Genotype - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how living things inherit traits through genetics!
What is Genotype?
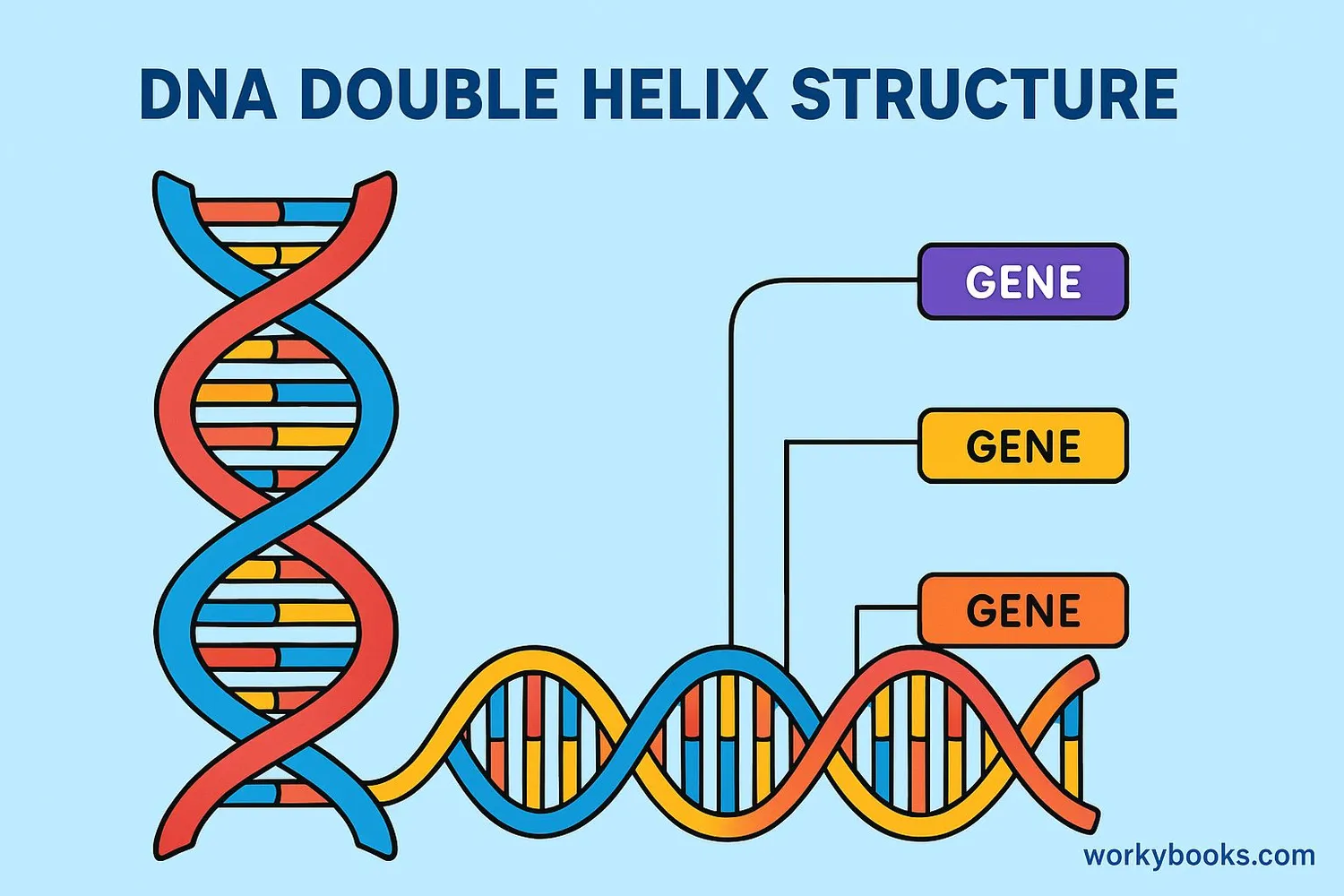
Genotype is the complete set of genes that an organism carries in its DNA. It's like the genetic blueprint that determines all your inherited characteristics!
Think of your genotype as the instruction manual inside every cell of your body. These instructions come from both your parents and determine things like:
• Your eye color
• Whether you can roll your tongue
• Your blood type
• And thousands of other traits!
Genetic Fact!
Humans have about 20,000-25,000 genes in their DNA, and each person has a unique combination!
