Ecosystem Balance - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how living and non-living things work together in harmony
What is Ecosystem Balance?
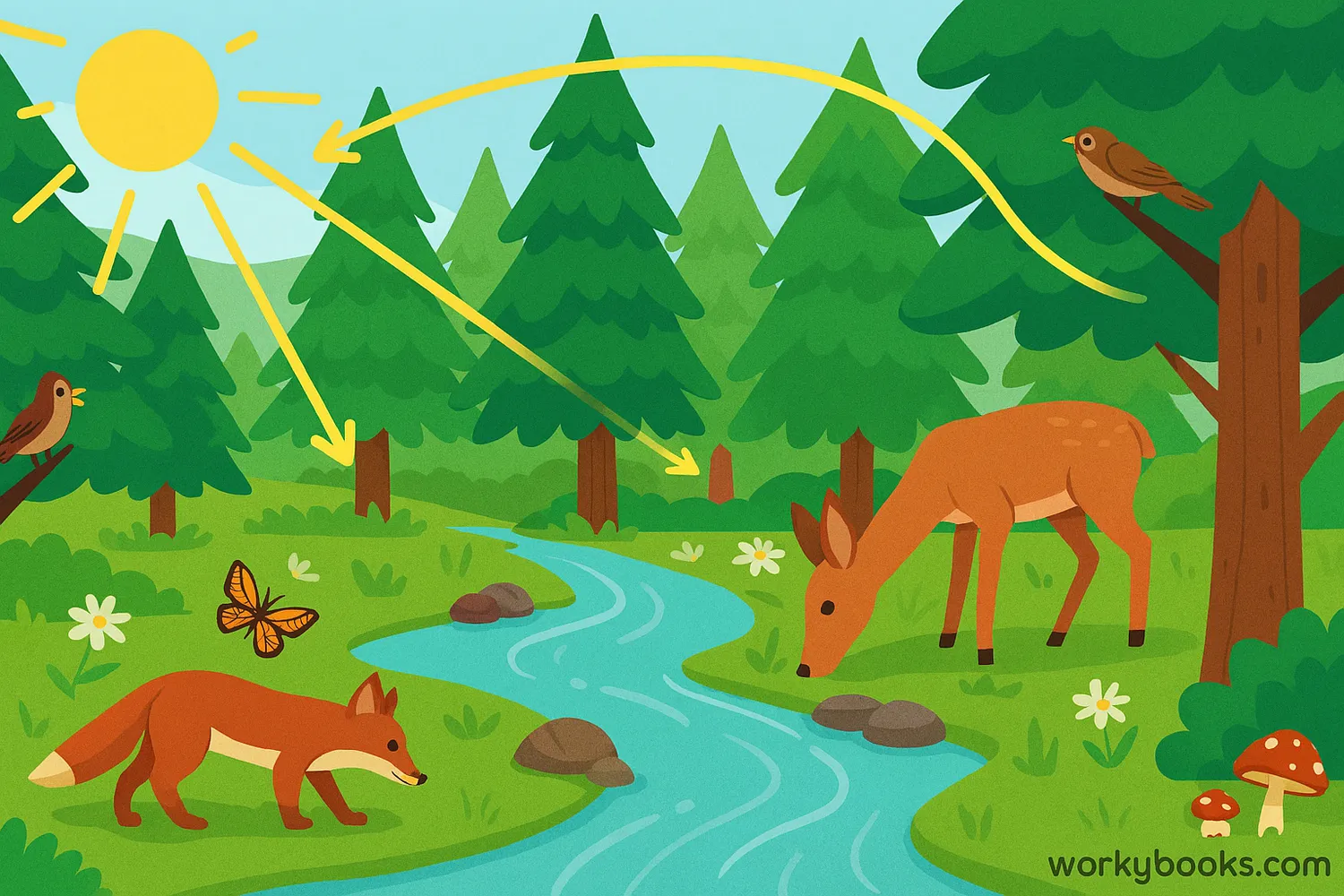

Ecosystem balance (also called ecological balance) is the stable relationship between living organisms and their environment. It's like a natural community where plants, animals, and other organisms work together in harmony.
