Wetlands - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the amazing world of wetlands and why they are so important to our planet.
What are Wetlands?

Imagine a place where land and water meet. That's a wetland! A wetland is an area of land that is either covered by water or has very wet soil for at least part of the year. The water can be fresh, salty, or a mix of both. These unique ecosystems are filled with plants and animals that are specially adapted to live in wet conditions.
Key Concept
Wetlands are special ecosystems where water is the main factor controlling the environment. They are like a "bridge" between land and water, and they are home to many different kinds of living things.
Types of Wetlands
Not all wetlands are the same! There are four main types of wetlands, and they are different depending on the types of plants and the kind of water they have.
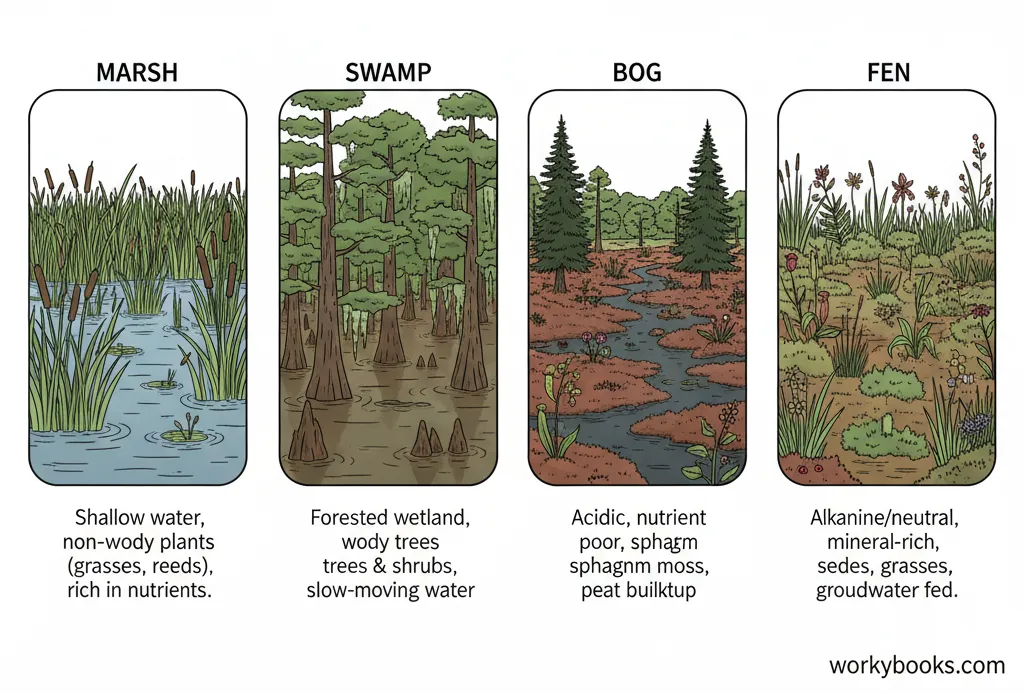
Marshes
Marshes are a type of wetland with soft-stemmed plants like grasses, reeds, and cattails. They are usually found along the edges of rivers and lakes, and they have shallow water. Marshes are full of life!
Swamps
A swamp is a wetland dominated by trees and woody plants, like cypress or mangrove trees. Swamps have slow-moving water and can be found in both freshwater and saltwater areas.
Bogs
Bogs are spongy wetlands with very acidic water and thick layers of moss, especially sphagnum moss. They get their water from rainfall and are often found in cooler climates. Because of the acidic soil, they have special plants like pitcher plants.
Fens
Fens are similar to bogs but are less acidic. They get their water from groundwater, which brings in more minerals. Fens are covered in grasses, sedges, and wildflowers, and are home to many different kinds of wildlife.
Why are Wetlands Important?
Wetlands are some of the most important ecosystems on Earth. They are often called "nature's kidneys" because they help clean our water!
