Net Force - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how forces work together to create motion and change!
What is Net Force?
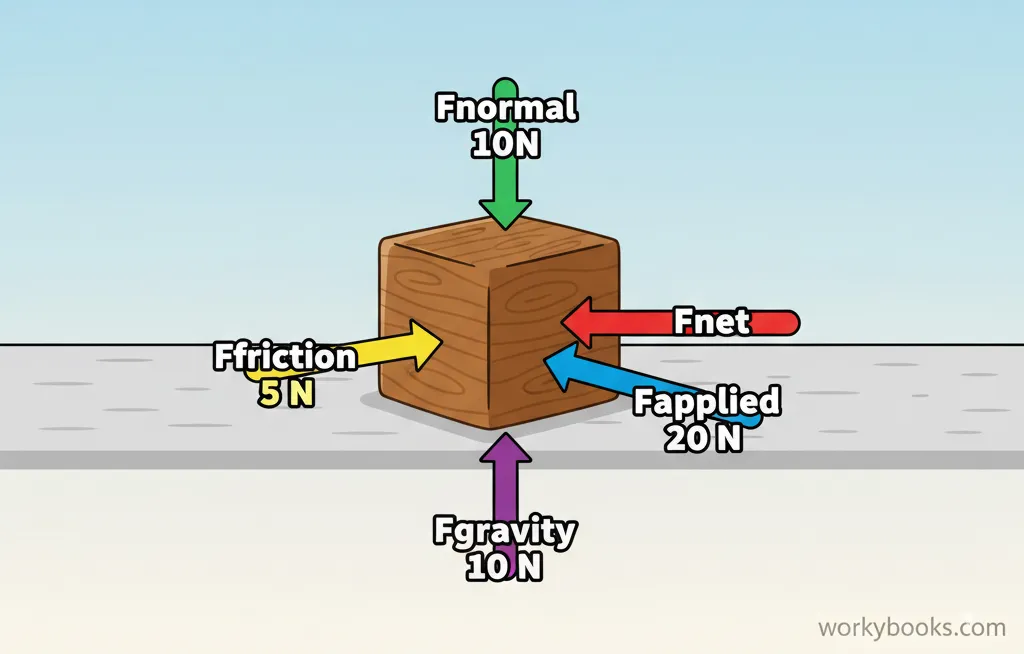
Net force is the overall force acting on an object when all the individual forces are combined together. Think of it like a tug-of-war: if both teams are pulling with equal strength, the rope doesn't move. But if one team pulls harder, the rope moves in their direction.
In physics, we use the symbol Fnet to represent net force. When Fnet equals zero, we say the forces are balanced and the object won't change its motion. When Fnet is not zero, the forces are unbalanced and the object will accelerate in the direction of the net force.
Science Fact!
Sir Isaac Newton described how forces affect motion in his Three Laws of Motion, which form the foundation of classical mechanics!
Types of Forces
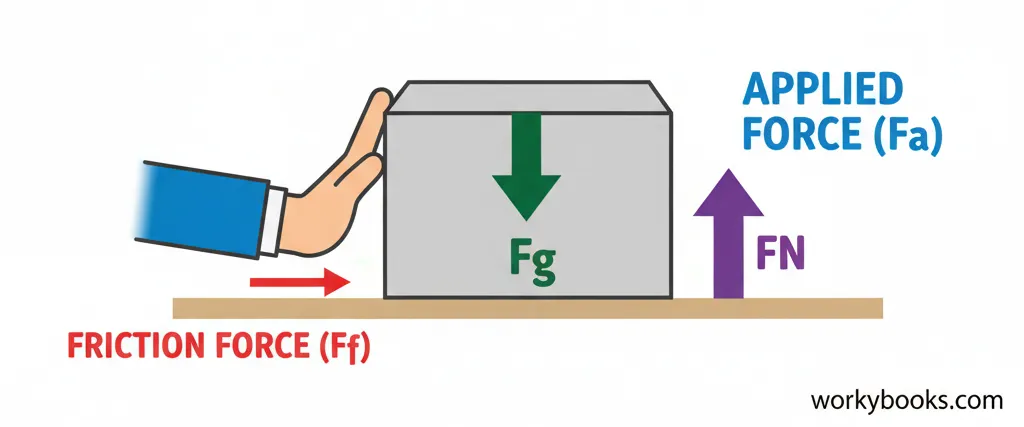
Many different forces can act on objects. Here are some common ones you'll encounter:
Applied Force (Fa)
A force that is applied to an object by a person or another object
Gravitational Force (Fg)
The force of attraction between objects with mass
Normal Force (FN)
The support force exerted on an object that is in contact with another stable object
Friction Force (Ff)
The force that opposes motion when two surfaces are in contact
These are just a few examples of forces. Others include tension force, spring force, and air resistance. When calculating net force, we need to consider all forces acting on an object.
