Cartilage - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how this amazing tissue cushions your joints and shapes your body!
What is Cartilage?
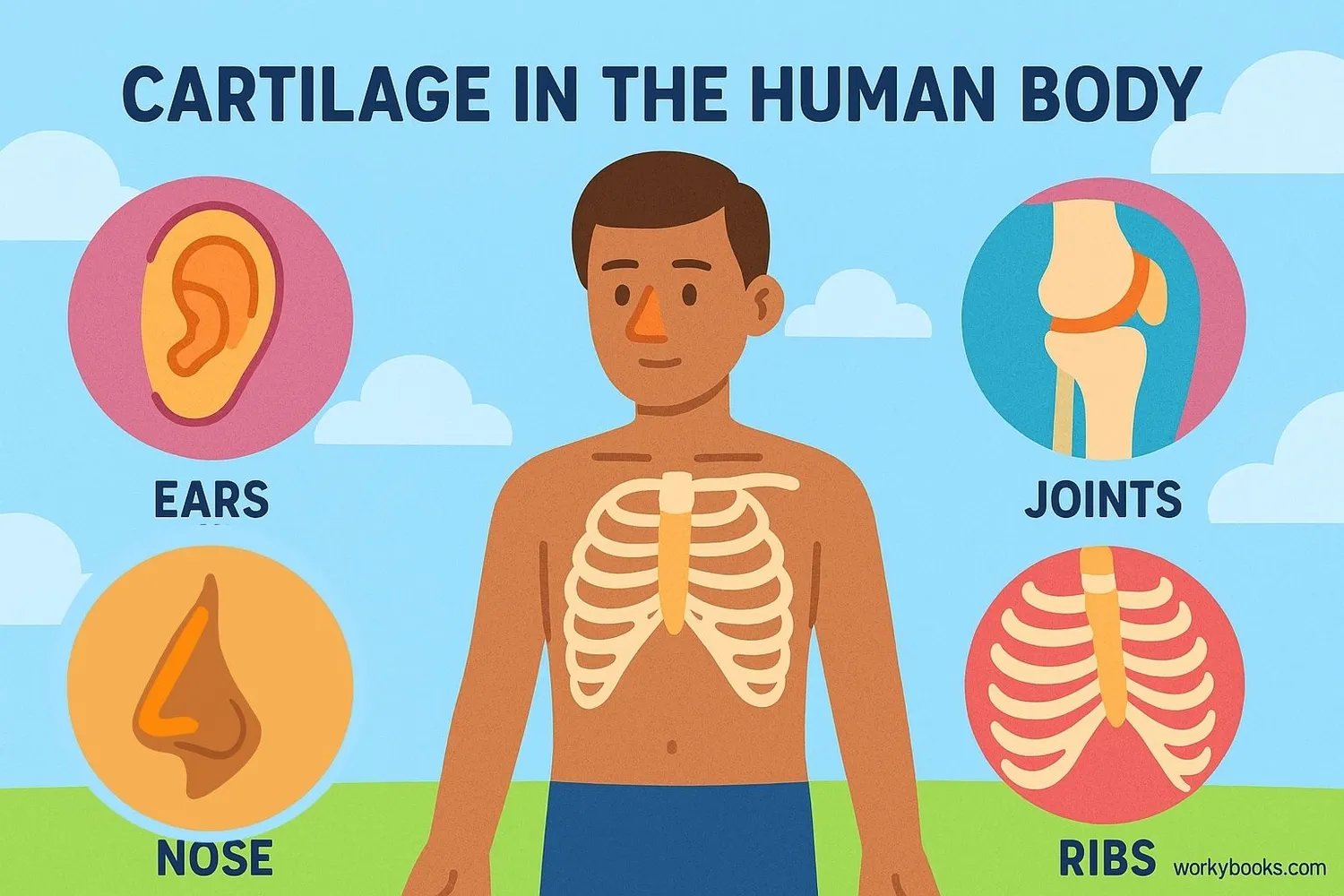
Cartilage is a strong, flexible connective tissue that's found throughout your body. It's not as hard as bone but much stronger than muscle!
Think of cartilage as your body's natural shock absorber. It's smooth and rubbery, which makes it perfect for cushioning your joints and helping your bones move smoothly against each other.
You can feel cartilage in your own body! Touch the tip of your nose or the top of your ear - that flexible part is cartilage. It's also found in your knees, elbows, ribs, and between the bones in your spine.
Fun Fact!
Sharks have skeletons made entirely of cartilage, not bone! That's why their skeletons are flexible and lightweight.
