Temperature Gradient - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how heat flows from warmer to cooler places!
What is Temperature Gradient?
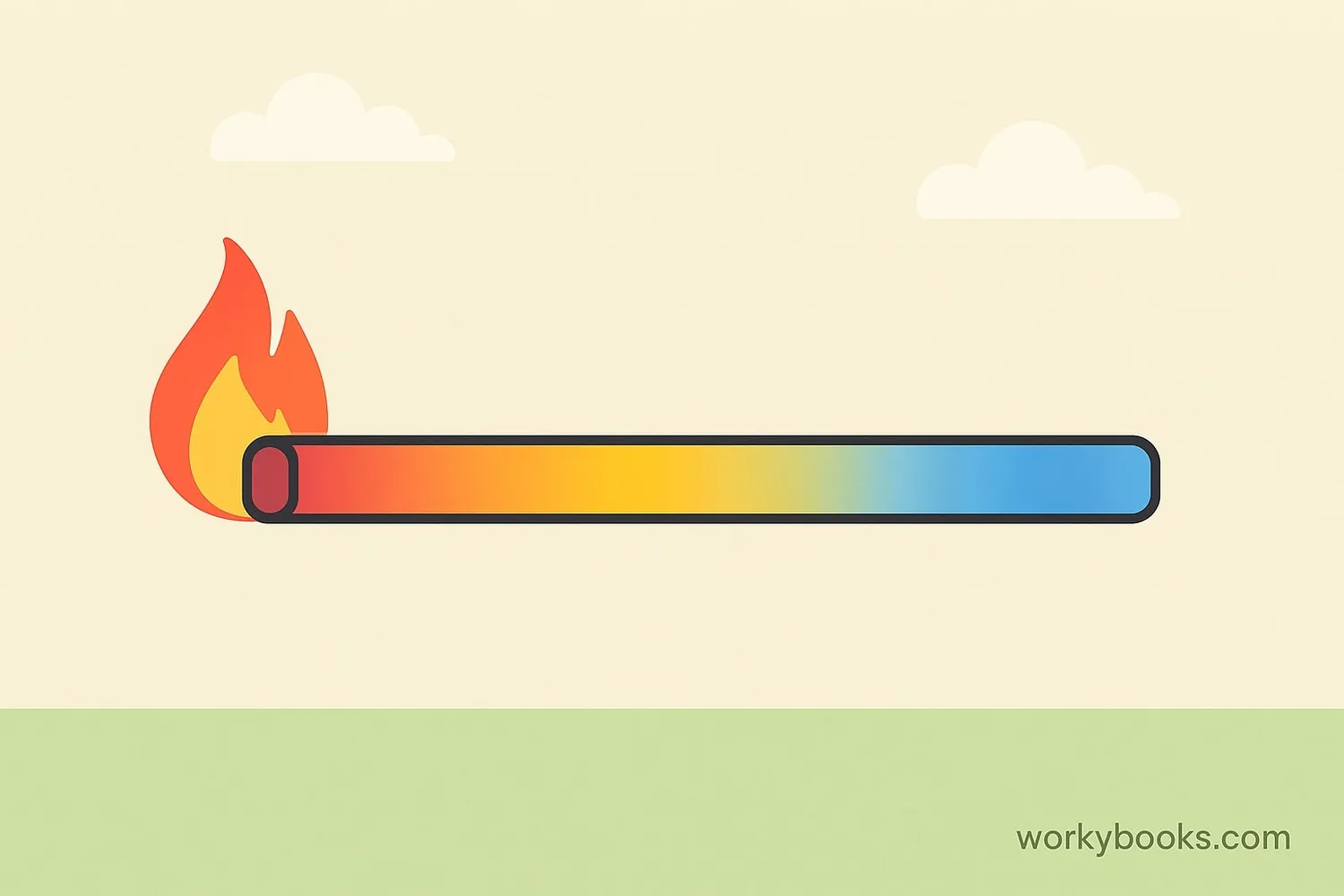
A temperature gradient is like a temperature slope! It's how temperature changes from one place to another. Imagine holding a metal rod with one end in a fire. The end in the fire gets hot, while the other end stays cooler. The difference in temperature along the rod is the temperature gradient.
Definition: A temperature gradient is the rate at which temperature changes over a distance. It shows how quickly temperature rises or falls as you move from one point to another. The steeper the gradient, the faster the temperature changes.
