Cumulonimbus Clouds - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Understanding Thunderstorm Clouds and Their Impact on Weather
What are Cumulonimbus Clouds?
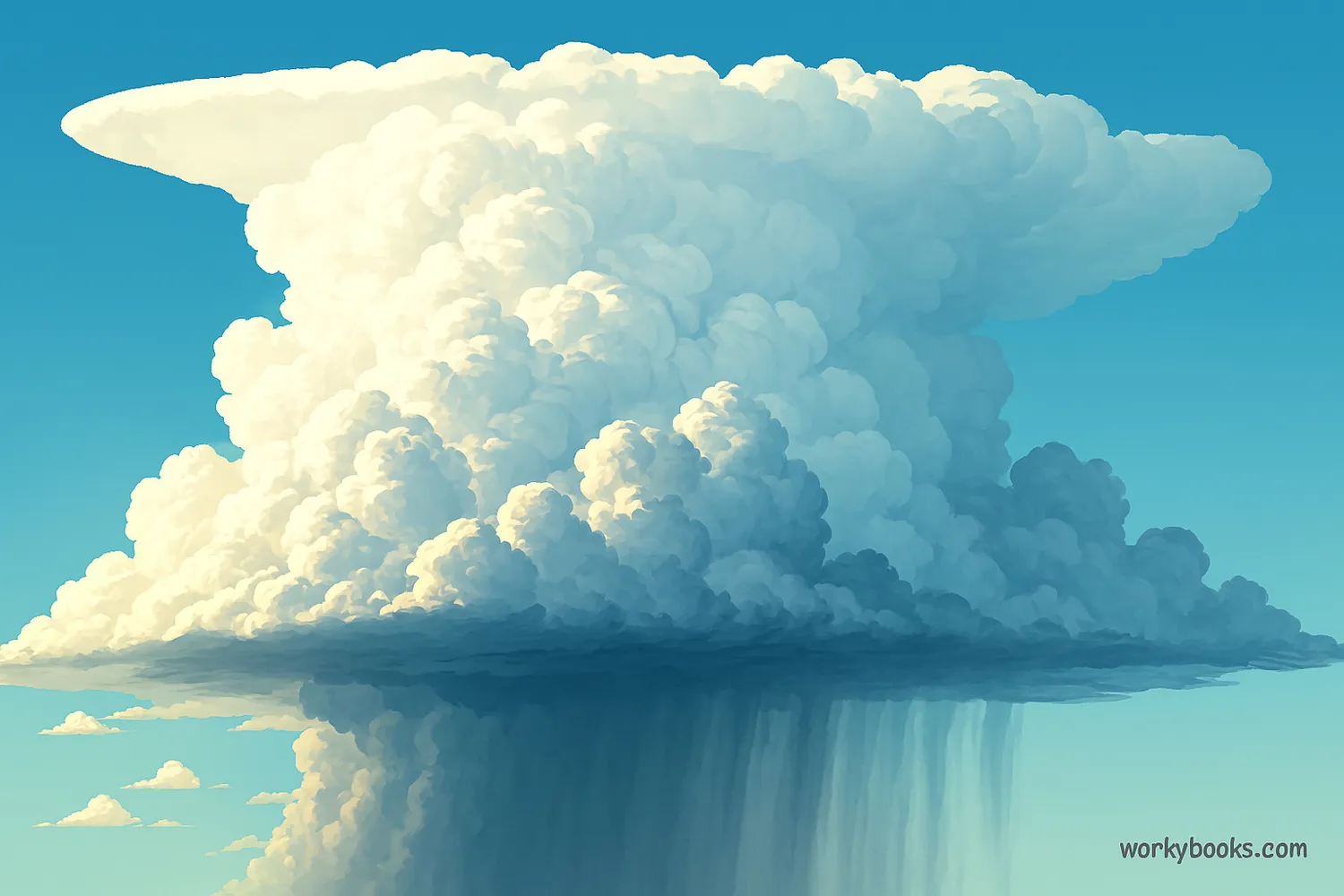

Cumulonimbus clouds are the king of all clouds - massive, towering clouds that can reach incredible heights in the sky! They're often called thunderstorm clouds because they're responsible for most thunderstorms.