Types of Cartilage
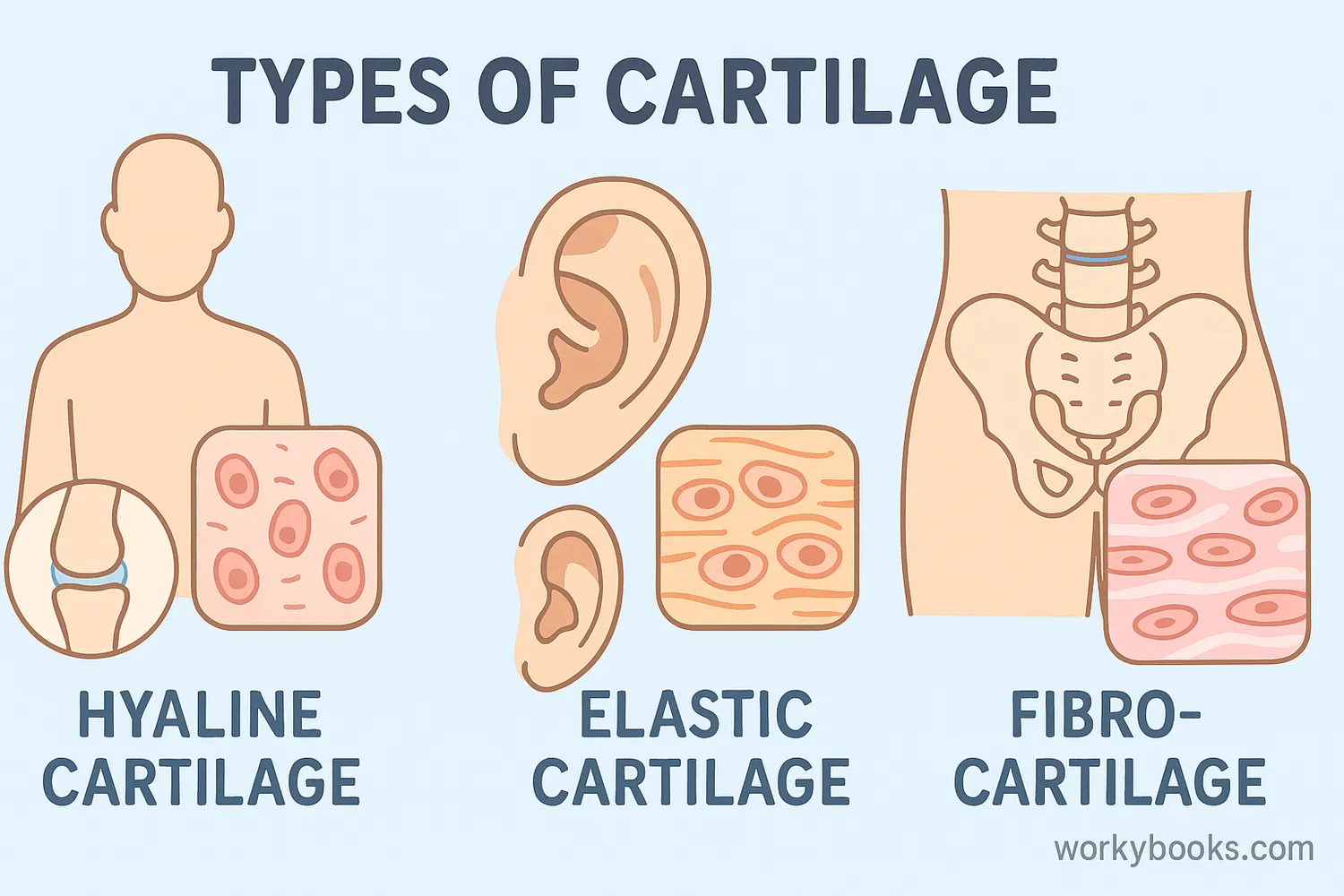
Your body has three different types of cartilage, each with special jobs:
Hyaline Cartilage
The most common type. Found in joints, ribs, nose, and windpipe. Smooth and glassy surface.
Fibrocartilage
The toughest type. Found in spinal discs and knee meniscus. Great at absorbing shock.
Elastic Cartilage
The most flexible type. Found in ears and epiglottis. Contains elastic fibers.
Each type of cartilage has a unique structure that makes it perfect for its location. Hyaline cartilage is smooth for joints, fibrocartilage is tough for shock absorption, and elastic cartilage is flexible for ears.