Science Fact!
Temperature gradients exist everywhere - from your hot cocoa cooling on the table to the difference between the equator and the poles!
How Heat Transfer Works
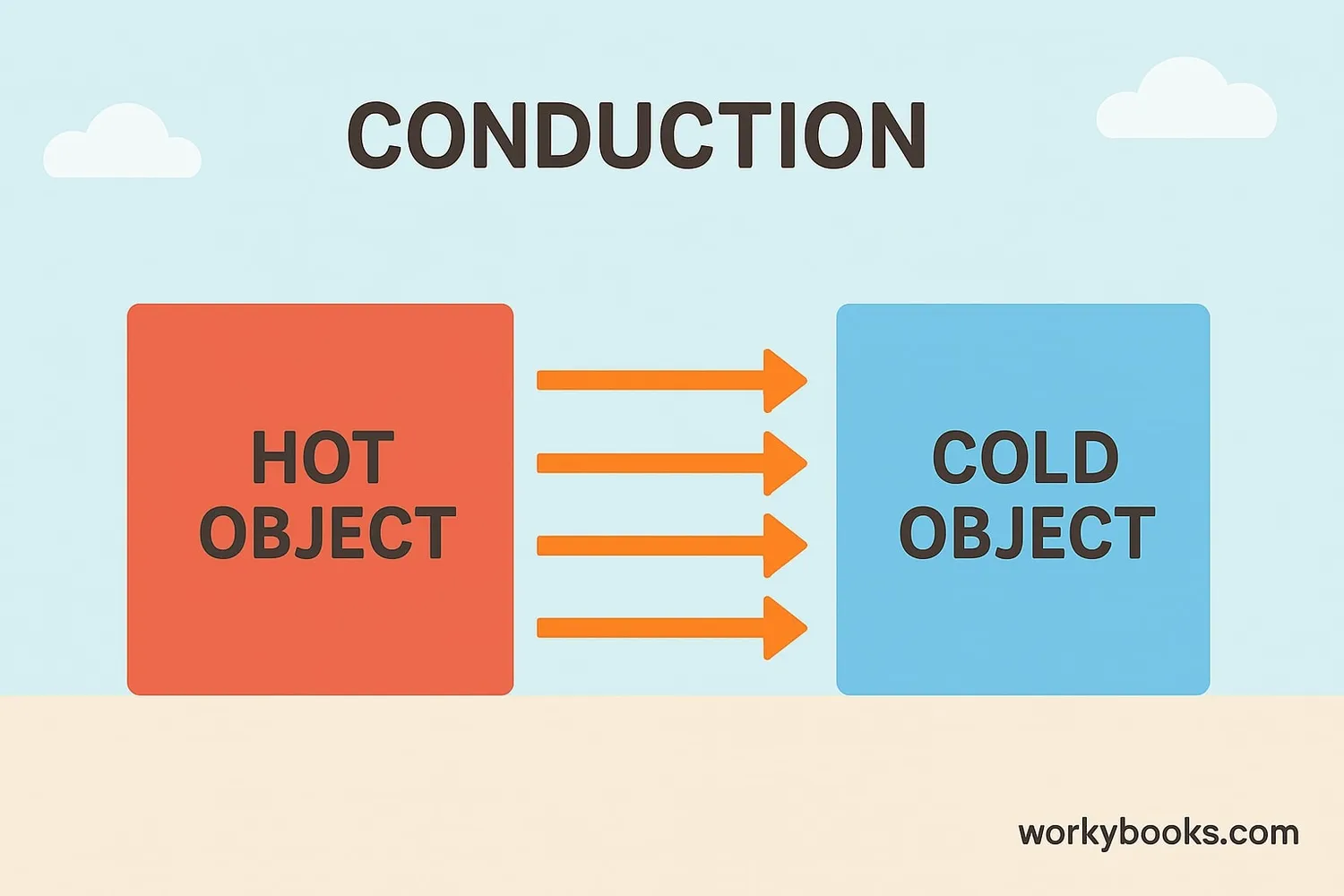
Heat always flows from warmer places to cooler places, and temperature gradients make this happen! This movement of heat is called heat transfer. There are three main ways heat moves:
Conduction
Heat moving through solid materials like metal
Convection
Heat moving through liquids and gases like air
Radiation
Heat traveling as invisible waves through space
The rate of heat flow depends on:
• The size of the temperature difference (gradient)
• The distance between hot and cold areas
• The material's thermal conductivity (how well it conducts heat)
Example: Metal has high thermal conductivity, so heat flows quickly through it. Wood has low conductivity, so it's a good insulator.
