Classification in Mathematics - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn how to group objects and numbers based on their properties and characteristics
What is Classification in Math?
Classification in math means grouping things based on their properties or characteristics.
It's like organizing your toys by putting all the red toys together, all the blue toys together,
and all the green toys together. We classify to make information easier to understand and work with.
When we classify, we look for things that are alike in some way. For example, we might classify shapes by:
- Number of sides (triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons)
- Color (red shapes, blue shapes, green shapes)
- Size (small, medium, large)
Classification Definition
The process of organizing things into categories based on their properties
Key Concept
Classification helps us find patterns and make sense of information. It's an important skill in math and science!
How to Classify Objects
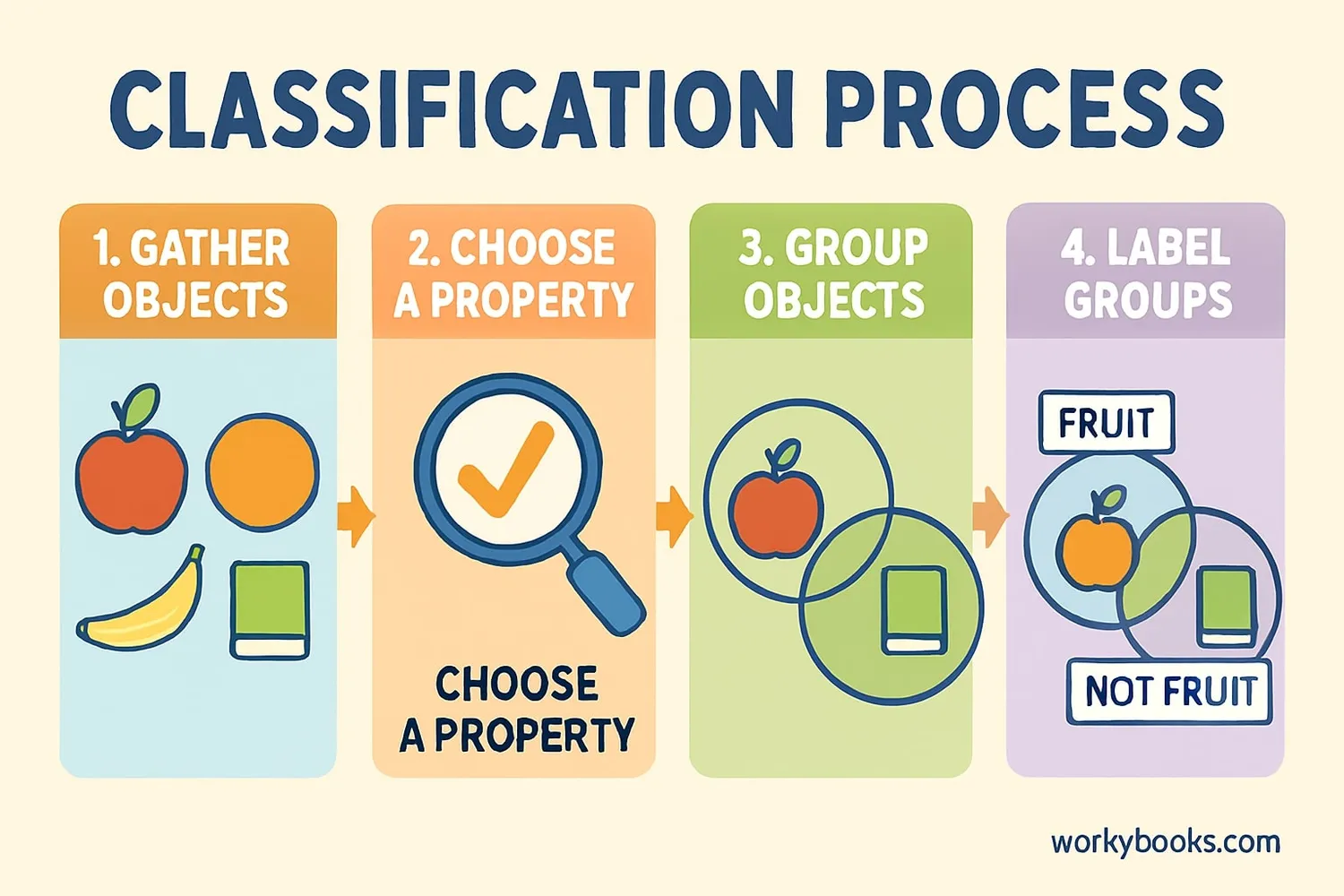
Classifying objects is simple when you follow these steps:
Step 1
Look at all your objects
Examine what you have and notice different features
Step 2
Choose a property
Decide how you want to group them (by color, shape, size, etc.)
Step 3
Sort into groups
Put objects with the same property together
Step 4
Name your groups
Give each group a descriptive label
Example: Let's classify these shapes: 🔺🔺🔵🔺🟦🔺🟦
We can classify by:
- Shape: Triangles (🔺🔺🔺🔺) and Circles (🔵🟦🟦)
- Color: Red (🔺🔺🔺🔺), Blue (🟦🟦), and Blue Circle (🔵)
Remember
Objects can belong to multiple groups depending on how you classify them. A blue triangle could be in the "blue" group and the "triangle" group.