Cartilage Function
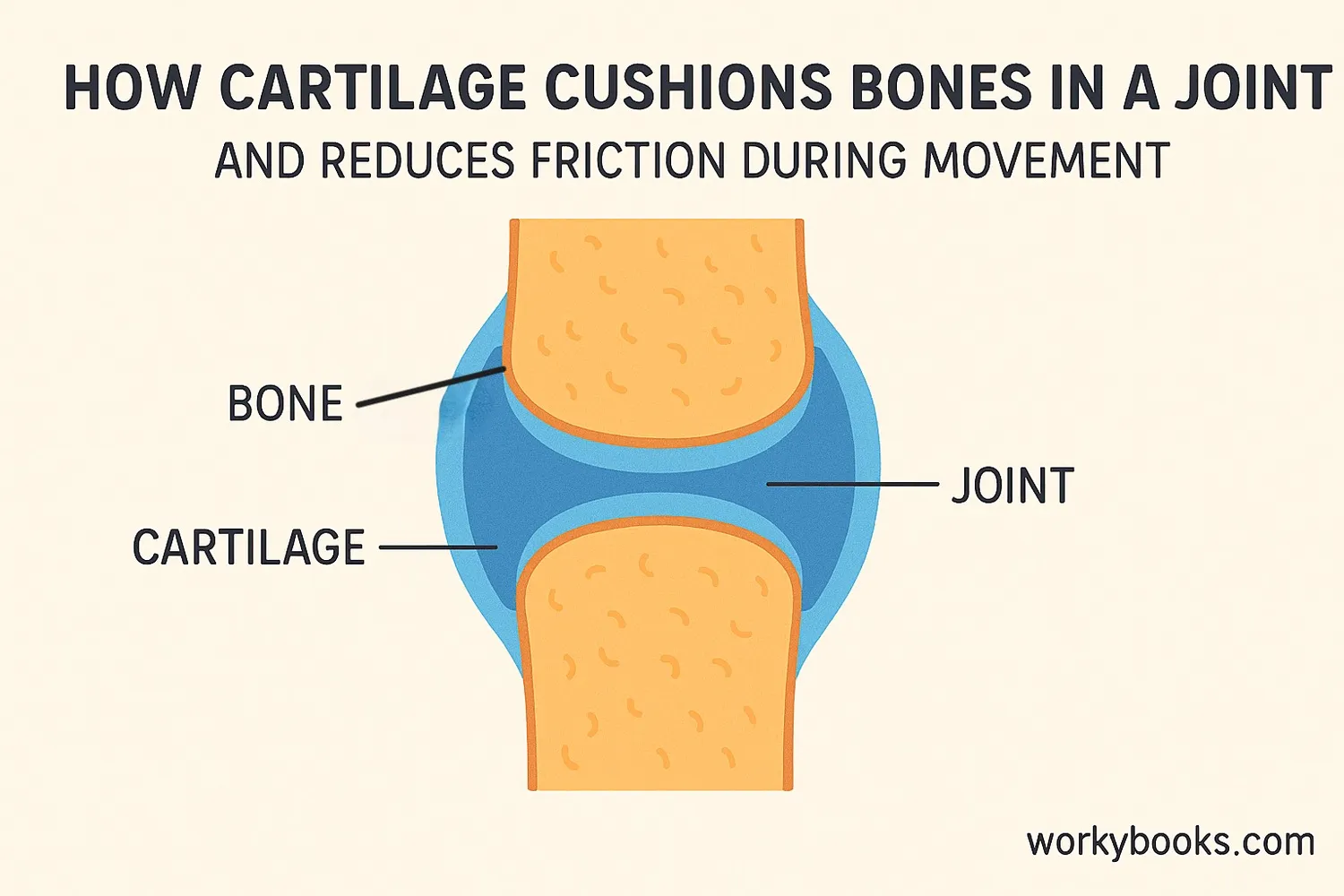
Cartilage has several important jobs in your body:
Shock Absorption
Cushions joints during walking, running, and jumping
Smooth Movement
Reduces friction between bones in joints
Support & Structure
Gives shape to ears, nose, and airways
Without cartilage, your bones would rub against each other, causing pain and damage. Cartilage acts like a cushion and lubricant, making movement smooth and comfortable. It also provides structure to flexible body parts like your ears and nose.