Key facts about ecosystem balance:
• Every living thing has a role to play in the ecosystem
• Energy flows from the sun to plants to animals
• Nutrients cycle through the system
• Changes to one part affect the whole system
Think of an ecosystem like a web. If you pull one thread, the whole web moves. When all parts are working well together, the ecosystem stays healthy and balanced.
Key Concept
Ecosystem balance is maintained when all living and non-living components interact in ways that allow the system to remain stable over time. This includes predator-prey relationships, nutrient cycling, and energy flow.
Producers
Plants that make food from sunlight
Consumers
Animals that eat plants or other animals
Decomposers
Organisms that break down waste
Why Biodiversity Matters
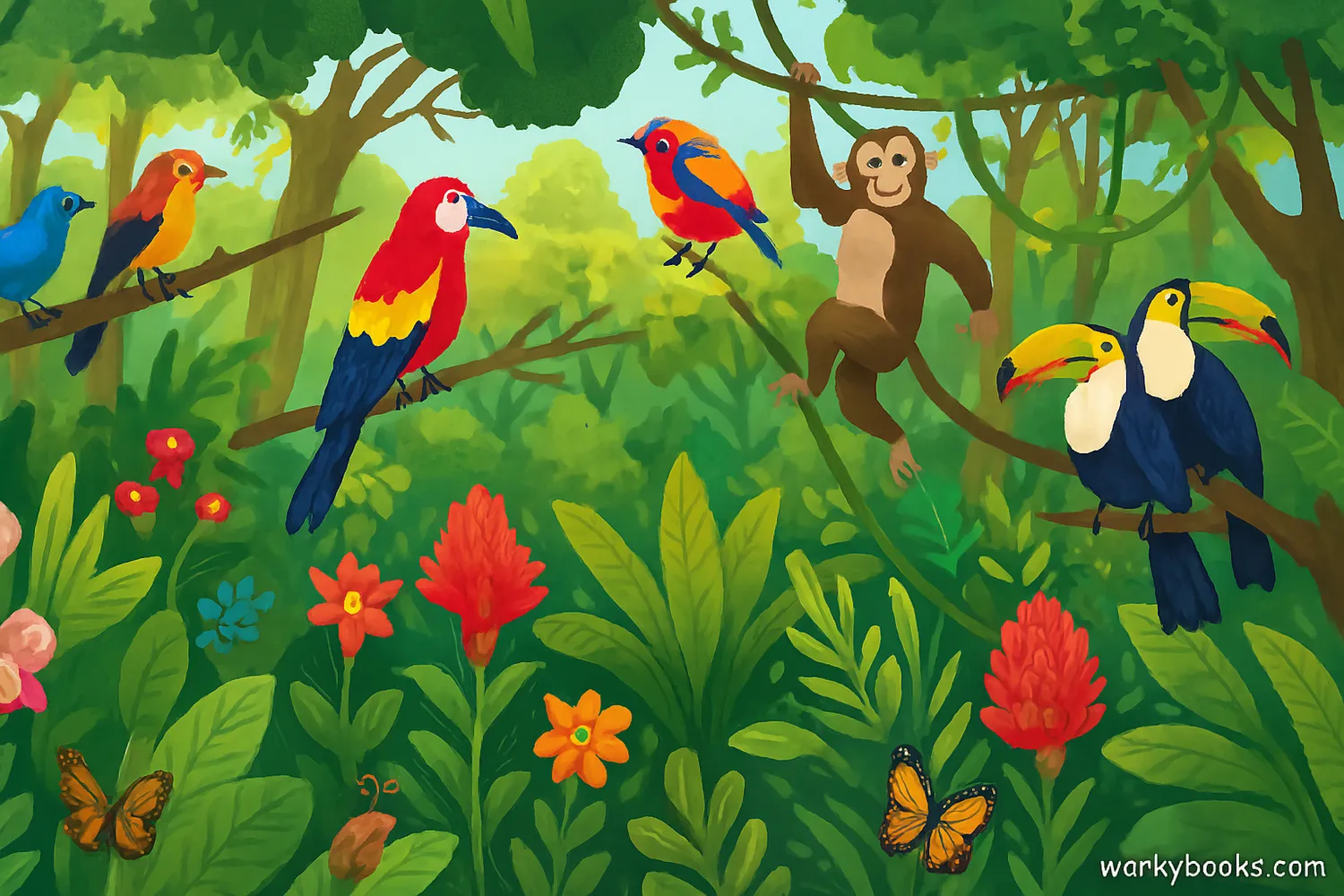

Biodiversity means the variety of life in an area. The more species that live together in an ecosystem, the healthier and more stable that ecosystem tends to be.
