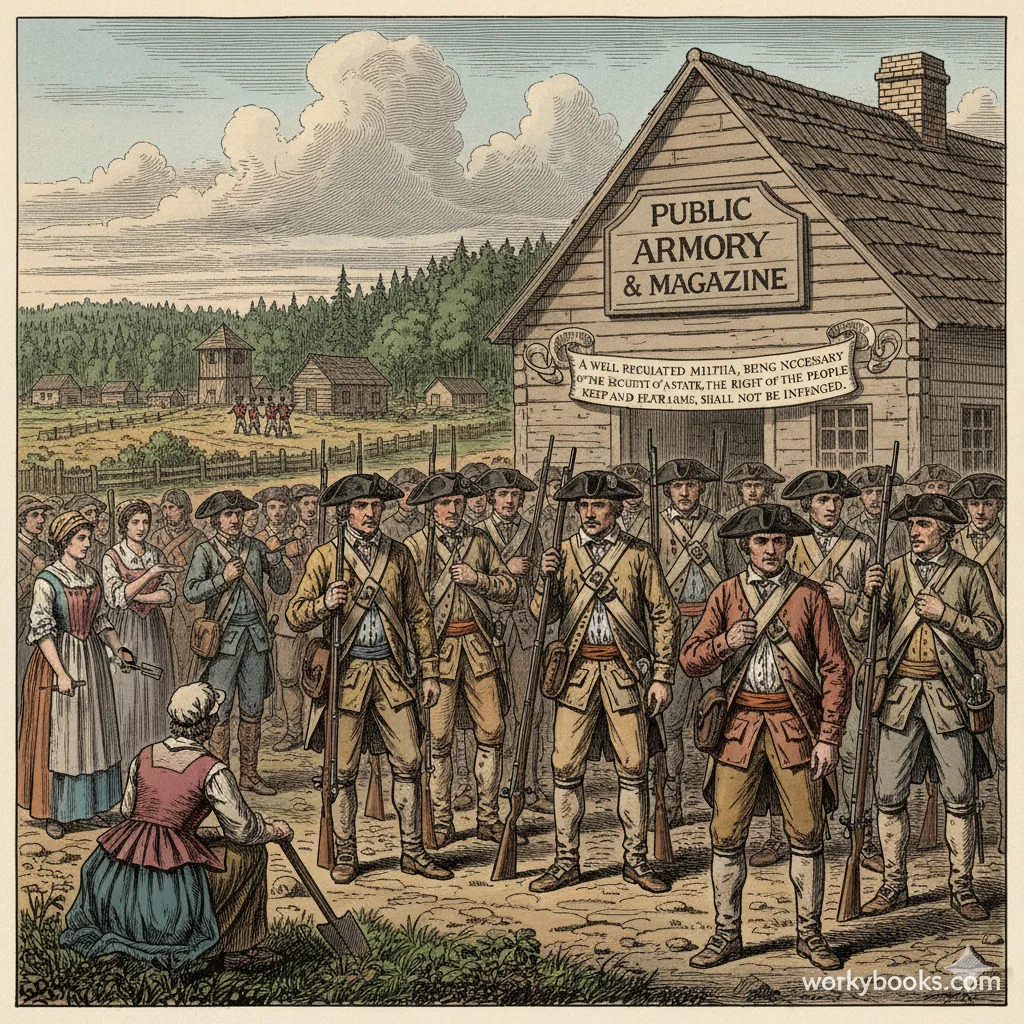

The Second Amendment protects the right to keep and bear arms. The exact wording is: "A well regulated Militia, being necessary to the security of a free State, the right of the people to keep and bear Arms, shall not be infringed."
This amendment was important to the founders because they had just fought a war against Britain, where they needed citizens to have weapons to form militias. Today, there is much debate about what this amendment means in modern times and how it should be applied.
Important Note
Like all rights, the Second Amendment has limits. For example, laws regulate who can own guns and what types of weapons are allowed.
Other Important Amendments

The Bill of Rights includes eight more amendments that protect important rights:
No Quartering Soldiers
Protects homeowners from having to house soldiers in peacetime
Search and Seizure
Requires police to have a warrant to search your property
Rights of the Accused
Protects against self-incrimination and double jeopardy
Right to Fair Trial
Guarantees speedy public trial by jury and right to a lawyer
Jury in Civil Cases
Right to jury trial in civil cases involving money
No Cruel Punishment
Prohibits excessive bail and cruel/unusual punishment
Other Rights
States that people have other rights not listed in Constitution
States' Rights
Says powers not given to federal government belong to states
Why the Bill of Rights Is Important

The Bill of Rights is crucial because it:
- Protects individual freedoms from government overreach
- Ensures fair treatment for anyone accused of crimes
- Limits government power to prevent tyranny
- Guarantees basic rights for all Americans
- Serves as a model for other countries creating their own constitutions
Without the Bill of Rights, the government could potentially restrict speech, religion, press, and other fundamental freedoms. These amendments help maintain the balance between government authority and individual liberty that is essential to American democracy.
Bill of Rights Quiz
Test your knowledge about the Bill of Rights! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about the Bill of Rights:
Bill of Rights Trivia
Discover amazing facts about the Bill of Rights!
Original Copies
There were originally 14 copies of the Bill of Rights - one for the federal government and one for each of the 13 states. Only 12 are known to survive today.
Proposed Amendments
James Madison originally proposed 12 amendments, but the first two weren't ratified initially. The second proposed amendment was finally ratified in 1992 as the 27th Amendment!
Global Influence
The Bill of Rights has inspired similar documents in countries around the world, including the Universal Declaration of Human Rights adopted by the United Nations in 1948.
Final Ratification
Virginia became the 11th state to ratify the Bill of Rights on December 15, 1791, making the amendments officially part of the Constitution. We now celebrate Bill of Rights Day on December 15th.