Cartilage Damage
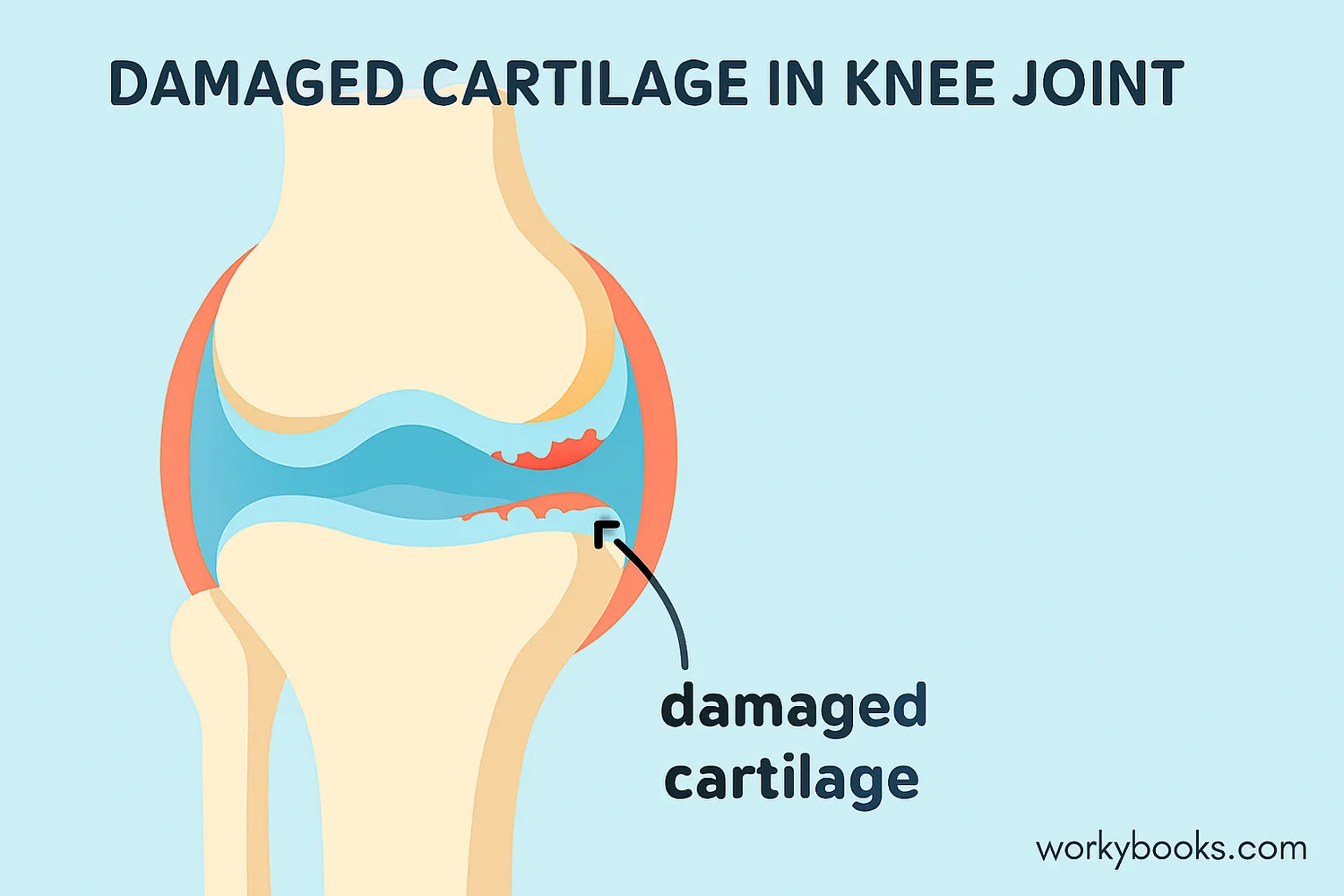
Cartilage can get damaged in several ways:
Injury
Sports injuries, falls, or accidents can tear cartilage
Overuse
Repeating the same motions can wear down cartilage
Arthritis
Conditions like osteoarthritis damage cartilage over time
When cartilage gets damaged, you might experience:
• Joint pain or stiffness
• Swelling around the joint
• A clicking or grinding sound when moving
• Difficulty moving the joint fully
Cartilage damage is especially common in knees, hips, and shoulders - joints we use frequently.