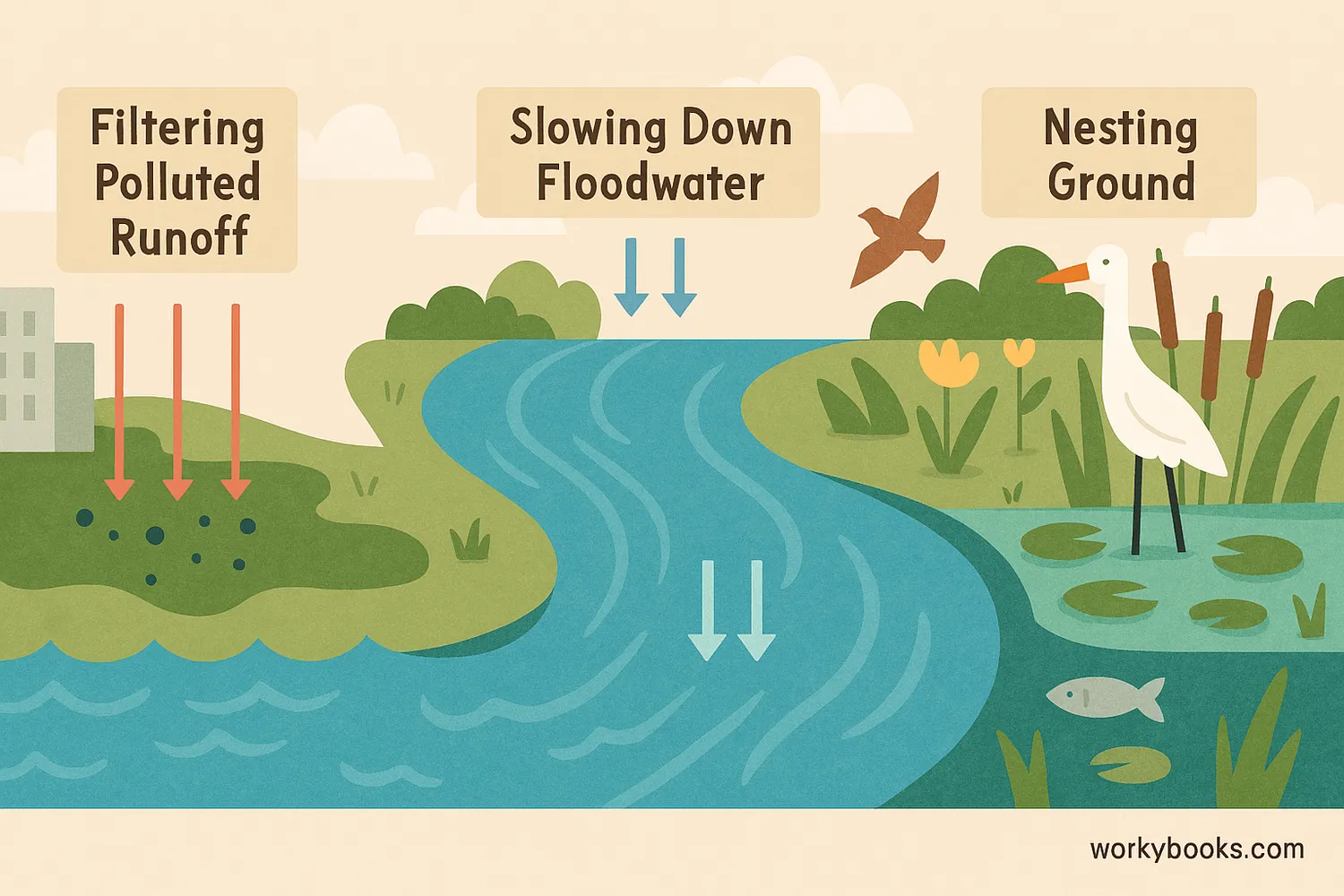
Here are some of the amazing things wetlands do:
- Natural Water Filters: The plants and soil in wetlands act like a big sponge, soaking up pollutants and extra nutrients from the water. This helps keep our rivers, lakes, and oceans clean.
- Flood Protection: Wetlands can absorb a lot of water from heavy rain or melting snow, which helps prevent floods in nearby towns and cities. They act like giant sponges that hold excess water.
- Wildlife Habitat: Wetlands provide food, water, and shelter for a huge variety of animals, including birds, fish, amphibians, and insects. Many birds use wetlands as a rest stop during their long migrations.
- Home to Special Plants: Many plants, like cattails and cypress trees, can only grow in wet soil. These plants help prevent soil from washing away and provide a safe place for animals to live.
Wetlands Quiz
Test your knowledge about wetlands with this short quiz. Choose the best answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about wetlands:
Science Trivia
Here are some interesting facts about wetlands:
Bird Hotels
Wetlands are super important for migratory birds. About half of all North American migratory bird species rely on wetlands for breeding, nesting, and food.
Cleaner than a Sponge
One acre of wetland can filter out more than 2,000 pounds of phosphorus and over 170,000 pounds of nitrogen in a single year!
Found Worldwide
Wetlands are found on every continent except Antarctica. They are one of the most widespread ecosystems on the planet.




