Nanomaterials: Tiny Things with Big Impact - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how materials at the nanoscale are changing our world!
What are Nanomaterials?
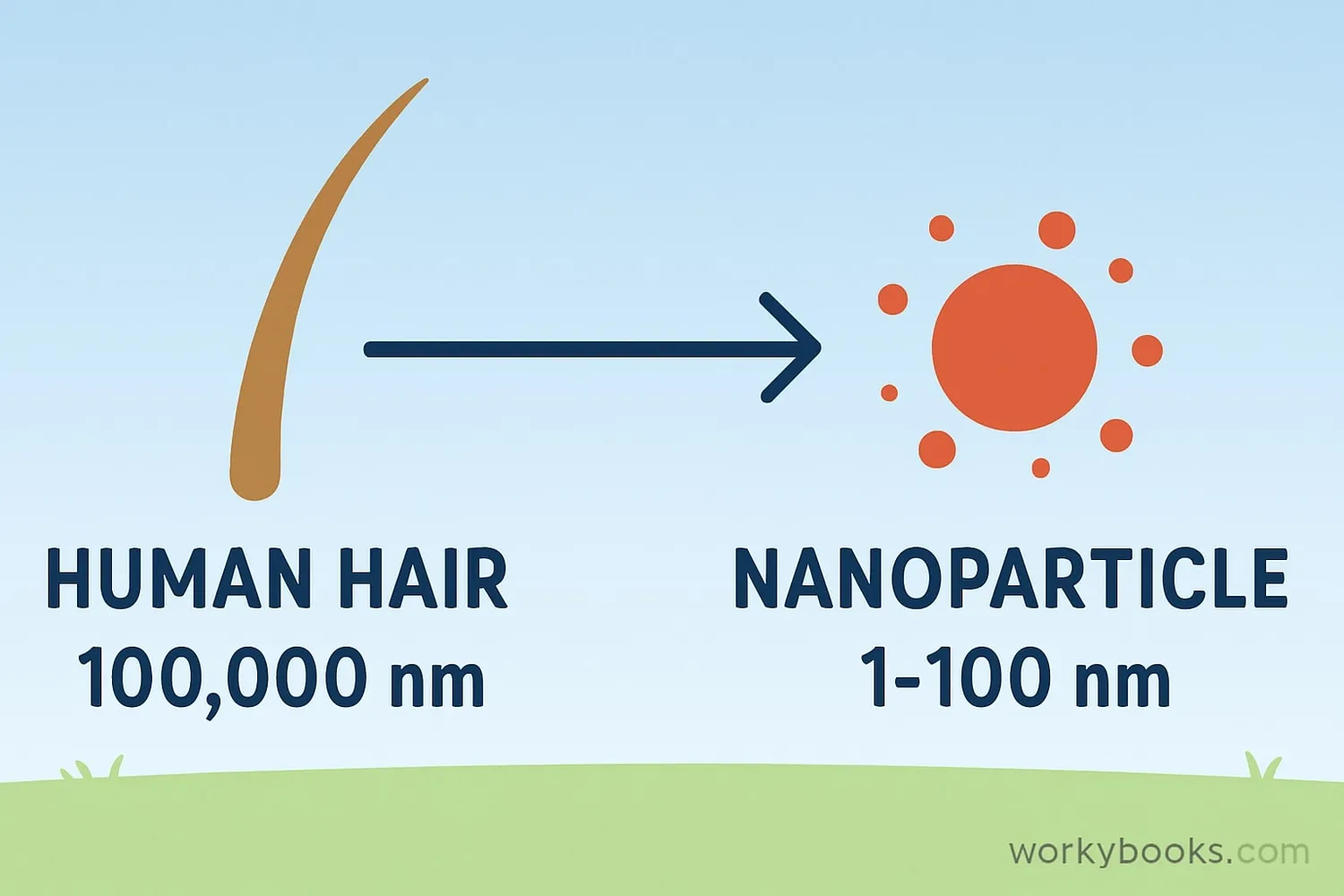
Nanomaterials are incredibly tiny materials that measure between 1 and 100 nanometers. But how small is a nanometer? It's one billionth of a meter! To understand this scale:
Example: If a marble were one nanometer wide, then the entire Earth would be about one meter wide! At this tiny scale, materials behave differently and have special properties.
Nanotechnology is the science of working with these extremely small materials to create new products and solutions. Scientists study nanomaterials to understand their unique properties and how we can use them to improve our world.
Did You Know?
Your fingernails grow about one nanometer every second! That's how incredibly small these materials are.