These clouds are like weather factories that can produce heavy rain, lightning, thunder, hail, and even tornadoes. They form when warm, moist air rises very quickly into the colder upper atmosphere.
Science Fact!
Cumulonimbus clouds can grow so tall that they reach the top of the troposphere (the lowest layer of our atmosphere), sometimes extending over 12 miles (20 kilometers) high!
How Cumulonimbus Clouds Form
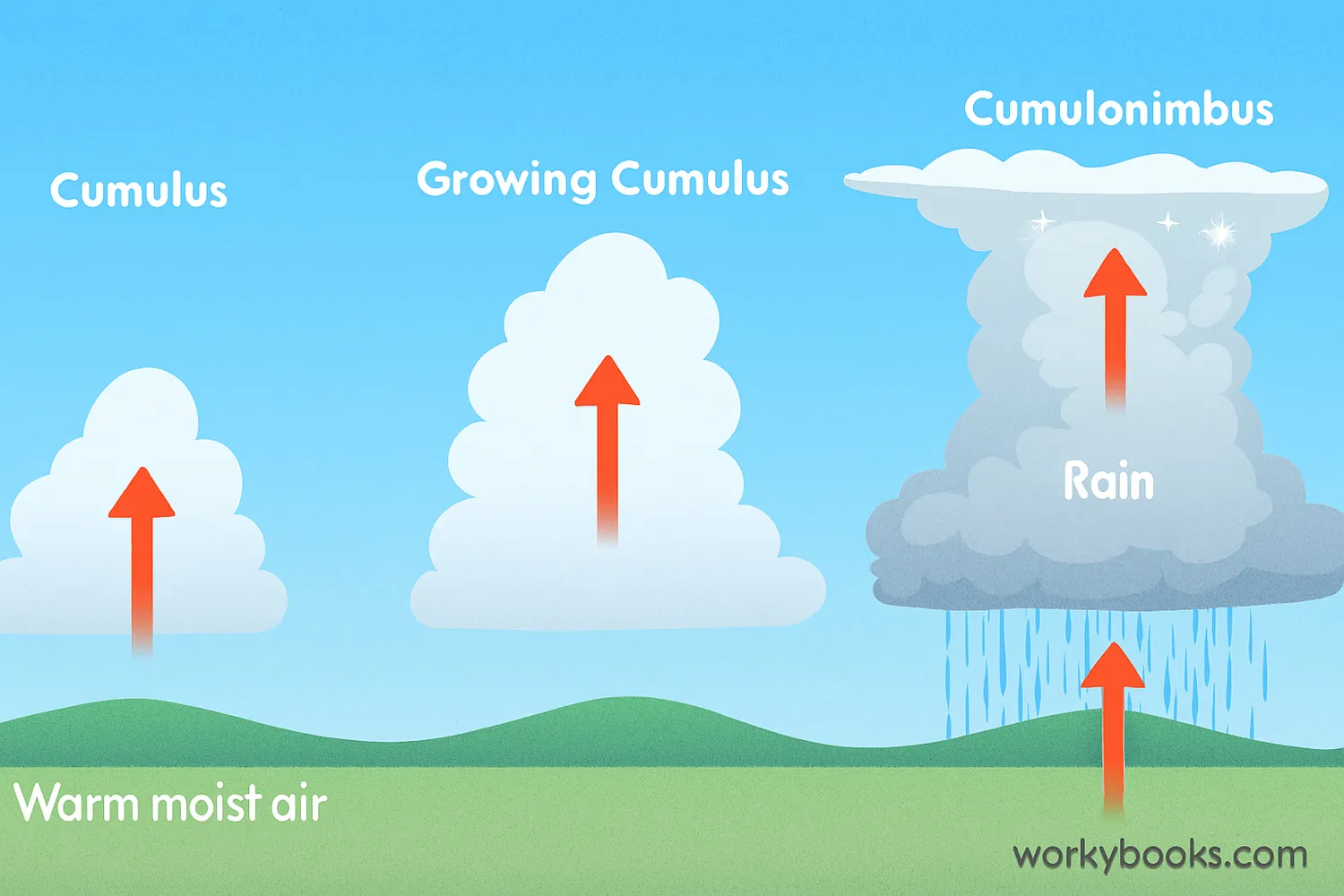
Cumulonimbus clouds form through a process called convection. Here's how it works:
Warm Air Rises
The sun heats the ground, warming the air above it
Moisture Condenses
As warm air rises, it cools and water vapor condenses into tiny droplets
Cumulus Stage
Droplets form puffy cumulus clouds that continue growing upward
Mature Stage
The cloud becomes a towering cumulonimbus with rain and updrafts
Dissipating Stage
The storm weakens as downdrafts cut off the warm air supply
This process needs three key ingredients: moisture, unstable air (air that wants to rise), and a lifting mechanism (like heating from the sun or air forced up over mountains).
