Ionic Bonding - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how atoms transfer electrons to form chemical bonds and create new substances!
What are Ionic Bonds?
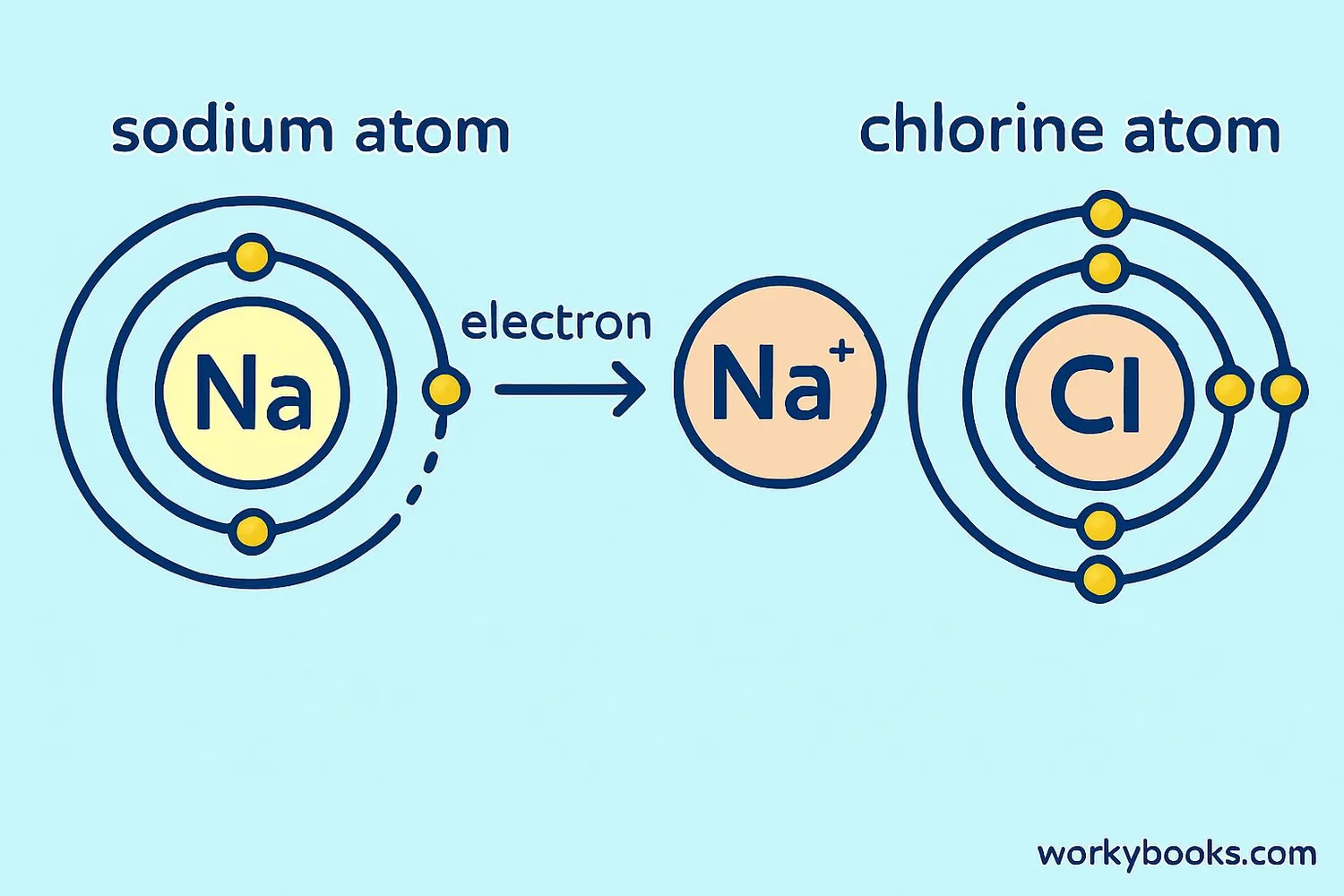
Ionic bonds are special connections between atoms that happen when one atom gives electrons to another atom. This creates positively and negatively charged particles called ions that are strongly attracted to each other.
Think of ionic bonding like a friendly exchange where one atom has extra electrons it wants to share, and another atom needs electrons to be stable. When a metal atom meets a nonmetal atom, the metal usually gives away one or more electrons to the nonmetal. This creates positive cations and negative anions that stick together like magnets!
Bonding Fact!
Table salt (sodium chloride) is one of the most common ionic compounds, formed when sodium atoms transfer electrons to chlorine atoms!