Net Force Formula
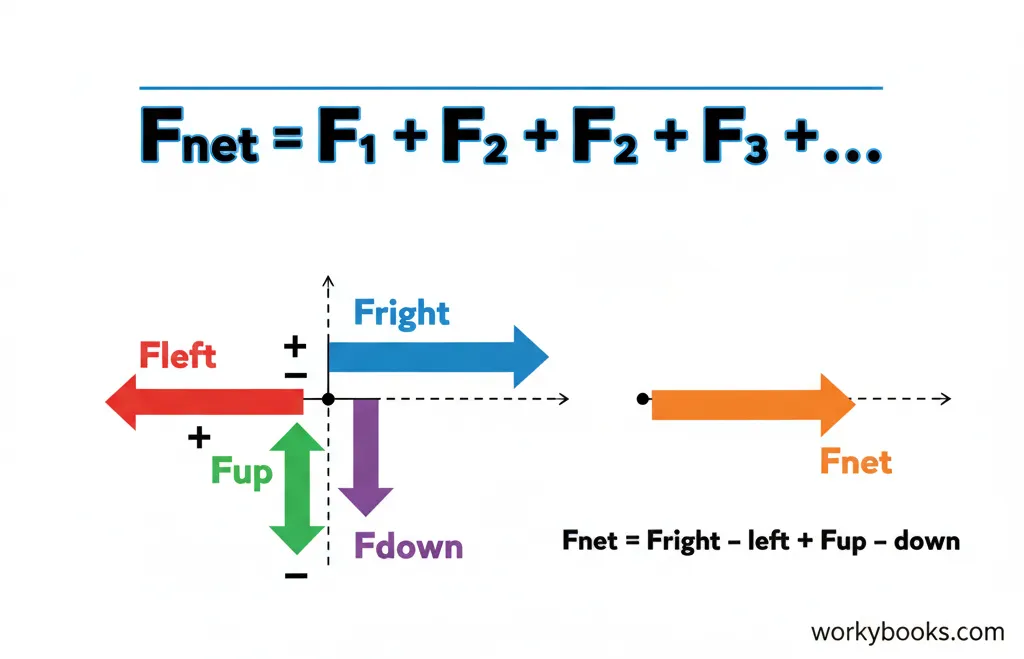
To calculate net force, we need to add up all the forces acting on an object. But it's not just simple addition - we must consider the direction of each force! Forces in opposite directions have opposite signs.
Here's how to calculate net force step by step:
Identify All Forces
List all forces acting on the object and their directions
Assign Signs
Choose a positive direction and assign signs accordingly
Add Forces
Add all forces together, considering their signs
Interpret Result
The result tells you the magnitude and direction of the net force
Remember: if forces are acting at angles, you might need to break them into components before adding. For now, we'll focus on forces acting along a straight line.
Net Force Examples
Let's look at some examples to understand how net force works in different situations:
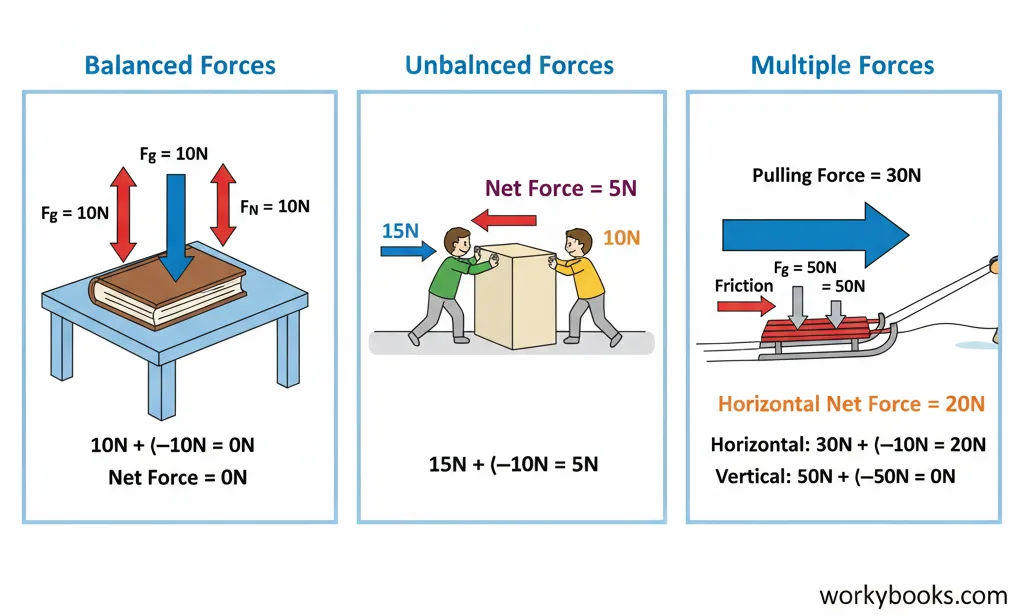
Example 1: Balanced Forces
A book rests on a table. The gravitational force pulling it down is 10N. The normal force pushing it up is also 10N.
The net force is zero, so the book doesn't move.
Example 2: Unbalanced Forces
Two people push a box. Person A pushes with 15N to the right. Person B pushes with 10N to the left.
The net force is 5N to the right, so the box moves to the right.
Example 3: Multiple Forces
A sled is pulled with 30N forward but experiences 10N of friction backward. Gravity pulls down with 50N and the ground pushes up with 50N.
Vertical: Fnet = (-50N) + 50N = 0N
The net force is 20N forward, so the sled accelerates forward.
Net Force Quiz
Test your knowledge about net force with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about net force:
Science Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about forces and motion!
Newton's Apple
The story of Isaac Newton discovering gravity when an apple fell on his head is probably exaggerated. He did think about gravity when seeing apples fall, but there's no evidence one hit him!
Zero Gravity Misconception
Astronauts in orbit experience weightlessness not because there's no gravity (gravity is about 90% as strong there), but because they're in constant freefall around Earth!
Strongest Force
The strongest fundamental force in nature is the strong nuclear force, which holds atomic nuclei together. It's about 100 times stronger than electromagnetism and much stronger than gravity!
Force Measurement
The newton (N) is the unit of force in the International System of Units. It's named after Isaac Newton. One newton is the force needed to accelerate one kilogram of mass at one meter per second squared.





