Altitude - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how height above sea level affects our world and our bodies
What is Altitude?
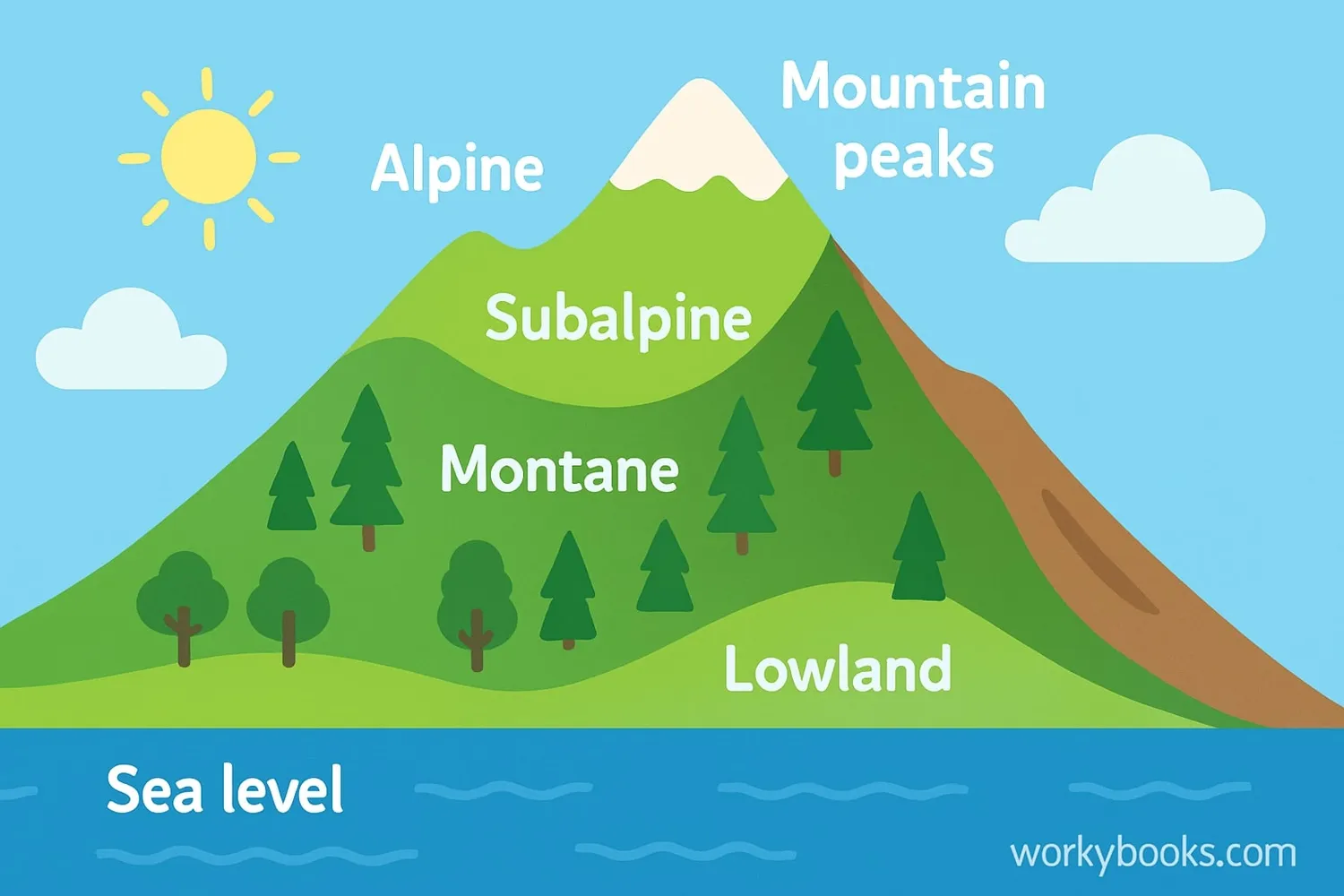
Altitude is the height above sea level of a location. Sea level is the average height of the ocean's surface, which we use as a reference point to measure how high something is.
When we talk about altitude, we're describing how high a place is compared to the ocean. For example, Denver, Colorado is called the "Mile High City" because it's exactly one mile (5,280 feet) above sea level. Mountains have high altitudes, while coastal cities and beaches have low altitudes.
Sea Level
The baseline for measuring altitude (0 feet/meters)
Low Altitude
Areas near coastlines (0-2,500 feet / 0-762 meters)
Moderate Altitude
Foothills and some cities (2,500-6,000 feet / 762-1,829 meters)
High Altitude
Mountainous areas (6,000-12,000 feet / 1,829-3,658 meters)
Very High Altitude
Tall mountain peaks (above 12,000 feet / 3,658 meters)
Did You Know?
Mount Everest, the highest point on Earth, has an altitude of 29,032 feet (8,849 meters) above sea level!
