Gravitational Force - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the invisible force that holds our universe together
What is Gravitational Force?
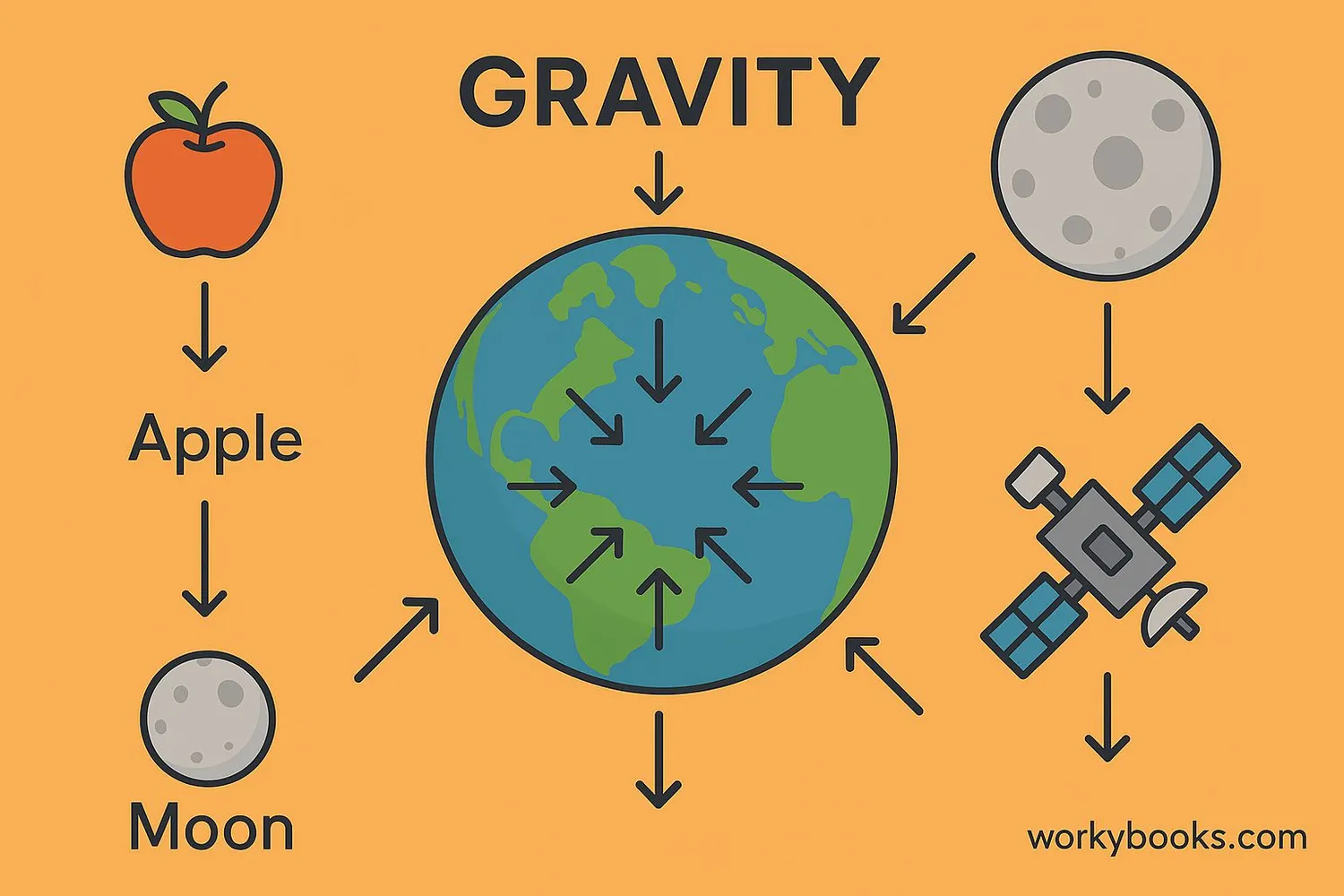
Gravitational force is the invisible pull that attracts all objects with mass toward each other. It's what keeps us firmly on the ground and holds the planets in orbit around the Sun. Without gravity, everything would float away into space!
Definition: Gravitational force is a natural phenomenon by which all things with mass or energy are brought toward one another. On Earth, gravity gives weight to physical objects.
Here are some key facts about gravity:
- Every object in the universe pulls on every other object
- The strength of gravity depends on mass and distance
- Earth's gravity is what makes things fall toward the ground
- Gravity holds planets, stars, and galaxies together
Gravity Fact!
Gravity is what keeps the Moon orbiting around Earth and Earth orbiting around the Sun!
Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation
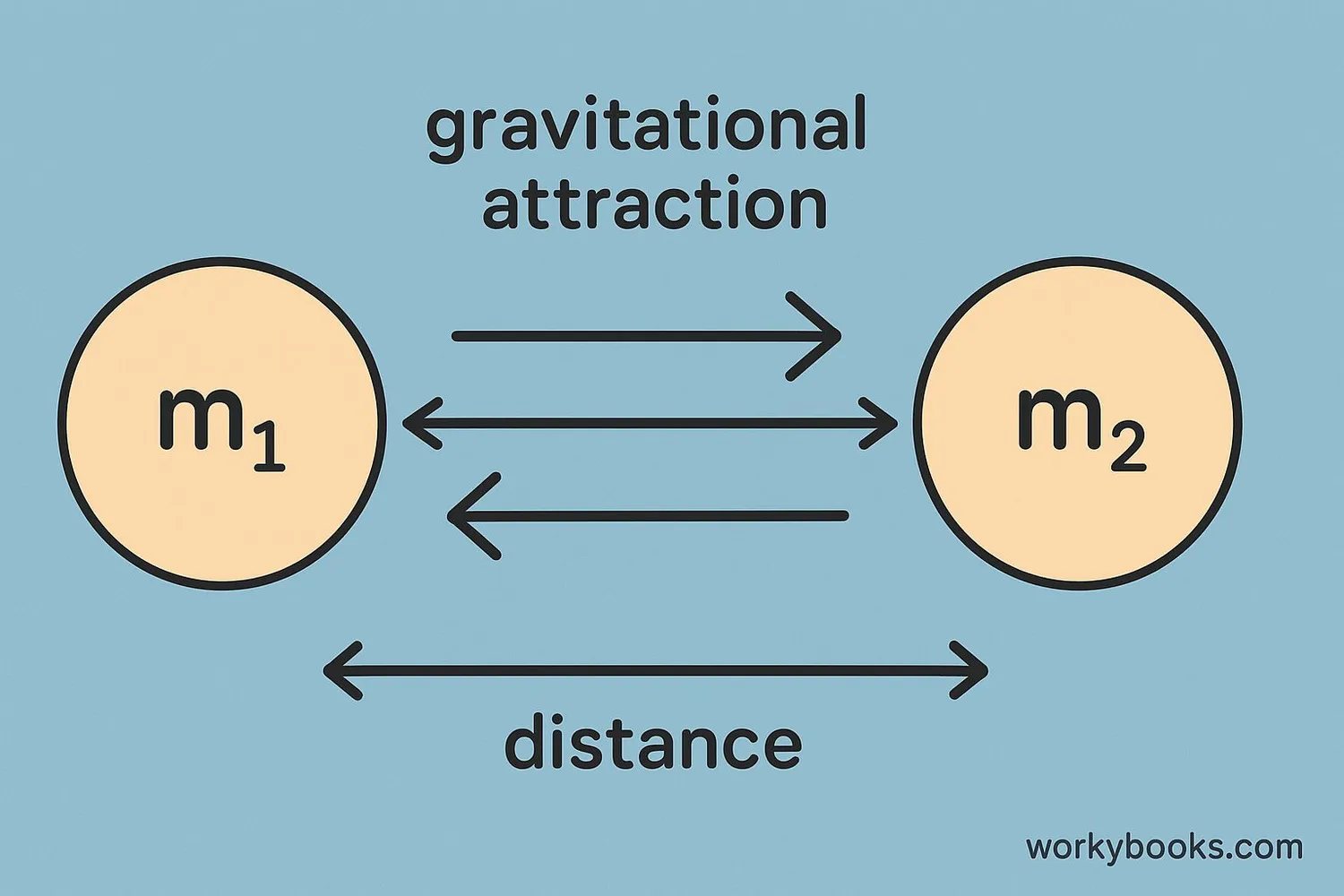
Sir Isaac Newton discovered that every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force that depends on two things:
1. The mass of the objects (more mass = stronger pull)
2. The distance between them (farther apart = weaker pull)
This discovery is called the Law of Universal Gravitation.
F = G × (m₁ × m₂) / r²
Where:
F = Gravitational force
G = Gravitational constant
m₁ and m₂ = Masses of the two objects
r = Distance between centers of the masses
Mass Matters
More massive objects have stronger gravitational pull
Distance Affects
Gravity weakens quickly as distance increases
Universal Force
Applies to all objects everywhere in the universe
Newton's Apple!
The story goes that Newton discovered gravity when an apple fell on his head, helping him realize that the same force pulls apples to Earth and keeps the Moon in orbit.
Gravitational Force Calculation
While we don't need to calculate complex equations, understanding how gravity works helps explain many things in our world. Here are some key points about gravitational force calculation:
Weight vs. Mass
Your mass is the same everywhere, but your weight changes with gravity
Planet Differences
On the Moon, you'd weigh about 1/6 of your Earth weight
Escape Velocity
The speed needed to break free from a planet's gravity
Example Calculation
Imagine two friends: Sam (mass 40kg) and Alex (mass 50kg) sitting 0.5m apart. The gravitational force between them is about 0.00000053 Newtons - too small to notice! But Earth's huge mass (5.97×10²⁴ kg) creates the gravity we feel.