Types of Cumulonimbus Clouds
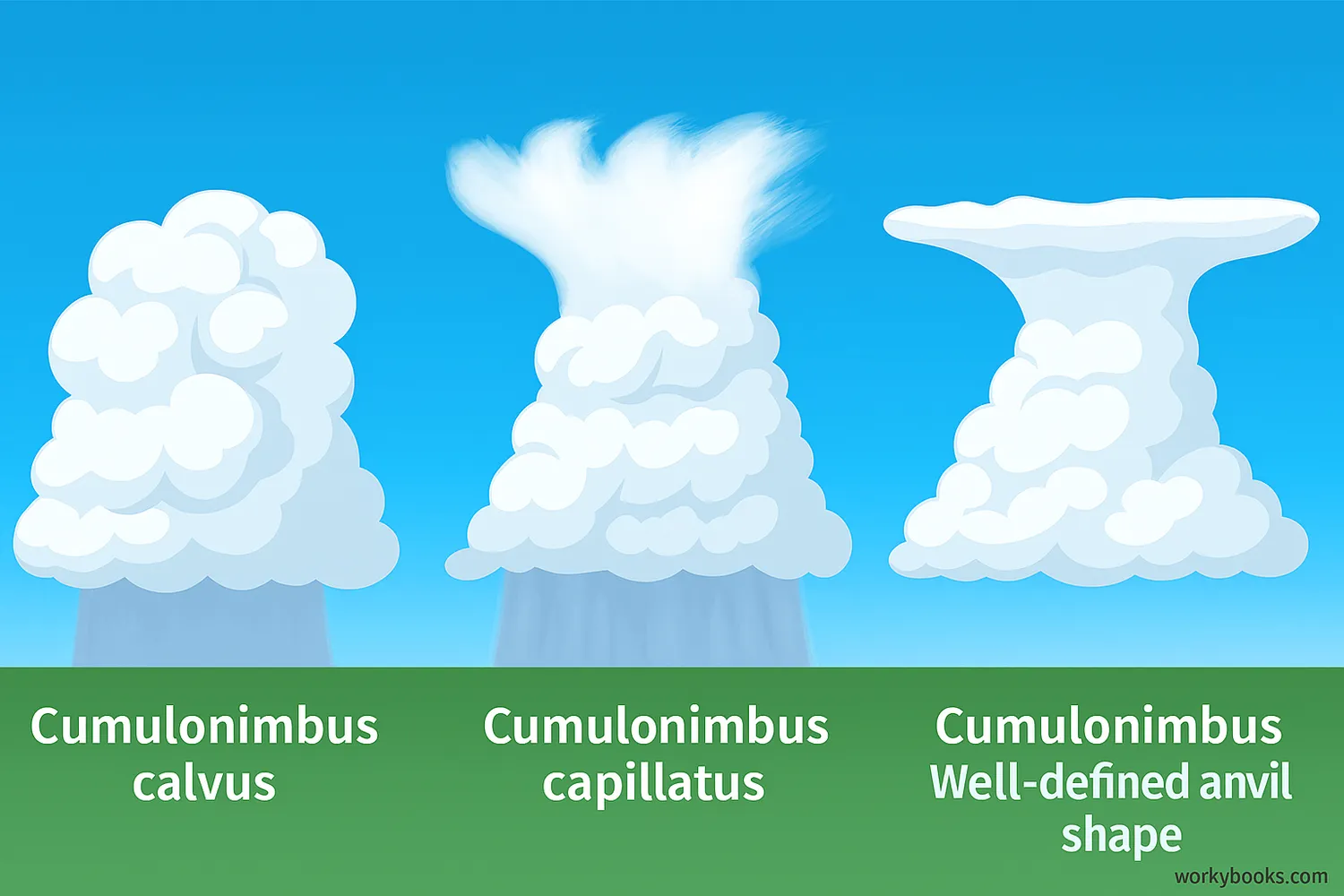
Meteorologists classify cumulonimbus clouds into different types based on their appearance and structure:
Cumulonimbus Calvus
The top of the cloud is still mostly rounded without a fibrous appearance
Cumulonimbus Capillatus
The top has a fibrous, hair-like appearance due to ice crystals
Cumulonimbus Incus
Has a well-defined anvil shape at the top as it hits the tropopause
Supercell
A rotating thunderstorm with a deep, persistent updraft
Squall Line
A line of thunderstorms that can form along a cold front
Supercell thunderstorms are the most dangerous type and are responsible for most tornadoes and large hail. They have a rotating updraft called a mesocyclone.
Cumulonimbus vs. Cumulus Clouds

While both cumulus and cumulonimbus clouds are formed by rising air, they have important differences:
Height
Cumulus: Low clouds (up to 6,500 feet)
Cumulonimbus: Tower through all cloud levels
Appearance
Cumulus: Fluffy, cotton-like with flat bases
Cumulonimbus: Massive, towering with anvil tops
Weather