How Altitude Affects Our Bodies
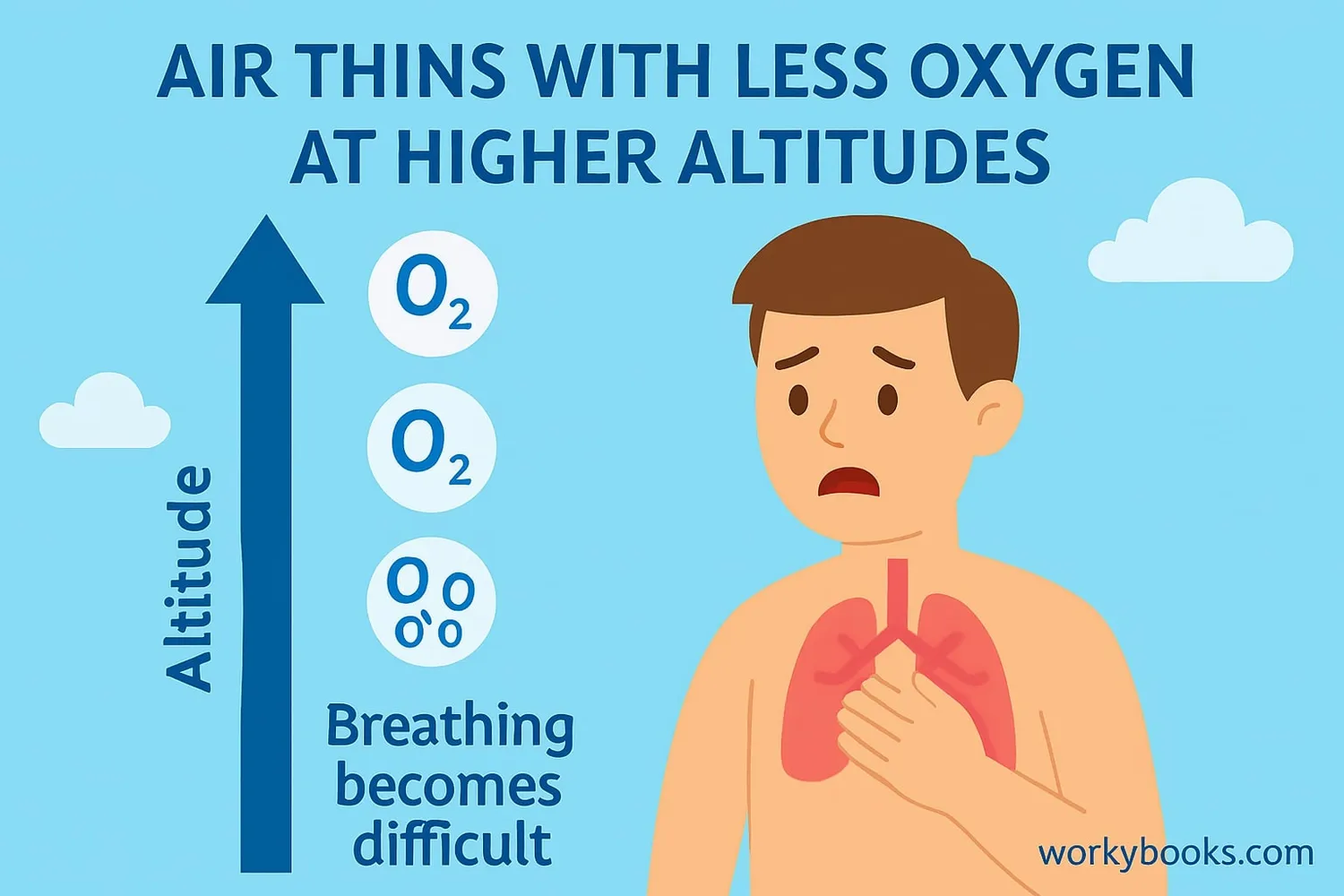
As we go higher in altitude, the air becomes thinner, which means there are fewer oxygen molecules in each breath we take. This happens because atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude - the weight of the air above us is less at higher elevations.
When our bodies get less oxygen, we might experience:
Faster Breathing
Your body tries to take in more oxygen by breathing faster
Faster Heartbeat
Your heart works harder to pump oxygen around your body
Altitude Sickness
Headache, nausea, or dizziness from not enough oxygen
This lack of oxygen is called hypoxia. Most people need time to acclimatize (get used to) higher altitudes. Athletes sometimes use altitude training to improve their performance by helping their bodies use oxygen more efficiently.
Adapting to Altitude
People who live at high altitudes, like in the Andes Mountains or Himalayas, have developed larger lungs and more red blood cells to carry oxygen better!
