Esophagus - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how food travels from your mouth to your stomach
What is the Esophagus?
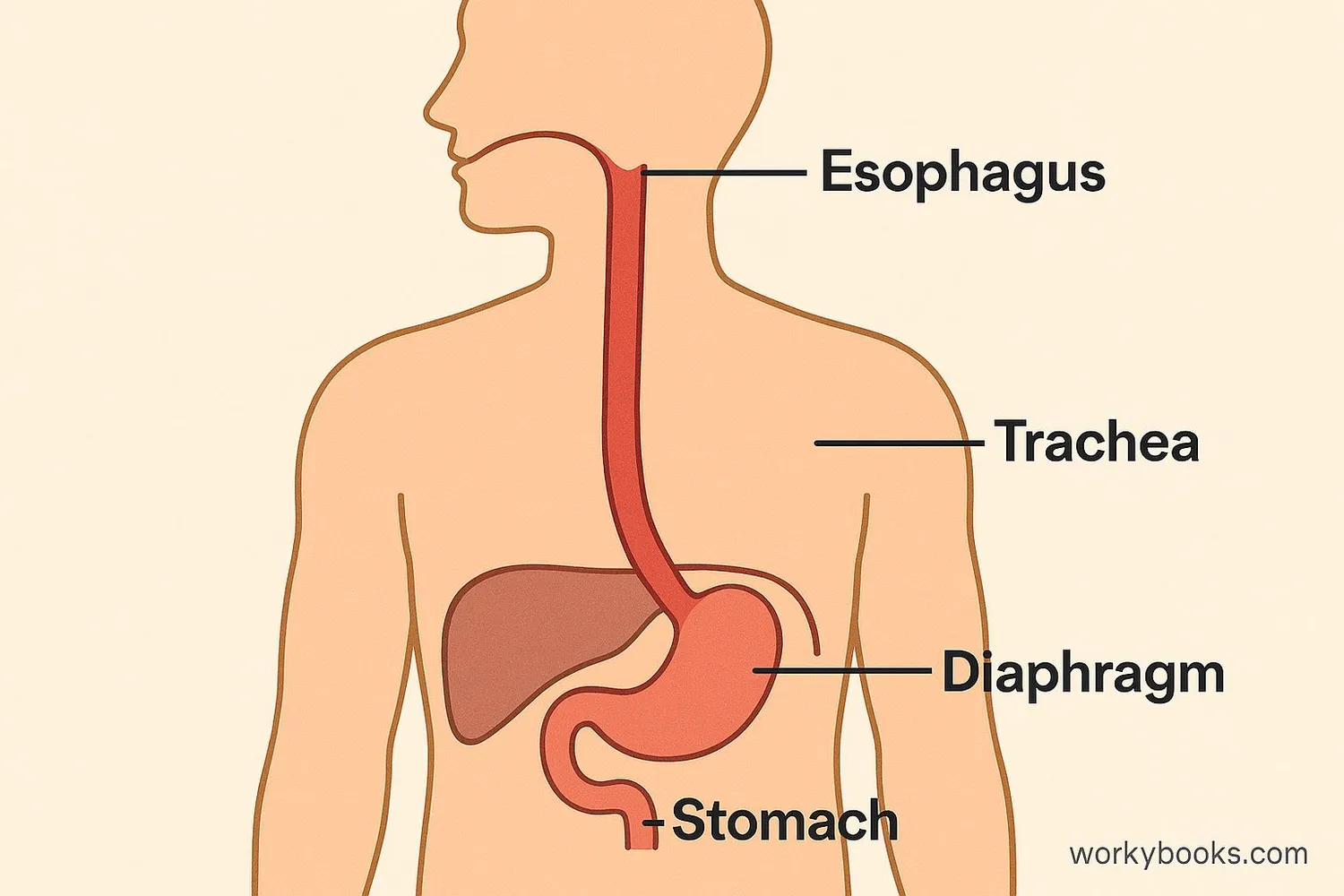
The esophagus is a muscular tube that connects your throat to your stomach. It's about 8-10 inches long in adults and plays a crucial role in your digestive system. When you swallow food or liquid, the esophagus carries it from your mouth to your stomach using wave-like muscle contractions.
The word "esophagus" comes from Greek words meaning "to carry" and "to eat." This makes perfect sense because that's exactly what it does—it carries the food you eat down to your stomach for digestion.
Did You Know?
Your esophagus has special muscles that work automatically to push food downward, even if you're standing on your head!