Cumulus: Fair weather, maybe light showers
Cumulonimbus: Storms with heavy rain, lightning, hail
Think of cumulus clouds as the friendly cousins and cumulonimbus clouds as the powerful giants of the cloud family. All cumulonimbus clouds start as cumulus clouds but continue growing under the right conditions.
Characteristics of Cumulonimbus Clouds
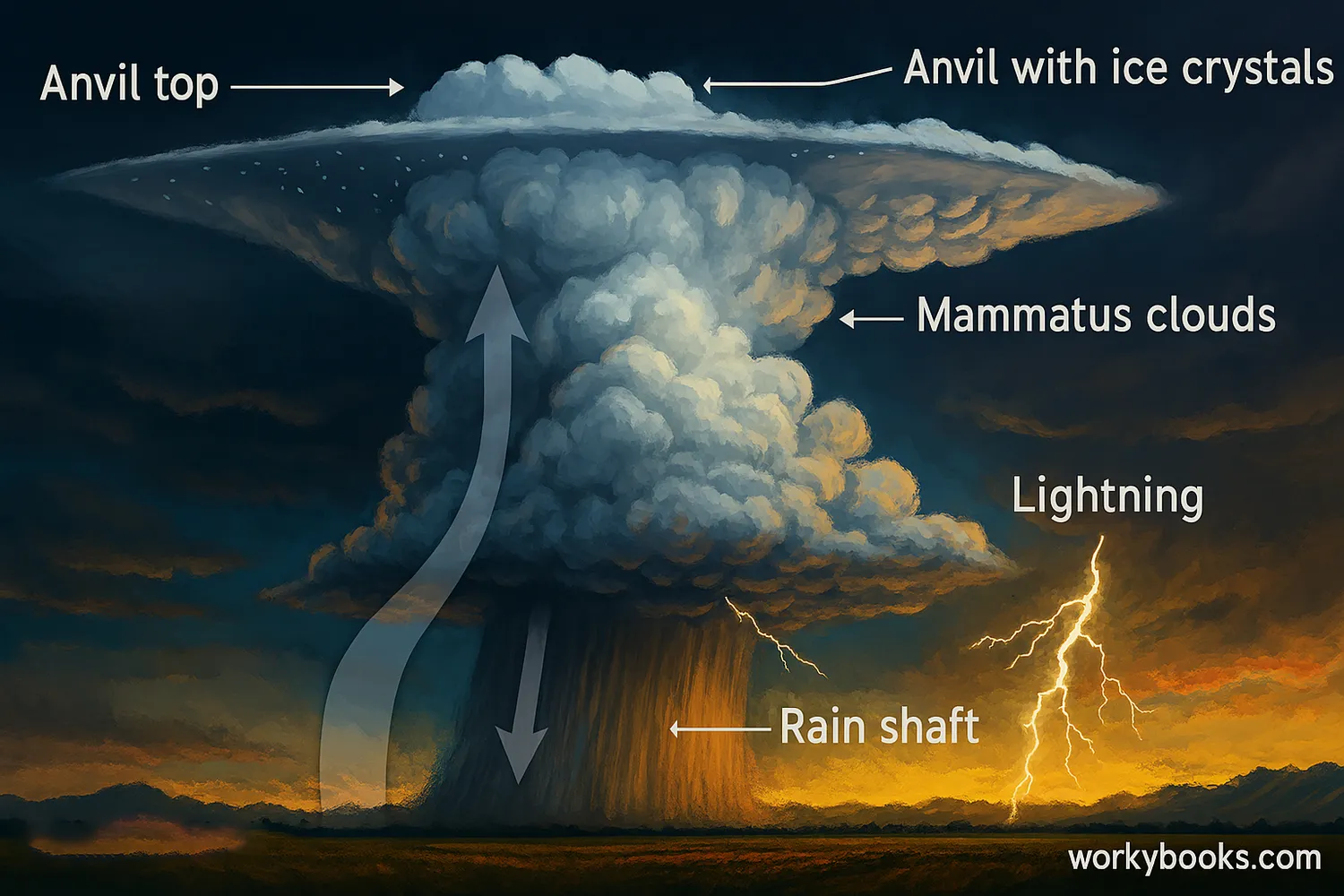
Cumulonimbus clouds have several distinctive features that help identify them:
Great Vertical Extent
They tower through low, middle, and high cloud levels
Anvil Shape
The top spreads out into an anvil shape as it hits the tropopause
Dark Base
The bottom appears very dark due to thickness and precipitation
Precipitation
Heavy rain, snow, or hail falls from the base
Updrafts & Downdrafts
Strong upward and downward winds within the cloud
The anvil top of a cumulonimbus cloud forms when the rising air reaches the tropopause (the boundary between the troposphere and stratosphere) and can't rise further, so it spreads out horizontally. This anvil can be blown downwind by strong upper-level winds.
