Homogeneous Mixtures - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how substances mix together evenly to create uniform combinations!
What is a Homogeneous Mixture?
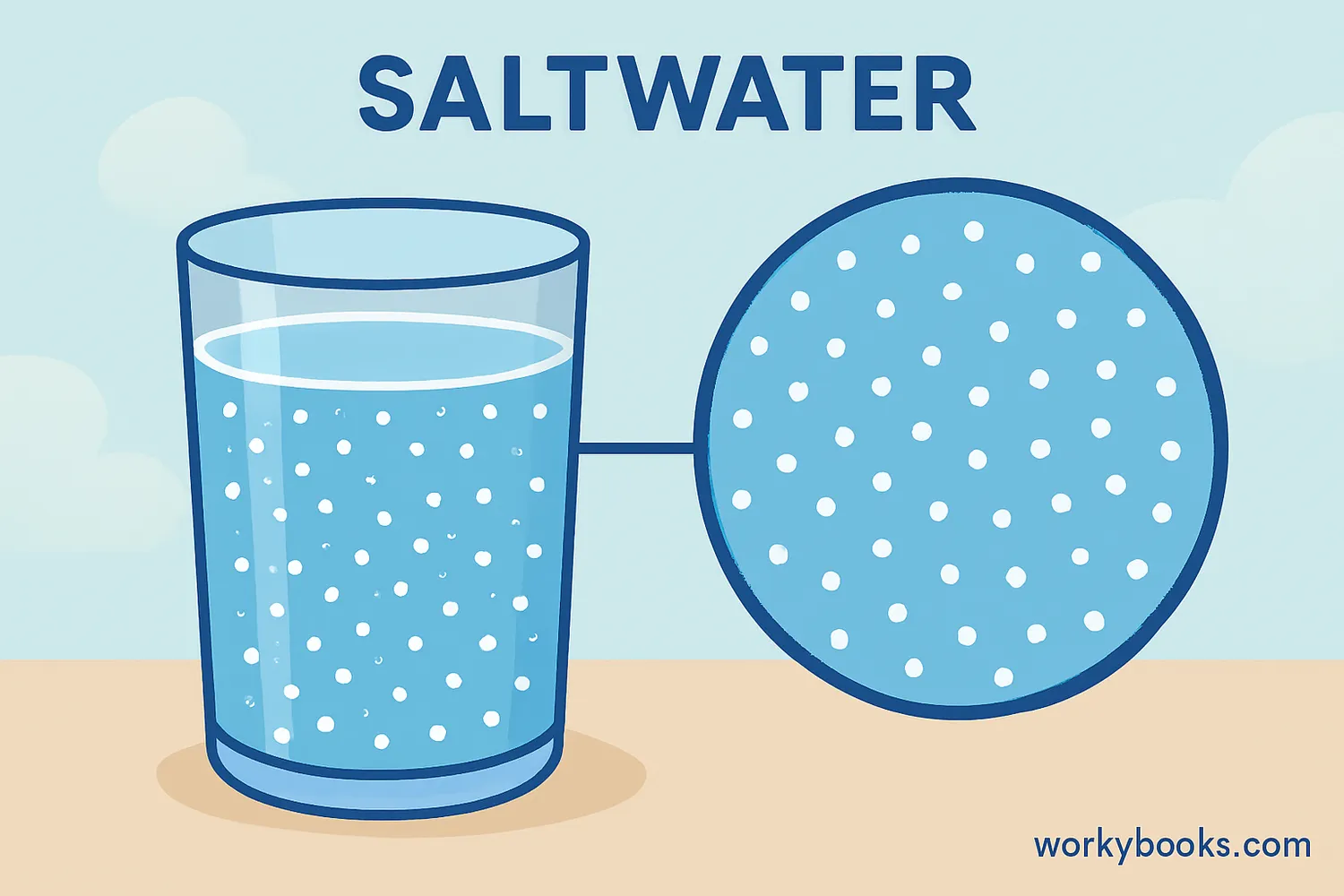
A homogeneous mixture is a type of mixture where the different substances are evenly distributed throughout. This means that every part of the mixture has the same composition and properties. The prefix "homo-" means same, and "geneous" means kind, so homogeneous means "the same throughout."
In a homogeneous mixture, you cannot see the different parts or components with your naked eye. The mixture appears uniform and consistent no matter where you look at it or sample it. Scientists also call these mixtures "solutions."
Did You Know?
The air we breathe is a homogeneous mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and other gases! All these gases are mixed together so evenly that we can't see the separate components.
Homogeneous vs Heterogeneous Mixtures
Understanding the difference between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures helps us classify different types of combinations. Here's how they compare:
| Feature | Homogeneous Mixture | Heterogeneous Mixture |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Uniform throughout | Not uniform; varies in different parts |
| Visibility of components | Components not visible to naked eye | Components often visible |
| Separation | Hard to separate by physical means | Easier to separate by physical means |
| Examples | Saltwater, air, brass | Salad, soil, granite |
Remember This!
