Muscular System - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how muscles power your body and enable movement!
What Are Muscles?
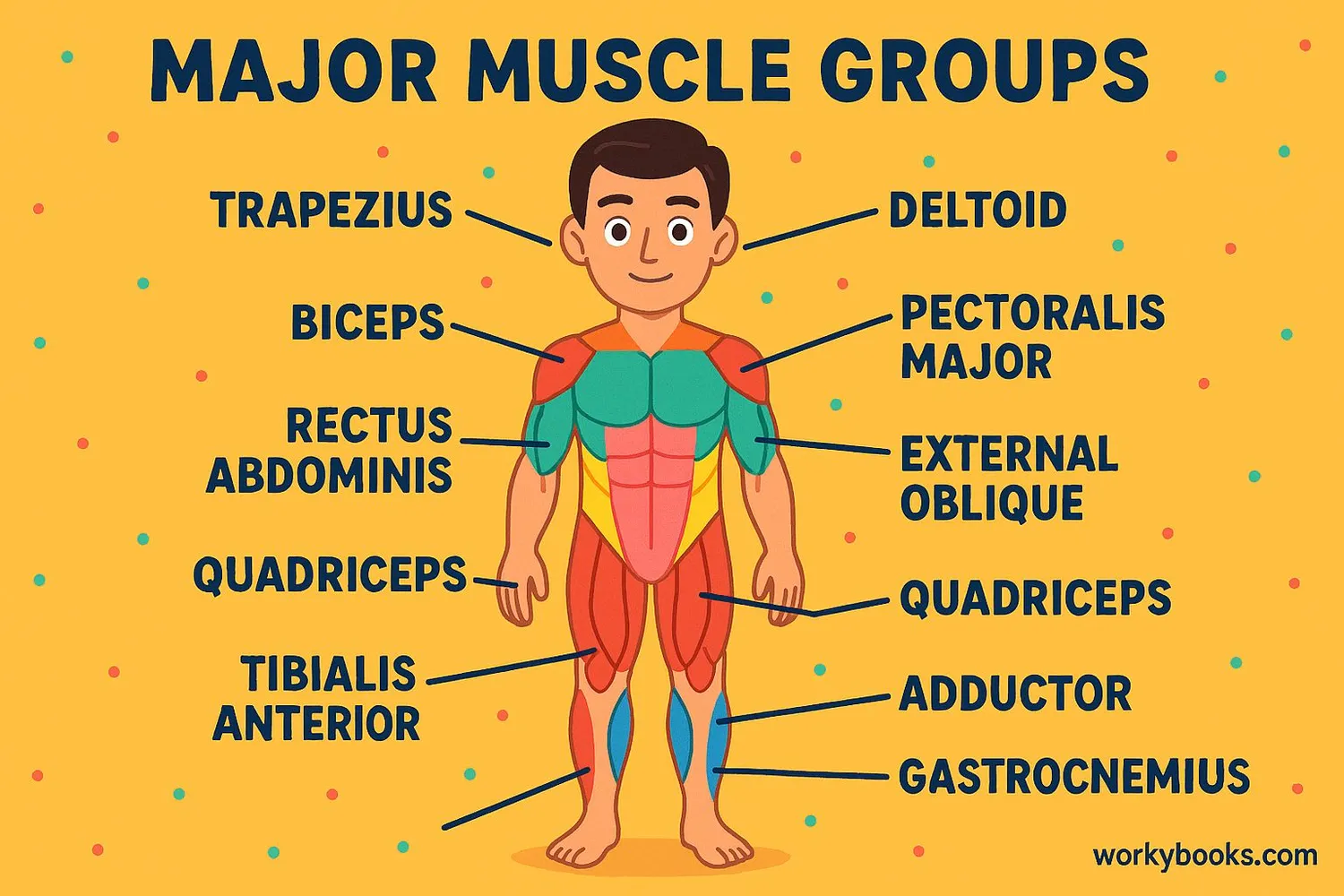
Muscles are the body's engines! They are special tissues that can contract (shorten) and relax to produce movement. Without muscles, we couldn't walk, talk, smile, or even blink!
Definition: The muscular system is a network of tissues that work together to help your body move and function. There are over 600 muscles in your body!
Muscles are made of thousands of tiny fibers bundled together. These fibers contain proteins that slide past each other to make muscles contract. This amazing process requires energy from the food you eat.
Muscle Facts!
The strongest muscle relative to its size is the masseter (jaw muscle). The largest muscle is the gluteus maximus (in your buttocks)!