How Ionic Bonds Form
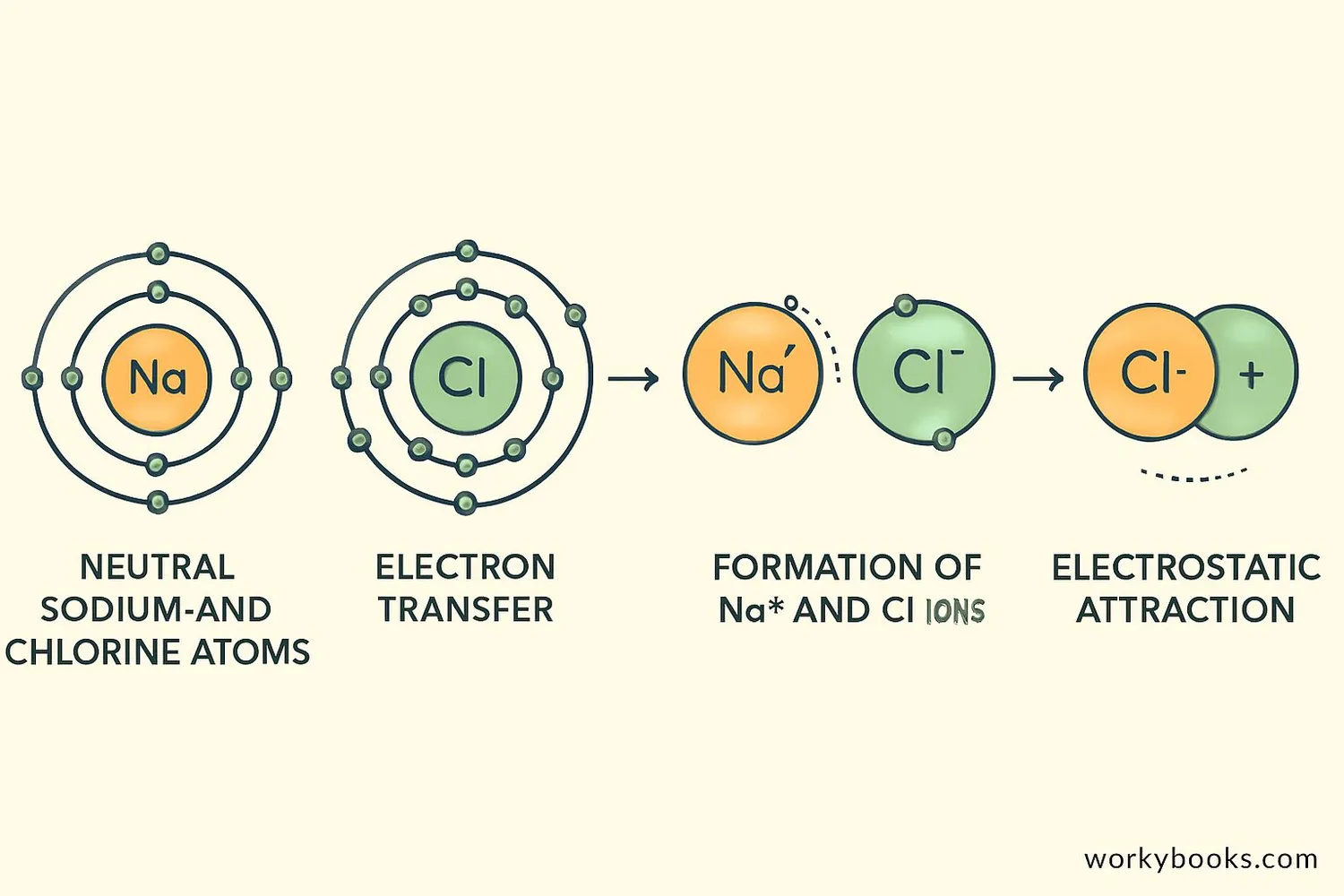
Ionic bonding happens in a fascinating three-step process:
Electron Transfer
A metal atom donates one or more electrons to a nonmetal atom
Ion Formation
The atom that loses electrons becomes a positive cation
Electrostatic Attraction
The positive and negative ions attract each other strongly
This process creates a powerful electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions. The resulting ionic compound forms a regular, repeating 3D pattern called a crystal lattice that makes ionic compounds solid at room temperature.
Electronegativity Matters!
Ionic bonds form when there's a large difference in electronegativity between atoms (usually greater than 1.7). This means one atom has a much stronger pull on electrons than the other.