Types of Nanomaterials
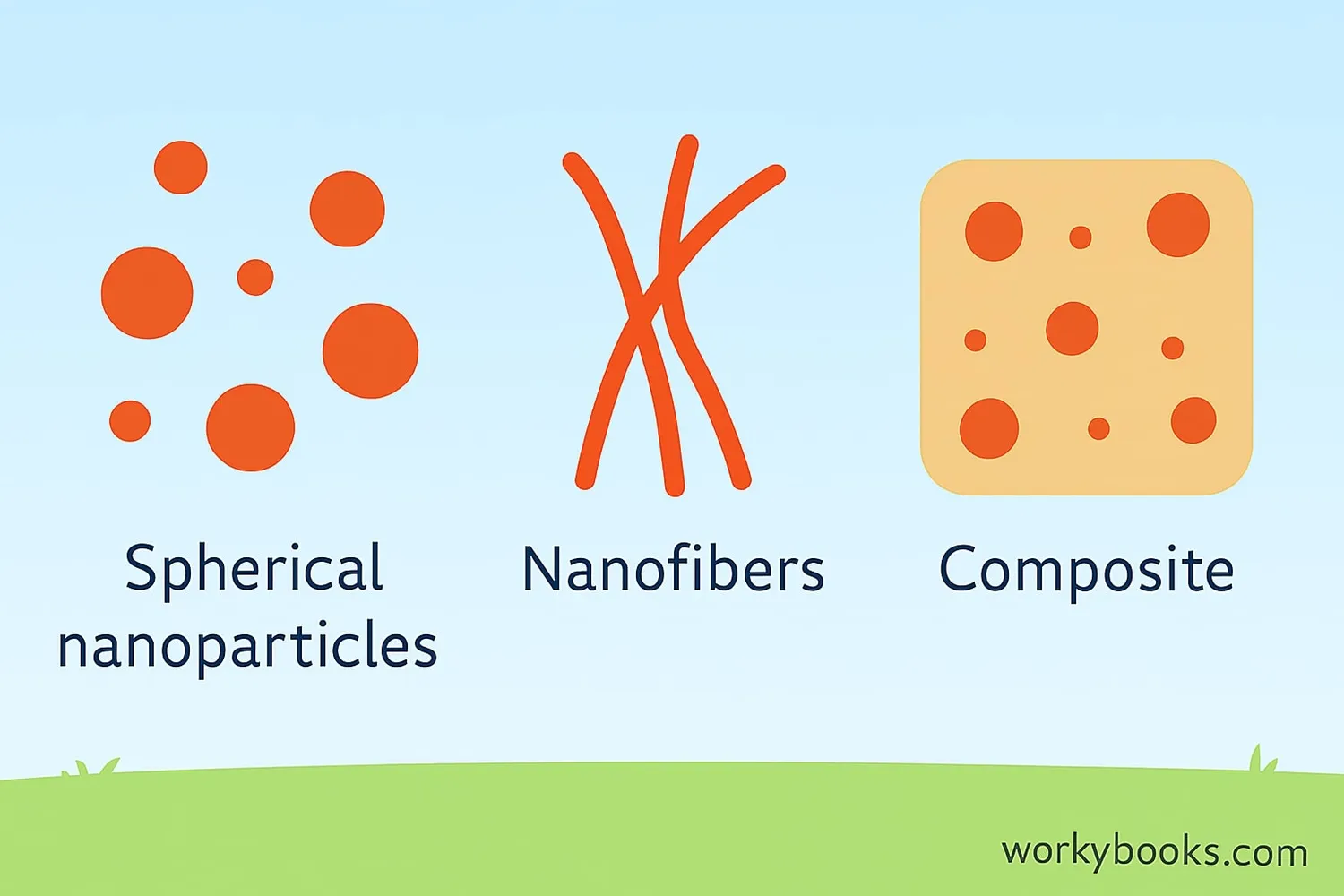
Nanomaterials come in different shapes and structures. Here are three common types:
Nanoparticles
Tiny particles with all dimensions at the nanoscale. Example: Silver nanoparticles used in antibacterial bandages.
Nanofibers
Thin fibers with diameters at the nanoscale. Example: Nanofibers in air filters that trap tiny pollutants.
Nanocomposites
Materials made by combining nanoparticles with other materials. Example: Tennis rackets made with carbon nanotubes for extra strength.
Each type of nanomaterial has special properties. For example, gold nanoparticles aren't gold-colored - they can appear red, purple, or blue! This happens because at the nanoscale, materials interact with light differently.
How Nanotechnology Works

Working with nanomaterials requires special tools and approaches:
Seeing Nanomaterials
Scientists use electron microscopes that can see objects thousands of times smaller than what regular microscopes can detect.
Manipulating Atoms
Special tools like atomic force microscopes can move individual atoms to build nanostructures.
Creating Nanomaterials
Scientists use chemical processes to grow nanomaterials or break larger materials down into nanoparticles.
Nanotechnology works because at the nanoscale, the rules of physics change. Materials have much more surface area compared to their size, which makes them more reactive. This is why nanomaterials can have such powerful effects even in tiny amounts.