Types of Muscles
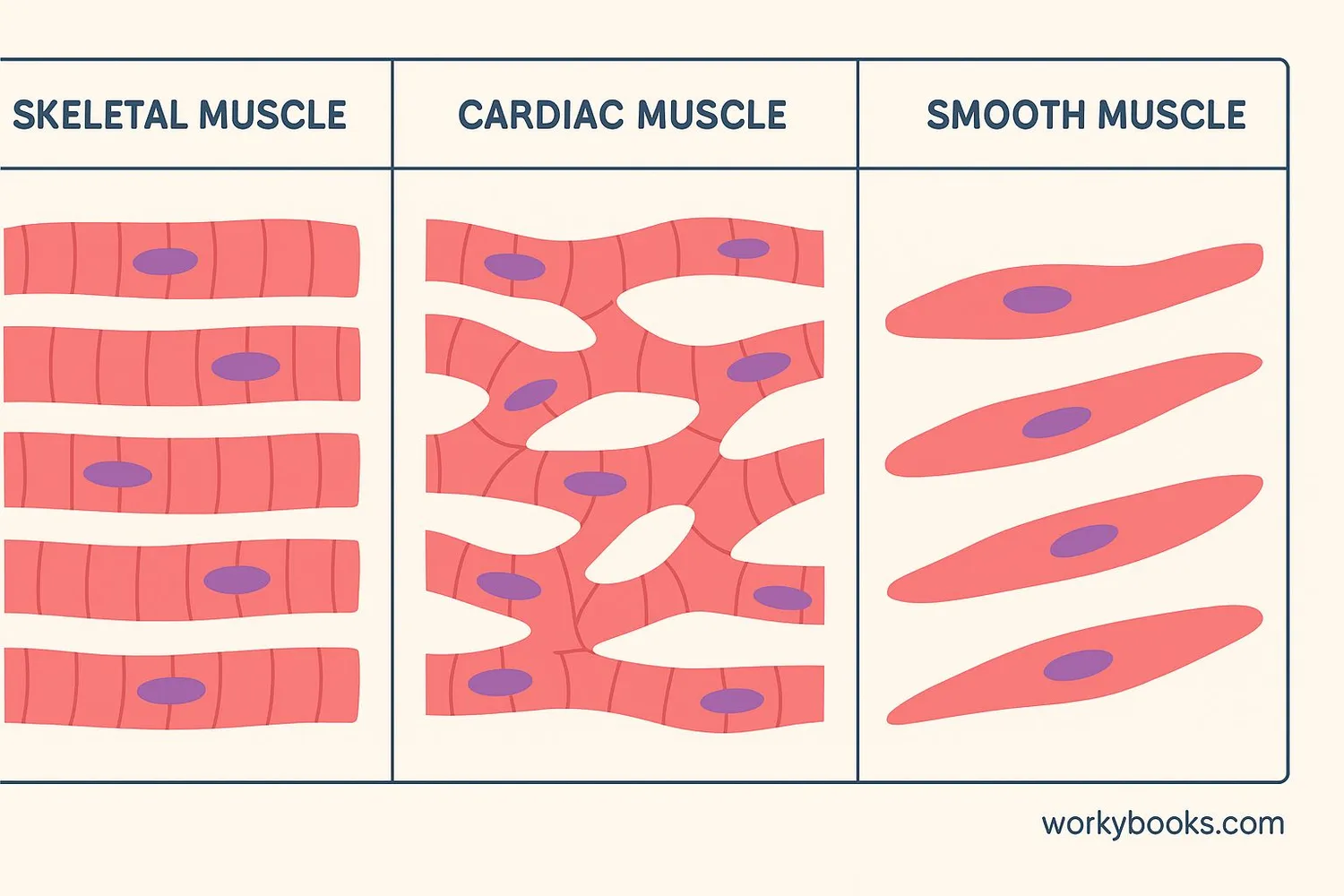
Your body has three different types of muscles, each with special jobs:
Skeletal Muscles
Attached to bones, they help you move voluntarily. They look striped under a microscope.
Smooth Muscles
Found in organs like stomach and blood vessels. They work automatically without you thinking.
Cardiac Muscle
Only found in the heart. It pumps blood automatically throughout your life!
Example: When you decide to kick a ball, your brain sends signals to your skeletal leg muscles to contract. But your heart keeps beating automatically thanks to cardiac muscle, and your digestive system keeps working with smooth muscle.