Homogeneous = "same throughout" | Heterogeneous = "different throughout"
Homogeneous Mixture Examples
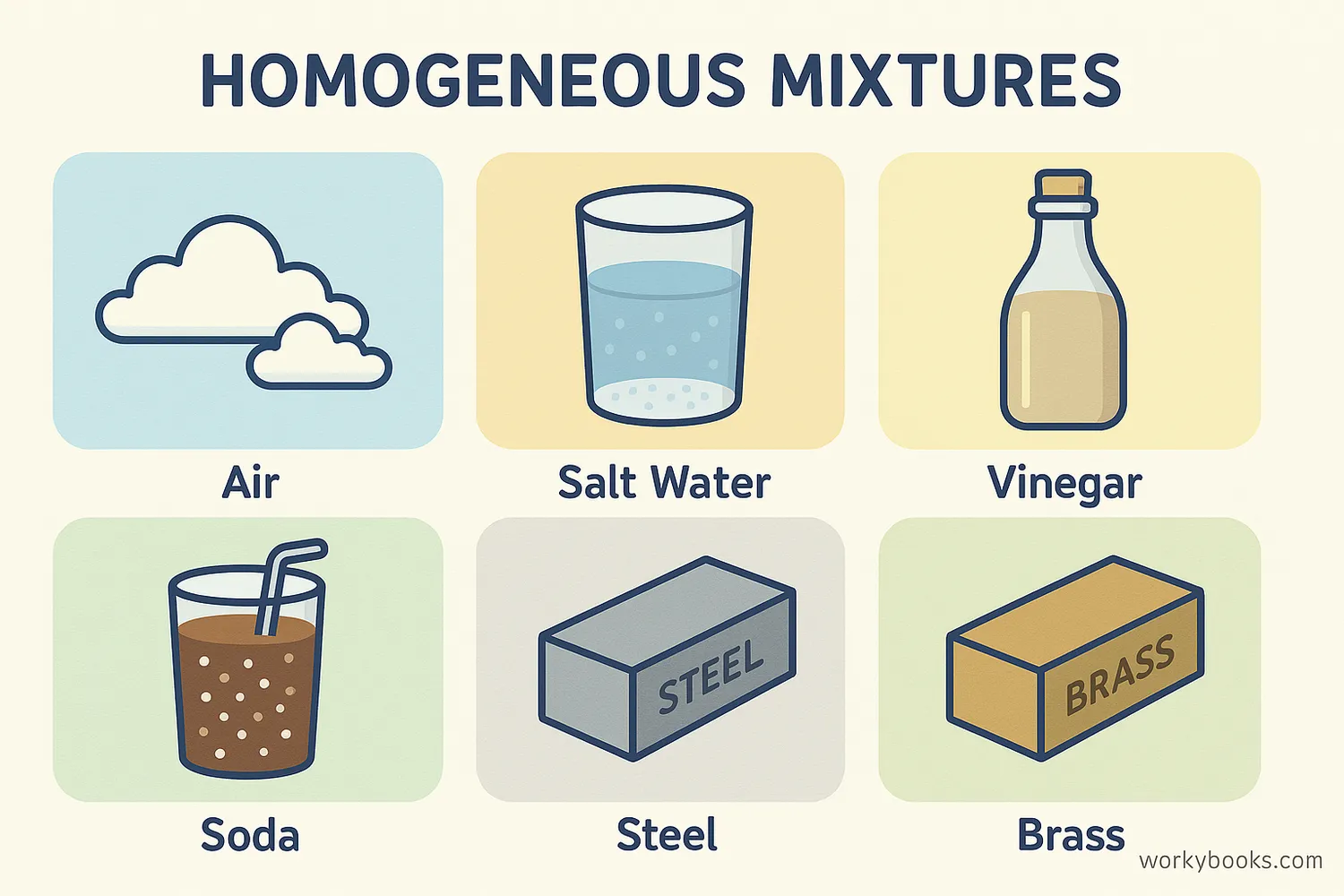
Homogeneous mixtures are all around us! Here are some common examples you encounter every day:
Saltwater
When salt dissolves completely in water, creating a uniform solution
Air
A mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and other gases blended evenly
Vinegar
A solution of acetic acid in water with uniform properties
Soda
Carbon dioxide gas dissolved in flavored water creates a uniform drink
Alloys
Brass (copper and zinc) and steel (iron and carbon) are solid homogeneous mixtures
These examples show that homogeneous mixtures can be solids, liquids, or gases. The key feature is that they have a uniform composition throughout.
Properties of Homogeneous Mixtures
Homogeneous mixtures have special properties that make them different from other types of mixtures:
Uniform Composition
Every sample taken from the mixture has the same composition
No Tyndall Effect
They do not scatter light (unlike heterogeneous mixtures)
Single Phase
They exist in only one phase (solid, liquid, or gas)
Components Not Visible
You cannot see the separate components with the naked eye
Hard to Separate
Components cannot be separated by simple filtration
To separate the components of a homogeneous mixture, you need special methods like evaporation (for saltwater), distillation (for alcohol and water), or chromatography (for ink components).
Separation Challenge!
It's difficult to separate homogeneous mixtures because the particles are mixed at the molecular or ionic level, not just physically combined.
Homogeneous Mixtures Quiz
Test your knowledge about homogeneous mixtures with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about homogeneous mixtures:
Fun Homogeneous Mixture Trivia
Discover some interesting facts about homogeneous mixtures!
Ocean Mixture
Seawater is a complex homogeneous mixture containing at least 70 different elements dissolved in water! The most abundant dissolved substance is sodium chloride (table salt).
Valuable Mixtures
Some homogeneous mixtures are very valuable! White gold is a homogeneous mixture (alloy) of gold with palladium, nickel, or other white metals. Rose gold contains copper mixed with gold.
Blood Plasma
The liquid part of blood, called plasma, is a homogeneous mixture. It's about 92% water, with proteins, nutrients, hormones, and waste products dissolved in it.
Space Mixtures
The air inside the International Space Station is a carefully controlled homogeneous mixture similar to Earth's air, but with more emphasis on removing carbon dioxide and other waste gases.