Dangers of Cumulonimbus Clouds
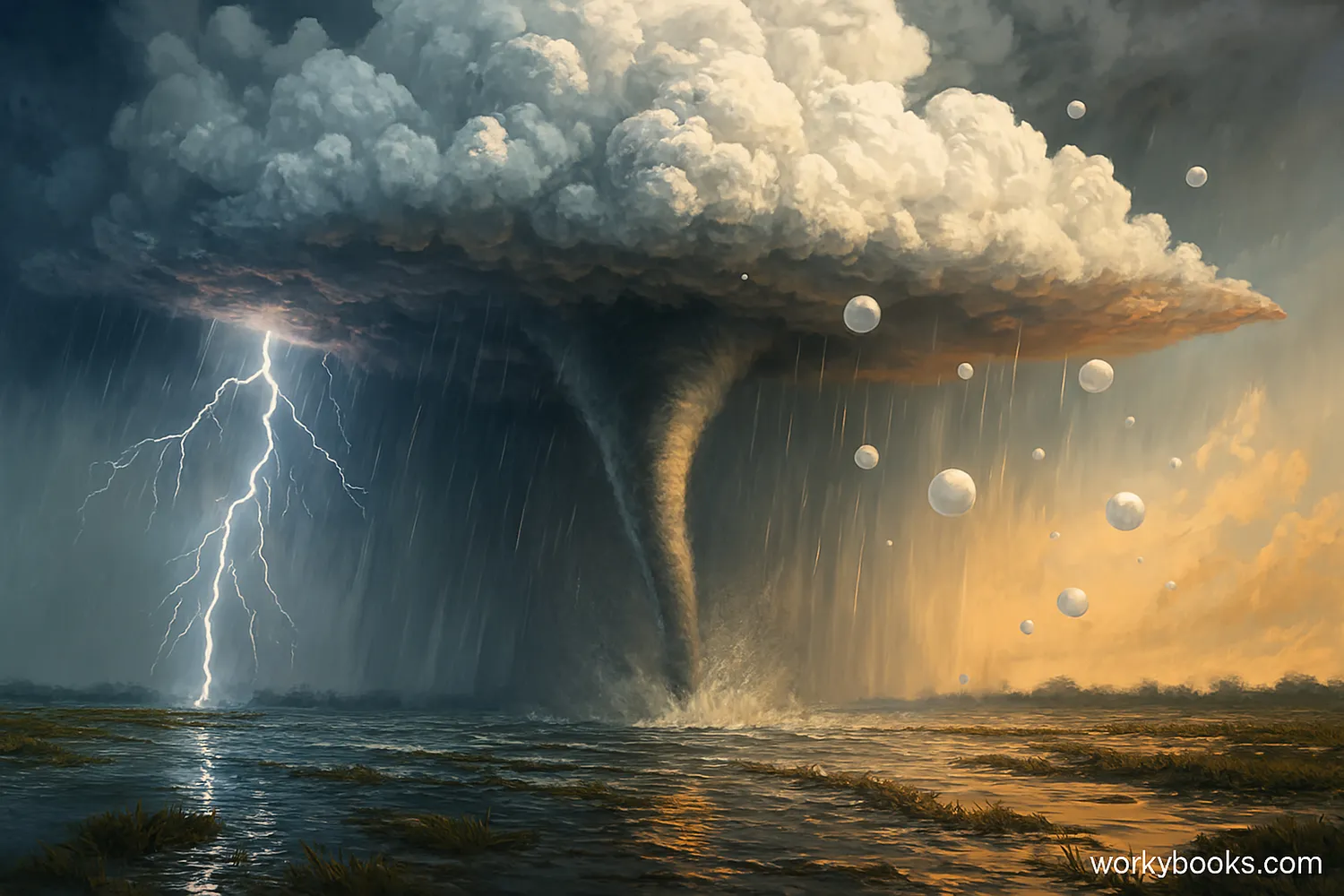

While fascinating to observe, cumulonimbus clouds can produce dangerous weather conditions:
Lightning
Electrical discharges that can cause fires and harm people
Tornadoes
Violently rotating columns of air that can cause extreme damage
Flash Floods
Heavy rainfall can quickly overwhelm drainage systems
Hail
Balls of ice that can damage crops, vehicles, and buildings
Strong Winds
Downdrafts can create damaging straight-line winds
It's important to take shelter when cumulonimbus clouds are nearby. Remember the 30-30 rule for lightning safety: If you see lightning and can't count to 30 before hearing thunder, go indoors, and wait 30 minutes after the last thunder before going outside again.
Safety First!
If you see a cumulonimbus cloud approaching with a dark, threatening base, it's time to head indoors. These clouds can produce severe weather with little warning.
Cumulonimbus Clouds Quiz
Test your knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned about cumulonimbus clouds.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about cumulonimbus clouds:
Science Facts About Cumulonimbus Clouds
Discover some fascinating facts about cumulonimbus clouds and weather phenomena!
Powerful Energy
A large cumulonimbus cloud can release as much energy as 10 atomic bombs of the size dropped on Hiroshima! This energy comes from the condensation of water vapor, which releases heat into the atmosphere.
Icy Tops
The tops of cumulonimbus clouds are so high that they reach temperatures below -40°F (-40°C), causing water droplets to freeze instantly. This creates ice crystals that help generate lightning through friction.
Heavy Rainfall
A single cumulonimbus cloud can produce over 500 million gallons of water in the form of rain! That's enough to fill 750 Olympic-sized swimming pools from just one storm cloud.
Aviation Hazard
Pilots avoid flying through cumulonimbus clouds because of extreme turbulence, hail, and lightning. The strong updrafts and downdrafts can cause aircraft to gain or lose thousands of feet of altitude in seconds.