How Muscles Work
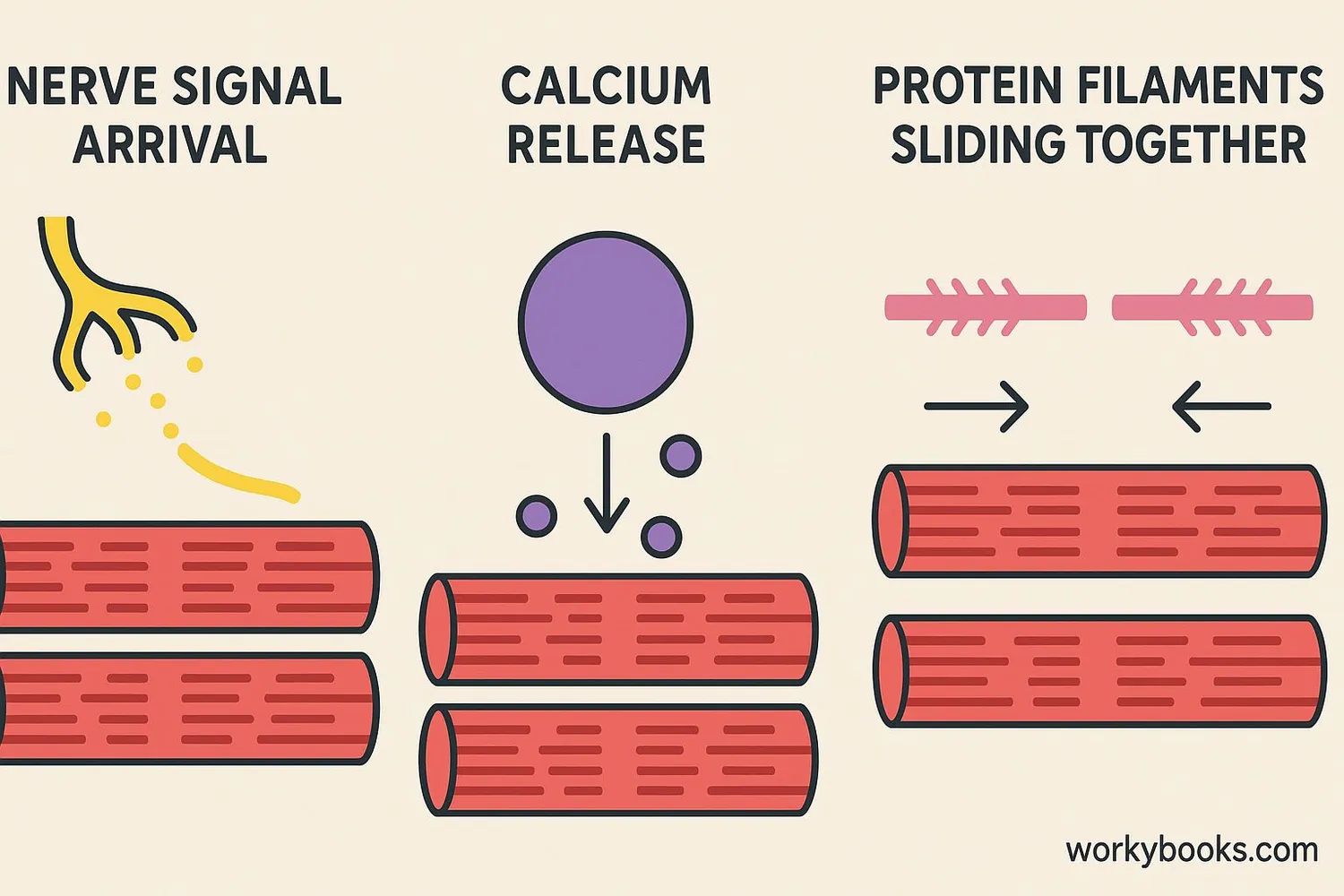
Muscle contraction is an amazing process! Here's how it works:
Signal from Brain
Your brain sends electrical signals through nerves to muscles
Chemical Release
Nerves release chemicals that tell muscle fibers to contract
Sliding Filaments
Proteins inside muscle fibers slide past each other
Muscle Shortens
As filaments slide, the entire muscle shortens (contracts)
Energy Use
This process uses energy from food (ATP molecules)
Muscles always work in pairs! When one muscle contracts (the agonist), its partner relaxes (the antagonist). For example, when you bend your elbow, your bicep contracts and your tricep relaxes. When you straighten your arm, they switch roles!