Classifying Numbers
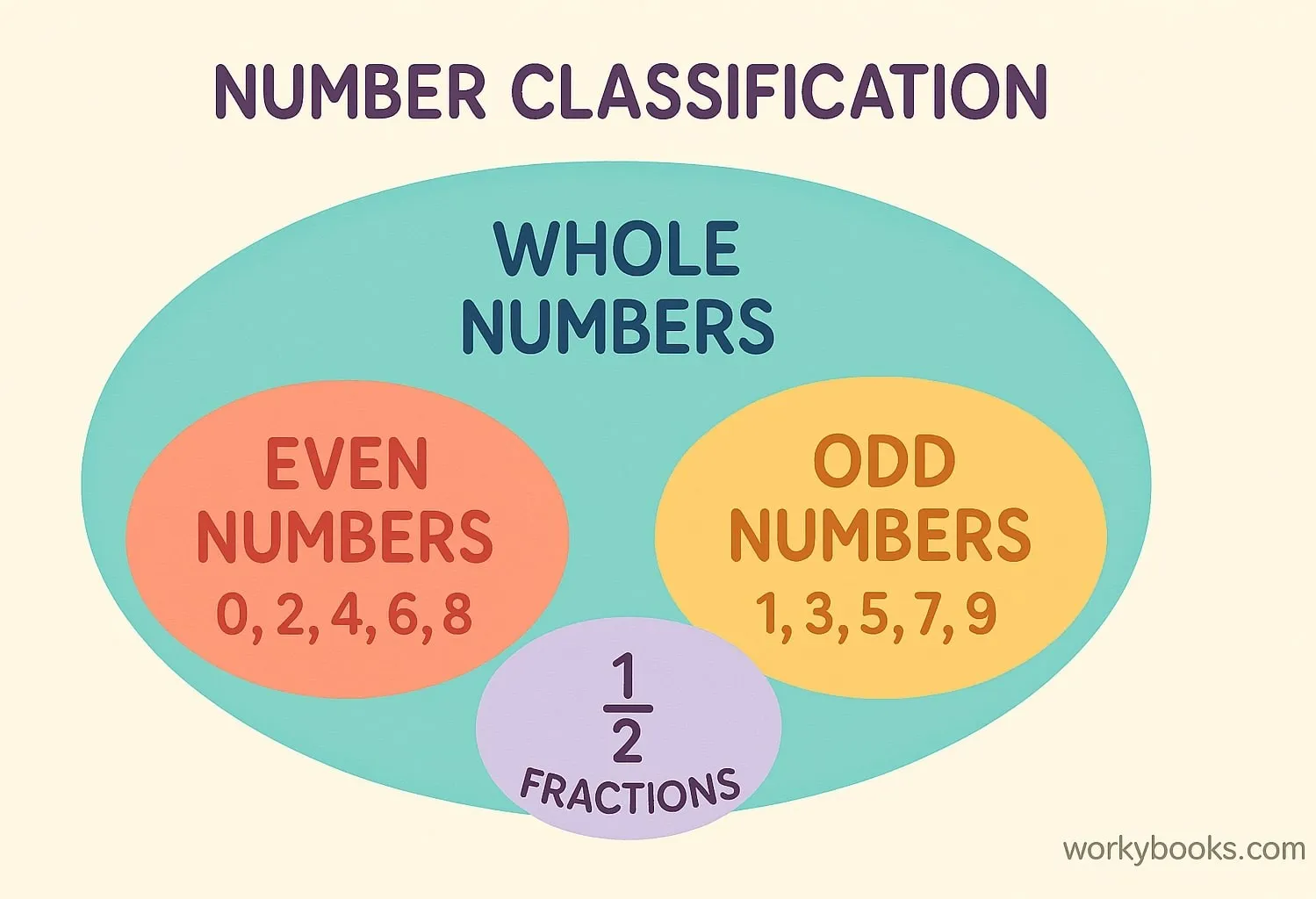
Numbers can be classified in many ways. Here are some common classifications:
Even and Odd Numbers
Even numbers: Can be divided evenly by 2 (0, 2, 4, 6, 8...)
Odd numbers: Cannot be divided evenly by 2 (1, 3, 5, 7, 9...)
Whole Numbers
All positive numbers starting from 0 (0, 1, 2, 3, 4...)
Does not include fractions or decimals
Fractions
Numbers that represent parts of a whole (½, ¾, ⅔)
Can be proper (less than 1) or improper (greater than 1)
Prime Numbers
Numbers greater than 1 that can only be divided by 1 and themselves (2, 3, 5, 7, 11...)
Classification Tip
Numbers can belong to multiple categories. For example, 2 is even, whole, and prime!
Classification Examples

Classification is all around us! Here are some real-world examples:
In the Library
Books are classified by genre: mystery, science fiction, biography, etc.
They might also be classified by reading level or author's last name
In the Grocery Store
Foods are classified into sections: fruits, vegetables, dairy, meats
Within sections, foods might be classified by brand or type
In Nature
Animals are classified into groups: mammals, birds, reptiles, fish, amphibians
Plants are classified as trees, flowers, grasses, etc.
In the Classroom
Students might be classified by birth month, favorite subject, or height
Supplies are classified as pencils, papers, books, etc.
Real-World Application
Scientists use classification to organize living things into groups like kingdoms, phyla, and species.
Classification Quiz
Test your classification skills with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about classification:
Math Classification Trivia
Discover interesting facts about classification:
Ancient Classification
The ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle created one of the first classification systems for animals over 2,300 years ago. He grouped animals based on how they moved and where they lived.
Plant Classification
Scientists have classified over 390,000 plant species! The largest plant family is the orchid family, with more than 28,000 classified species.
Number Classification
There are infinitely many prime numbers. Euclid proved this over 2,000 years ago, showing that no matter how many primes you have, you can always find another one.
Animal Kingdom
The animal kingdom is classified into more than 30 major groups called phyla. The largest phylum is Arthropoda, which includes insects, spiders, and crustaceans.