Cartilage Repair
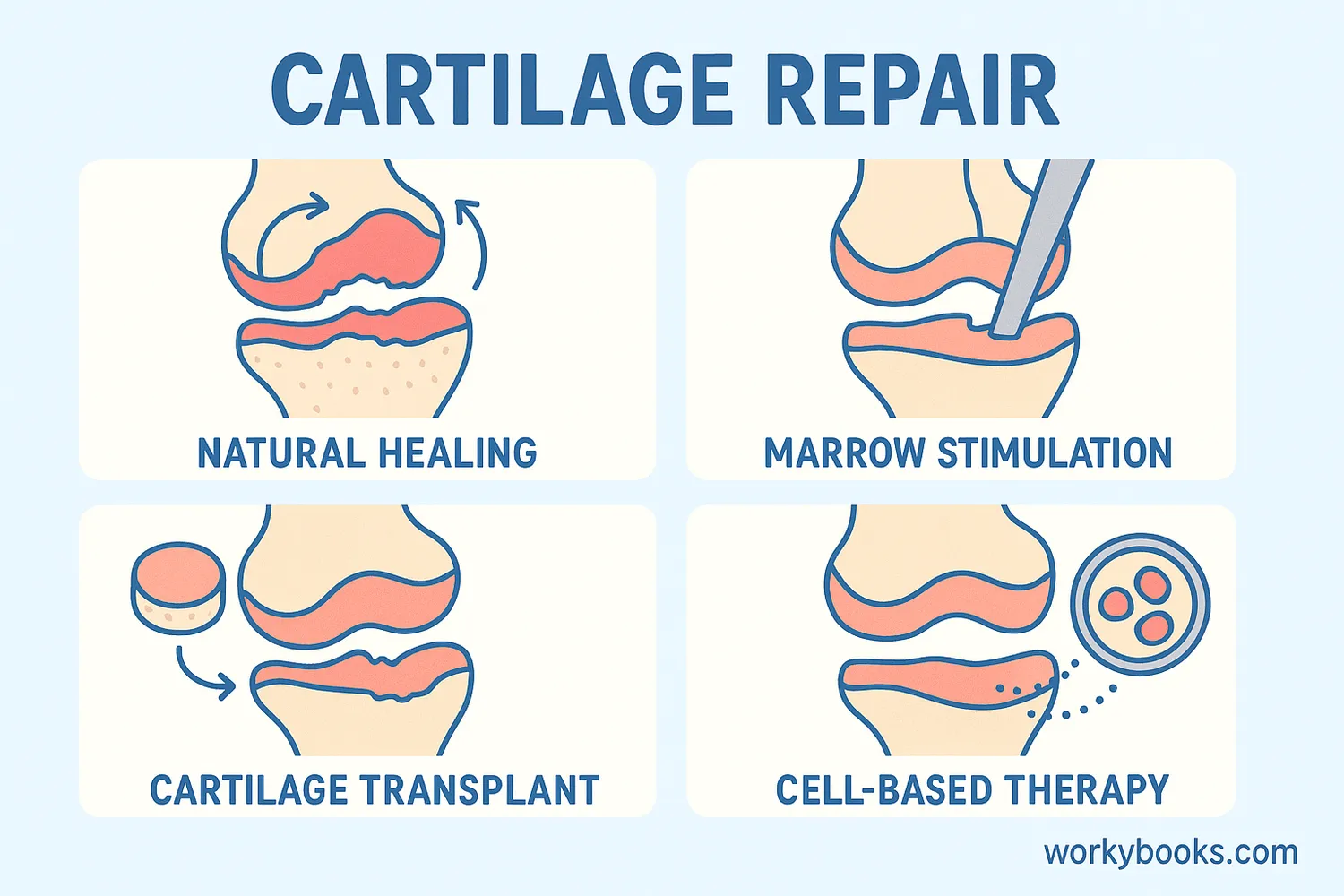
Cartilage has limited ability to repair itself because it doesn't have its own blood supply. But there are ways to help it heal:
Natural Healing
Rest, ice, and proper nutrition support healing
Medical Treatments
Physical therapy, medications, and injections
Surgical Options
Arthroscopy, microfracture, or cartilage transplantation
Scientists are working on exciting new ways to repair cartilage, including:
• Stem cell therapy: Using special cells to grow new cartilage
• Tissue engineering: Creating artificial cartilage in labs
• Scaffold implants: Structures that help new cartilage grow
Protecting your cartilage with proper exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding injuries is the best way to keep your joints healthy!
Cartilage Quiz
Test your cartilage knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about cartilage:
Fun Cartilage Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about cartilage!
Shark Skeletons
Sharks and rays have skeletons made entirely of cartilage! This makes them lighter and more flexible in water, helping them swim efficiently.
Baby Bones
Babies are born with about 300 bones, but many are made of cartilage that gradually turns to bone as they grow. Adults have 206 bones.
Ear Cartilage
Your ears and nose never stop growing! The cartilage in them continues to change throughout your life, making them appear larger as you age.
Salamander Superpower
Salamanders can regenerate entire limbs, including cartilage! Scientists study them to learn how humans might one day repair cartilage damage.