Why Muscles Matter
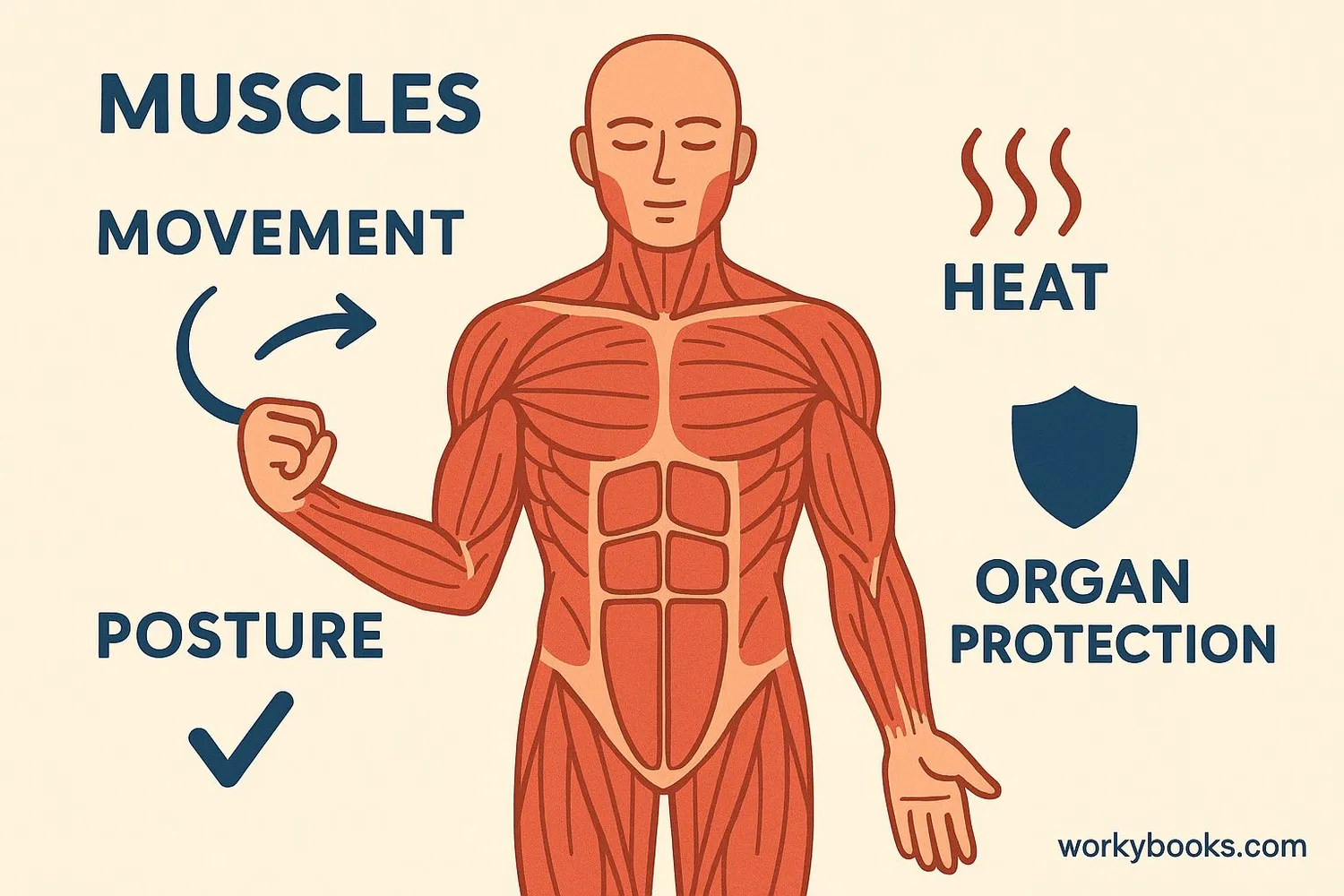
Muscles do much more than just help you move! They have several vital functions:
Movement
Enable walking, running, writing, and facial expressions
Posture
Keep your body upright against gravity
Heat Production
Generate body heat to maintain temperature
Protection
Support and protect internal organs
Keeping muscles healthy is essential for overall well-being. Exercise makes muscles stronger and more efficient. Without regular use, muscles can weaken and shrink (atrophy). Eating protein-rich foods helps build and repair muscle tissue.
Muscle Health Fact!
Regular exercise helps muscles grow stronger by creating tiny tears in muscle fibers that heal stronger than before!
Muscular System Quiz
Test your knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned about the muscular system.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about muscles:
Muscle Trivia
Discover amazing facts about muscles:
Tiny but Mighty
The smallest muscle is the stapedius in your ear - just 1.27 mm long! It protects your inner ear from loud sounds.
Animal Strength
Fleas can jump 150 times their own length! Their leg muscles accelerate 20 times faster than a space shuttle launch.
Space Effects
Astronauts can lose up to 20% of muscle mass in just 5-11 days in space! They exercise 2 hours daily to prevent this.
Muscle Memory
Muscles have "memory"! After training, your muscles rebuild faster if you start exercising again after a break.