Why Gravitational Force is Important

Gravity is fundamental to our existence and the structure of the universe. Here's why it's so important:
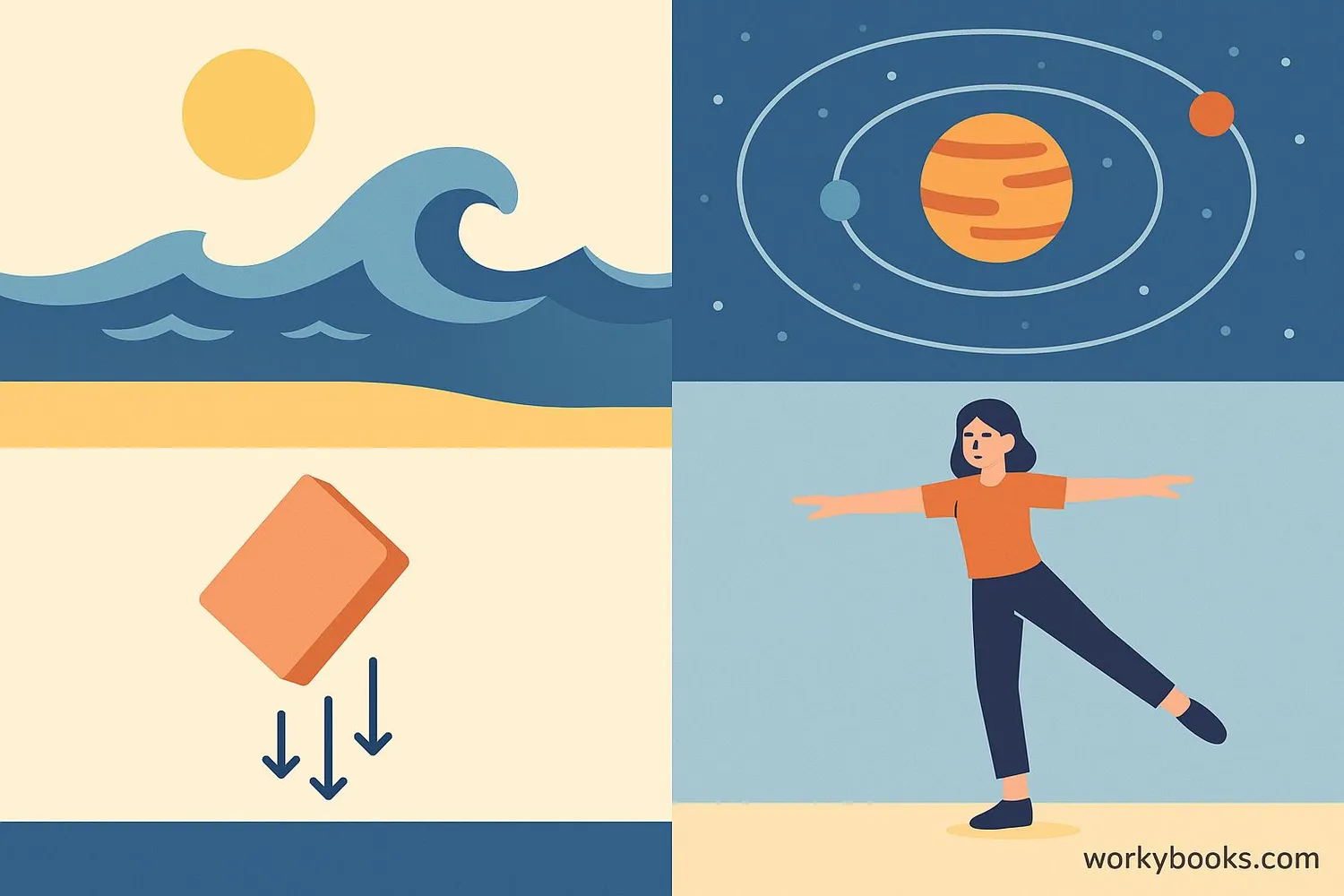
Planetary Orbits
Keeps planets orbiting stars and moons orbiting planets
Tides
The Moon's gravity creates ocean tides on Earth
Atmosphere
Holds Earth's atmosphere in place so we can breathe
Without gravity, there would be no:
• Stars or planets (just floating dust)
• Atmosphere to breathe
• Ocean tides
• Orbits - everything would drift apart
• Structure to galaxies or the universe itself
Gravity is the cosmic glue that holds our universe together!
Gravitational Force Quiz
Test your gravity knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about gravitational force:
Gravity Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about gravitational force!
Space Adaptation
Astronauts can grow up to 2 inches taller in space! Without gravity compressing their spines, the space between vertebrae expands.
Tall Trees
The tallest trees can only grow about 400 feet high. Beyond this height, gravity makes it impossible for trees to transport water to their tops.
Speed of Gravity
Gravitational waves travel at the speed of light! When two black holes collide, the ripples in spacetime move at 186,000 miles per second.
Uneven Gravity
Earth's gravity isn't uniform! It varies by location due to factors like mountains, ocean trenches, and differences in Earth's density.