How We Measure Altitude
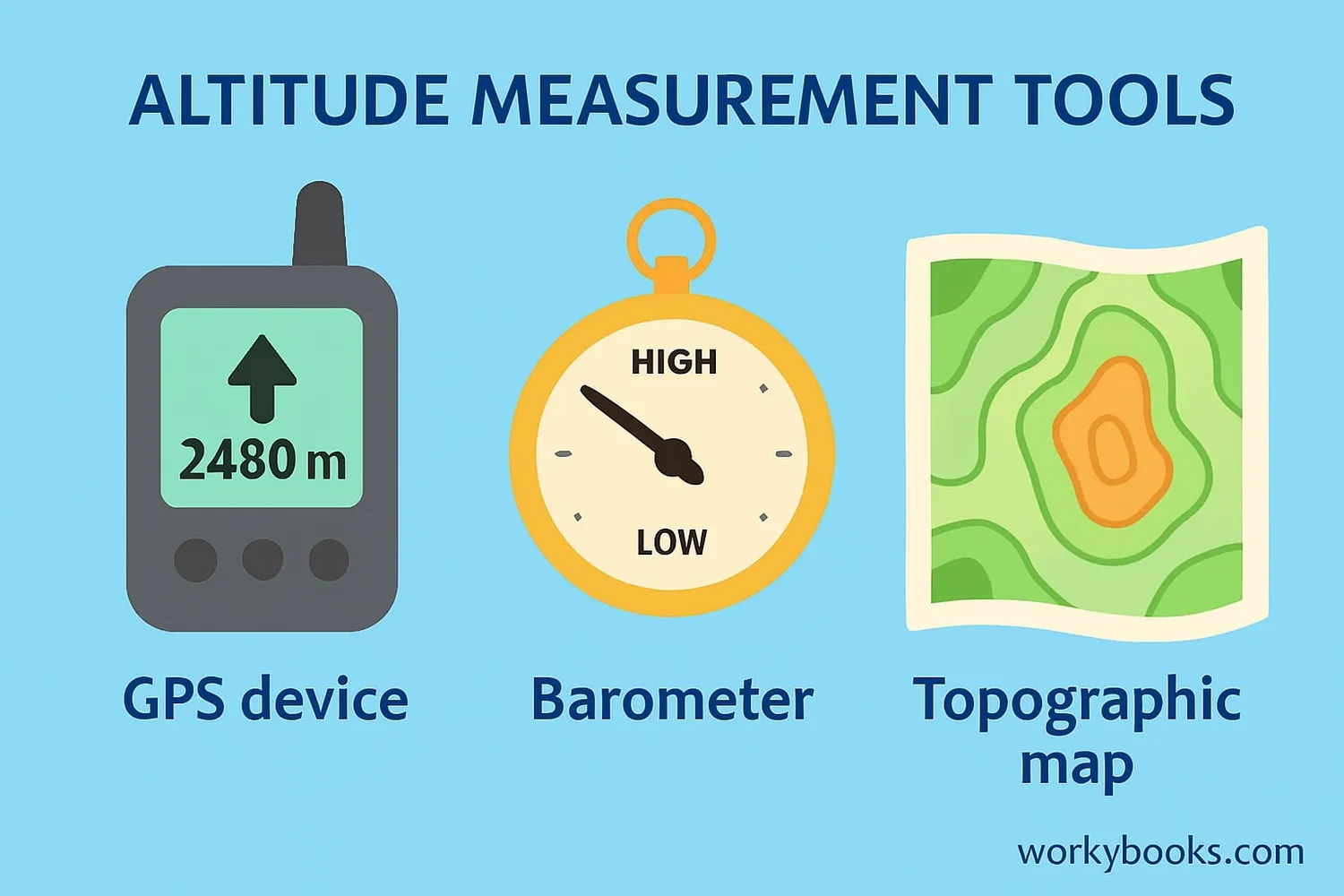
There are several ways to measure altitude, each with its own advantages:
GPS
Uses satellites to determine elevation based on GPS coordinates
Barometric Pressure
Measures air pressure, which decreases predictably with altitude
Topography Maps
Shows elevation changes using contour lines on topography maps
Pilots use flight levels measured in hundreds of feet (e.g., Flight Level 330 means 33,000 feet). Different activities have different ways of describing altitude - hikers might use feet or meters, while pilots use flight levels.
Barometric pressure changes with weather, so altitude measurements using pressure need to be adjusted for current conditions. This is why your phone might show slightly different elevations on different days at the same location!
Fun Fact
The lowest land altitude on Earth is the Dead Sea shore at about 1,412 feet (430 meters) below sea level!
Altitude Quiz
Test your altitude knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about altitude:
Interesting Altitude Facts
Discover some amazing facts about altitude!
Highest Inhabited Place
La Rinconada in Peru is the highest permanently inhabited town in the world at 5,100 meters (16,732 feet) above sea level. Mining workers live there despite the extreme conditions.
Athletic Advantage
Some athletes train at high altitudes to improve their performance. The body produces more red blood cells to compensate for less oxygen, which helps carry more oxygen when competing at lower altitudes.
High Altitude Flight
Commercial airplanes typically cruise at altitudes of 9,000-12,000 meters (30,000-39,000 feet). Cabins are pressurized to simulate an altitude of around 2,400 meters (8,000 feet) to keep passengers comfortable.
High-Flying Birds
Bar-headed geese migrate over the Himalayas at altitudes up to 7,290 meters (23,920 feet)—higher than Mount Everest's base camp! They have special hemoglobin that binds oxygen more effectively.