Properties of Ionic Compounds
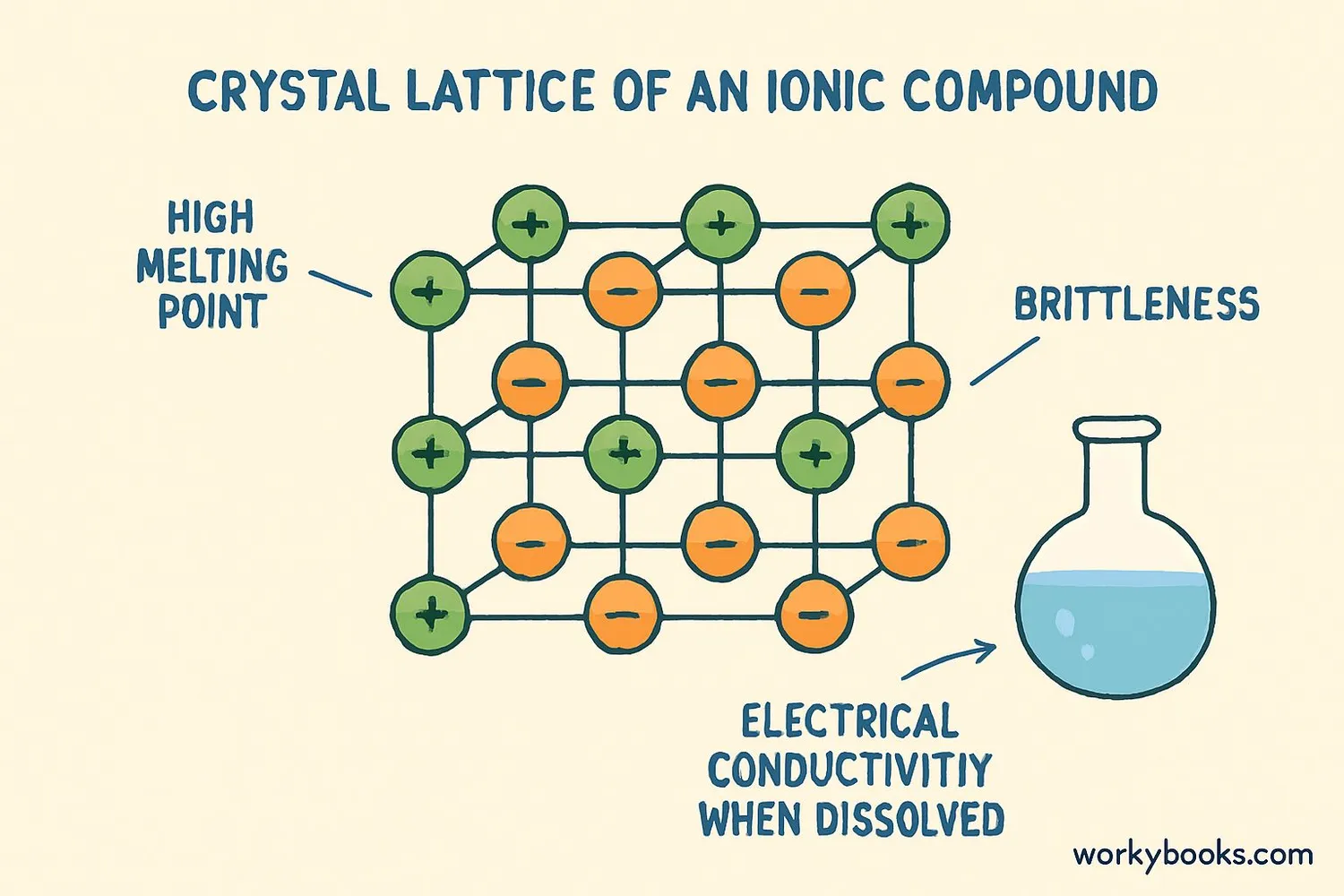
Ionic compounds have special properties that make them different from other substances:
High Melting Points
Strong ionic bonds require lots of energy to break, so they melt at high temperatures
Electrical Conductivity
They conduct electricity when melted or dissolved in water
Crystalline Solids
They form regular crystal structures with definite shapes
Additional properties of ionic compounds include:
• Brittleness - Ionic crystals shatter when force is applied
• Solubility - Many dissolve easily in water
• Hardness - They're often hard but brittle solids
• No conductivity as solids - Ions must be free to move to conduct electricity
Ionic Bonding Quiz
Test your ionic bonding knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about ionic bonding:
Ionic Bonding Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about ionic bonding!
Salt of the Earth
The ionic compound sodium chloride (table salt) is essential for life. Your body contains about 250 grams of salt, which helps with nerve function and fluid balance!
Crystal Clear
Many beautiful gemstones are ionic compounds! Rubies and sapphires are made of aluminum oxide with trace elements that give them their colors.
Strong Bonds
Ionic bonds are some of the strongest chemical bonds. It takes temperatures over 800°C to melt sodium chloride - that's hotter than a pizza oven!
Ocean Salts
Seawater contains many ionic compounds dissolved in it. If all the salt in the oceans were spread over the land, it would form a layer over 500 feet thick!