Applications of Nanomaterials
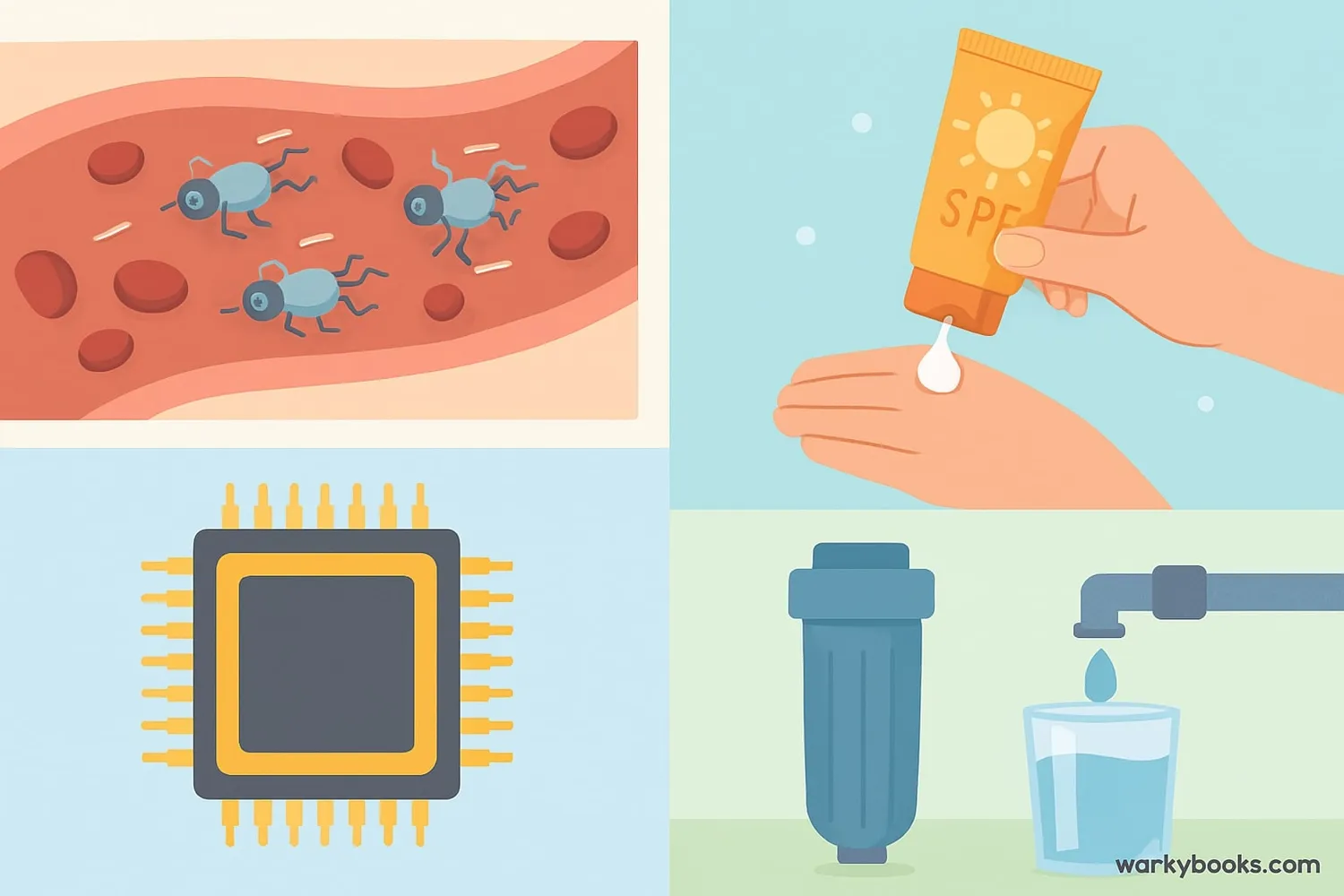
Nanomaterials are already making a big difference in many areas of our lives:
Medicine
Nanoparticles can deliver medicine directly to cancer cells, making treatments more effective with fewer side effects.
Electronics
Nanomaterials make computer chips smaller and more powerful, helping create faster smartphones and computers.
Energy
Nanomaterials improve solar panels and batteries, helping us use more clean energy.
Environment
Nanomaterials can clean polluted water by removing toxins and bacteria.
You might already be using products with nanomaterials! Some sunscreens contain nanoparticles that protect your skin without leaving a white film. Some stain-resistant clothing uses nanotechnology too. As scientists learn more, we'll see even more amazing applications of these tiny materials.
Nanomaterials Quiz
Test your knowledge about nanomaterials with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about nanomaterials:
Nanomaterials Trivia
Discover amazing facts about the world of nanotechnology:
Size Comparison
If a marble was one nanometer in diameter, then Earth would be about one meter in diameter! That's how incredibly small the nanoscale is.
Ancient Nanotechnology
The beautiful red color in some medieval church windows comes from gold nanoparticles! Artisans added gold to glass, creating nanoparticles that scatter light to produce rich red hues.
Nature's Nanotech
The iridescent colors on butterfly wings and peacock feathers come from nanostructures, not pigments! Tiny structures on their surfaces interact with light to create vibrant colors.
Future Possibilities
Scientists are working on nanobots that could travel through your bloodstream to find and repair damaged cells, acting like tiny doctors inside your body!