Key Genetic Components:
DNA
The molecule that carries genetic instructions
Genes
Sections of DNA that code for specific traits
Chromosomes
Structures that package DNA inside cells
Genotype & Phenotype
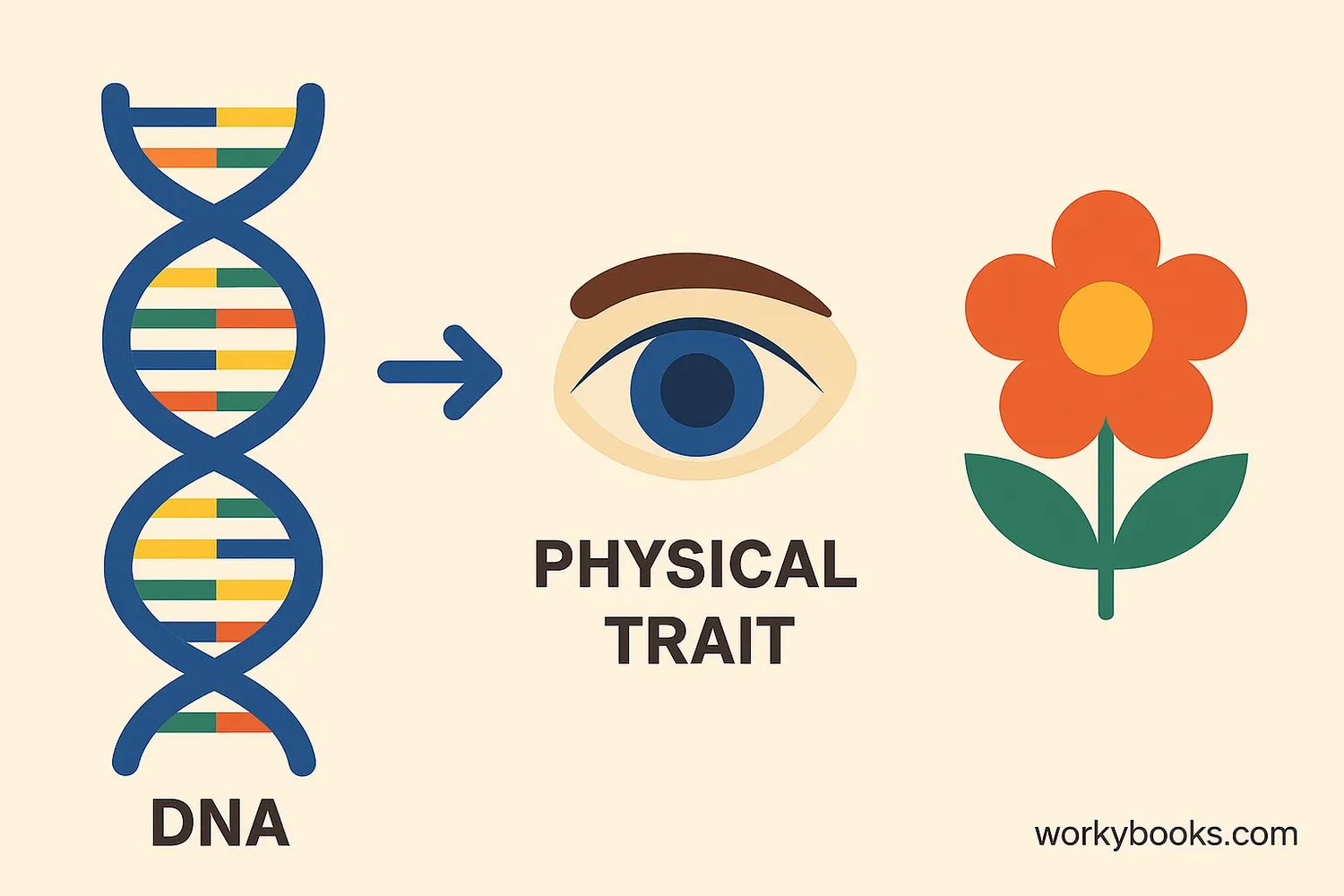
While genotype is your genetic code, phenotype is how those genes are physically expressed. It's the difference between what your genes say and what you actually look like!
Example: Your genotype might contain genes for brown eyes, but your phenotype is your actual brown eye color. Environmental factors can also influence how genes are expressed.
Homozygous
Two identical alleles for a trait (e.g., BB or bb)
Heterozygous
Two different alleles for a trait (e.g., Bb)
Alleles are different versions of the same gene. For example, the gene for eye color has alleles for blue, brown, green, etc.
Expression Fact!
Some traits like eye color involve multiple genes working together, not just one!