How the Esophagus Works
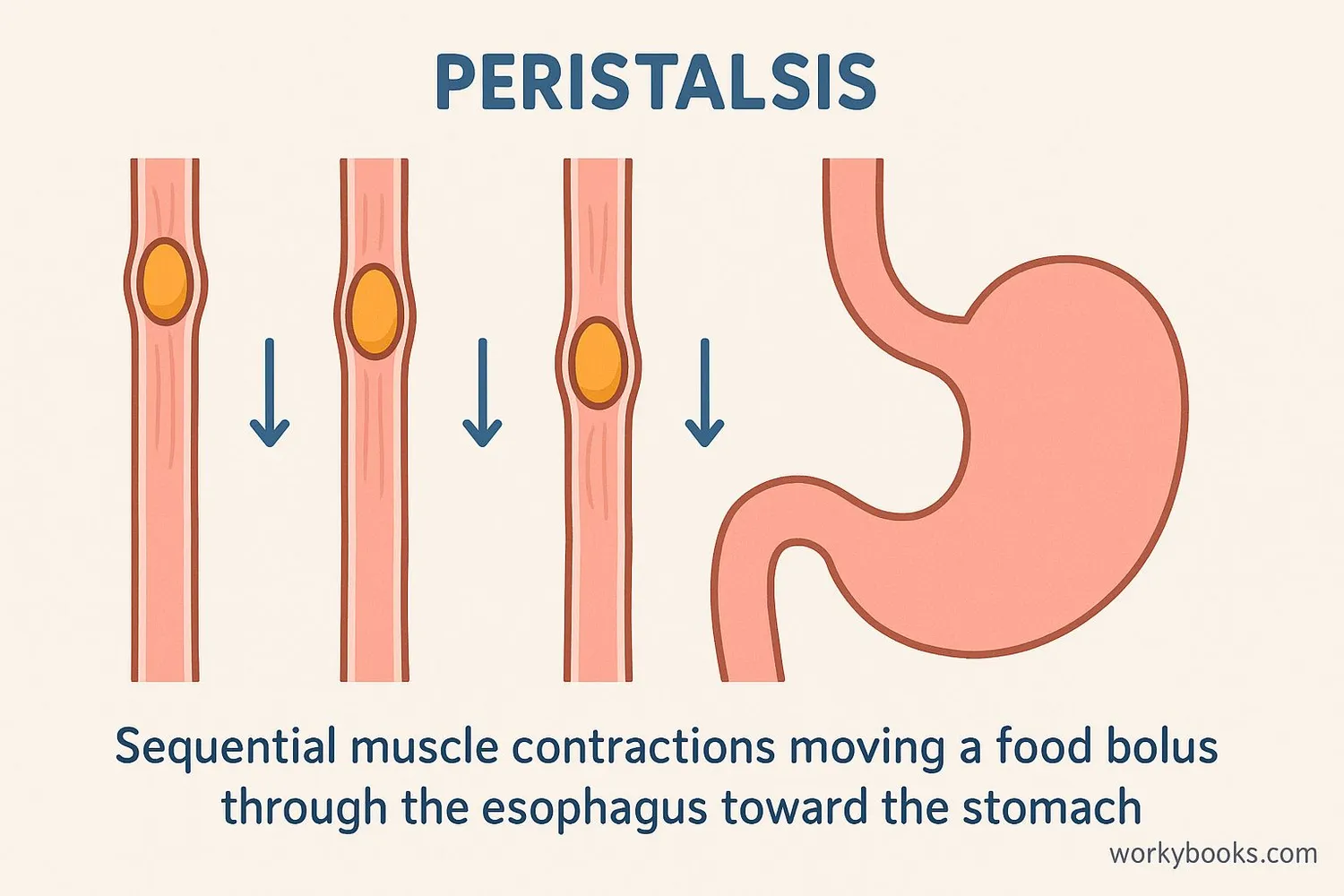
The esophagus works through a process called peristalsis—a series of wave-like muscle contractions that push food toward your stomach. Here's how this amazing process works:
Swallowing
Your tongue pushes food to the back of your throat to begin swallowing
Epiglottis
A small flap called the epiglottis covers your windpipe to prevent choking
Muscle Contractions
Muscles in the esophagus contract in waves to push food downward
Sphincter Relaxation
The lower esophageal sphincter opens to allow food into the stomach
Completion
The sphincter closes to prevent stomach contents from coming back up
The entire process of moving food through the esophagus usually takes only about 5-8 seconds. Liquids may pass through even faster, while larger or drier pieces of food might take a bit longer.
Muscle Power!
The esophagus has two types of muscles: voluntary muscles at the top that you control when swallowing, and involuntary muscles that work automatically.
Why the Esophagus is Important
The esophagus plays several vital roles in your body's digestive process:
Food Transport
Safely moves food and liquids from your mouth to your stomach for digestion
Protection
Prevents stomach acid from coming back up and damaging your throat
Breathing Safety
Works with the epiglottis to keep food out of your airway
Without a properly functioning esophagus, we would have difficulty:
• Getting nutrition from food to our bodies
• Protecting our airways from food particles
• Preventing painful acid reflux
• Digesting food efficiently
The esophagus works together with other digestive organs to break down food and provide our bodies with the energy and nutrients we need to grow and stay healthy.
Esophagus Quiz
Test your knowledge about the esophagus with this quiz. Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about the esophagus:
Interesting Esophagus Facts
Discover some amazing facts about the esophagus!
Muscle Power
The esophagus contains both voluntary muscles (that you control) at the top and involuntary muscles (that work automatically) further down.
Size Variations
An adult esophagus is typically about 10 inches long, but its size can vary depending on a person's height and build.
Animal Esophaguses
Birds have a special part of the esophagus called the crop where they can store food before digestion. Giraffes have extremely long esophaguses to match their long necks!
Not Just for Food
While mainly for food, your esophagus can also help move other things you might accidentally swallow back up through reverse peristalsis.