Why biodiversity is important:
• Resilience: Diverse ecosystems can recover better from disturbances
• Food webs: More species means more complex and stable food webs
• Ecosystem services: Different species provide different benefits
• Genetic diversity: Variety helps species adapt to changes
Did you know that a single tablespoon of soil can contain over 50,000 different species of microbes? That's biodiversity at the microscopic level!
Keystone Species
Some species have a bigger role in maintaining ecosystem balance than others. These are called keystone species. For example, sea otters help maintain kelp forests by eating sea urchins that would otherwise destroy the kelp.
Ecosystem Services
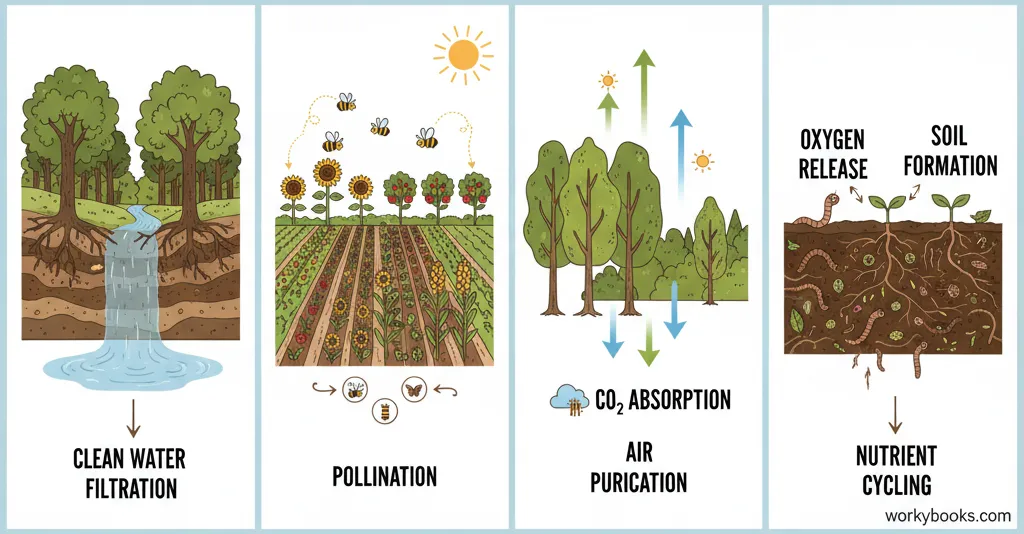
Ecosystem services are the benefits that nature provides to humans and other organisms. These services are essential for our survival and well-being.
Types of ecosystem services:
• Provisioning services: Food, water, wood, and other resources
• Regulating services: Climate control, water purification, pollination
• Cultural services: Recreation, beauty, spiritual value
• Supporting services: Soil formation, nutrient cycling
Healthy ecosystems provide these services for free! For example, bees pollinate crops worth billions of dollars each year, and wetlands naturally filter water.
Air Purification
Plants absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen through photosynthesis
Water Filtration
Wetlands and forests naturally filter and clean water
Pollination
Bees, birds, and insects pollinate crops and wild plants
Soil Health
Decomposers create rich soil that supports plant growth
Ecosystem Balance Quiz
Test your knowledge of ecosystem balance with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about ecosystem balance:
Science Trivia
Discover amazing facts about ecosystem balance:
Rainforest Diversity
A single hectare of Amazon rainforest may contain over 750 types of trees and 1,500 species of higher plants. This incredible biodiversity helps create a resilient ecosystem.
Soil Microbes
There are more microorganisms in one teaspoon of healthy soil than there are people on Earth. These tiny organisms are essential for nutrient cycling and ecosystem health.
Ocean Producers
Microscopic ocean plants called phytoplankton produce about half of the world's oxygen through photosynthesis. These tiny organisms are the foundation of marine food webs.
Valuable Services
Scientists estimate that ecosystem services are worth over $125 trillion per year globally. These include water purification, pollination, climate regulation, and soil formation.