Mendelian Inheritance
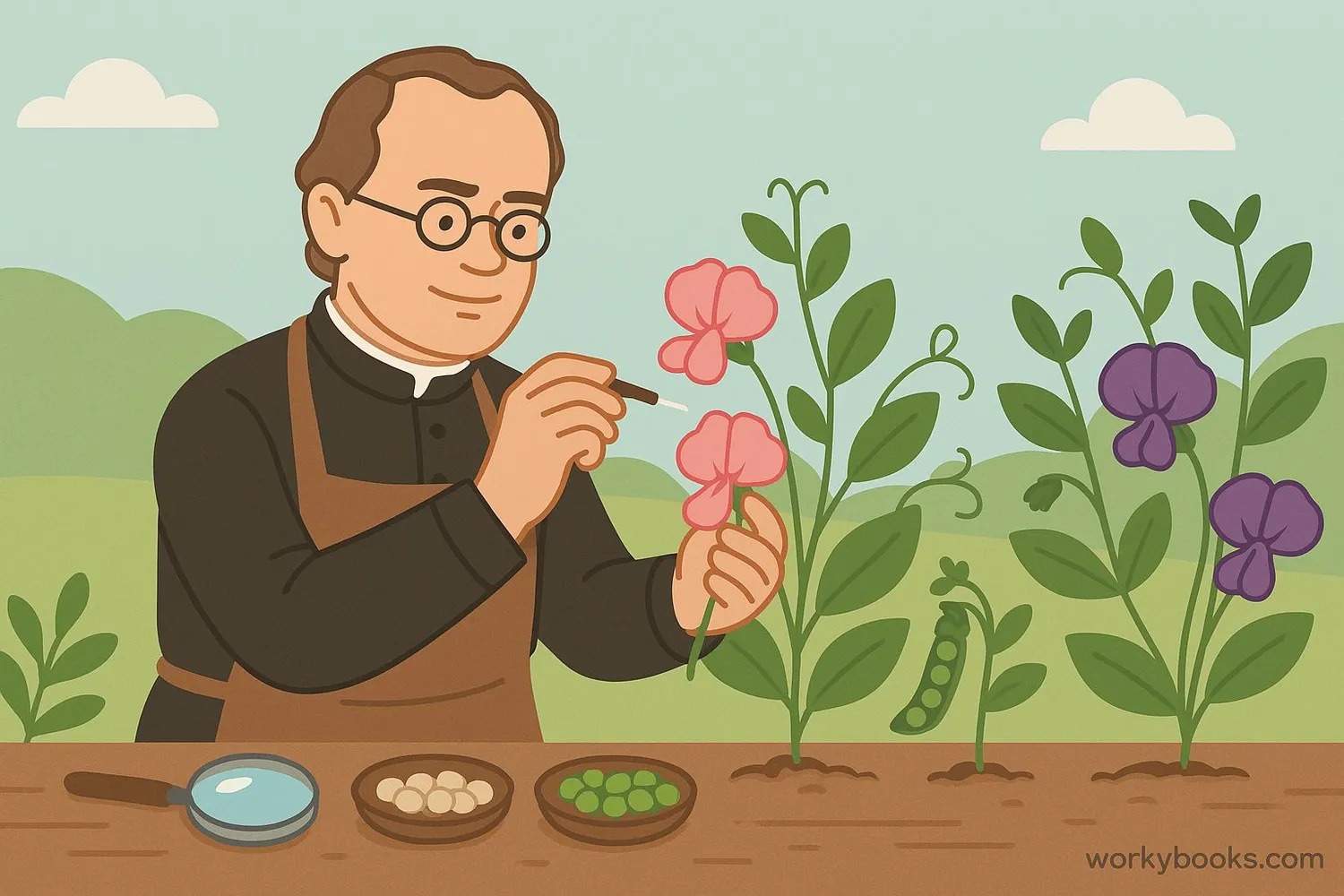

Gregor Mendel, known as the father of genetics, discovered how traits are passed from parents to offspring. His experiments with pea plants in the 1800s revealed the basic principles of inheritance.
Mendel discovered that traits are controlled by pairs of alleles (one from each parent) and that some alleles are dominant while others are recessive.
Punnett Square Example:
Brown eyes
Brown eyes
Brown eyes
Blue eyes
In this example of eye color inheritance, brown (B) is dominant over blue (b). Even if only one parent contributes a brown allele, the child will have brown eyes.
Genetic Variation

Genetic variation is what makes every living thing unique! It comes from:
• Different combinations of alleles from parents
• Mutations (changes in DNA)
• Genetic recombination during reproduction
Genotyping is the process scientists use to determine an organism's genetic makeup. This helps in:
Medicine
Understanding genetic diseases
Agriculture
Developing better crops
Evolution
Studying how species change
Genotype Quiz
Test your genetics knowledge with this fun quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about genotypes:
Fun Genetics Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about genetics and genotypes!
DNA Length
If you stretched out all the DNA in your body, it would reach to the sun and back over 300 times! That's about 10 billion miles of DNA.
Banana Similarity
Humans share about 60% of their DNA with bananas! We also share 98% with chimpanzees and 85% with mice.
Identical Twins
Identical twins have the same genotype but different fingerprints! This happens because fingerprints are influenced by the womb environment.
Human Genome
The Human Genome Project took 13 years to sequence the first human genome. Today, the same process takes less than a day!