Heat Transfer Fact!
The steeper the temperature gradient (bigger difference over shorter distance), the faster heat flows!
Why Temperature Gradient Matters
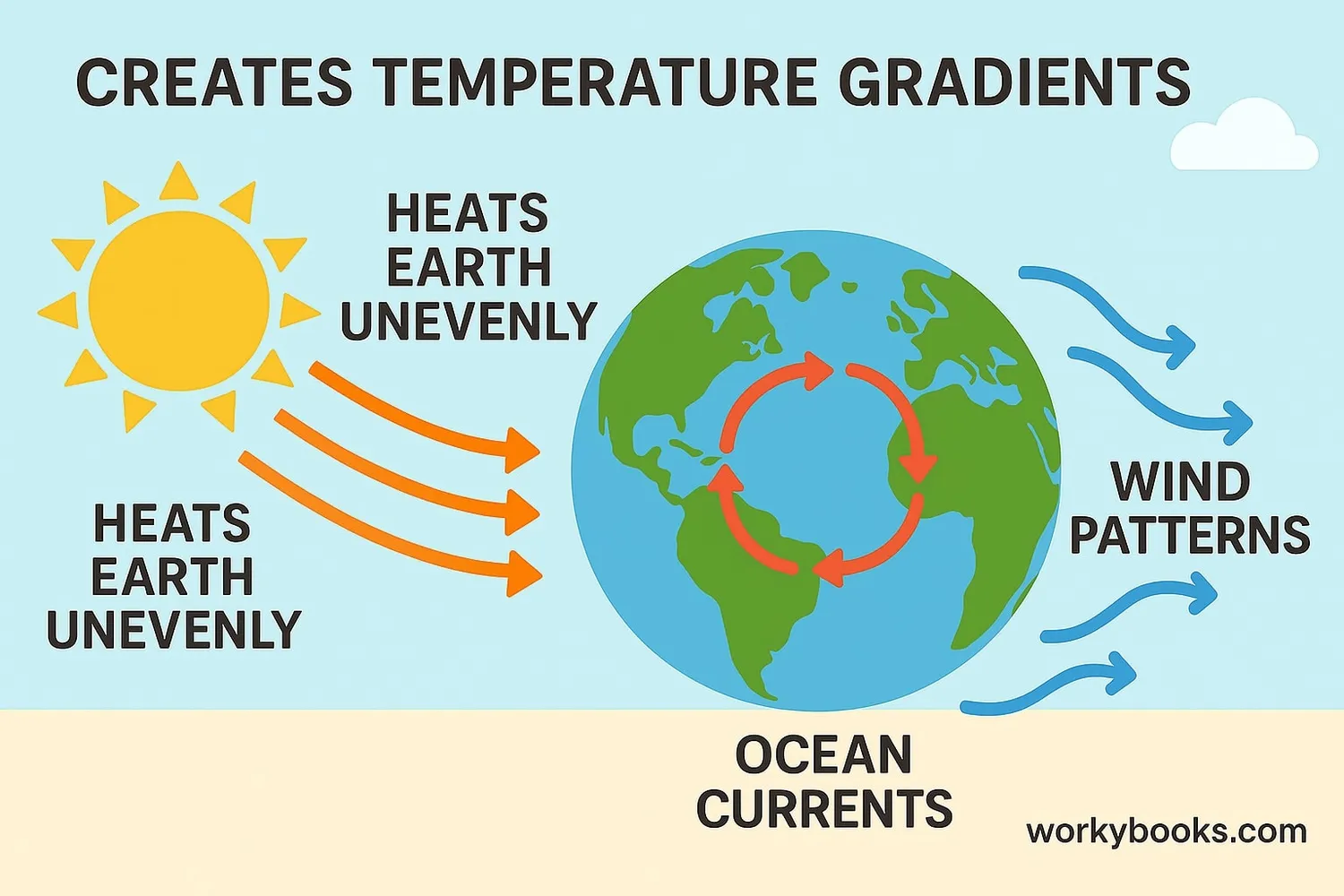
Temperature gradients are incredibly important in our world! They drive many natural processes and help us in everyday life:
Weather Patterns
Differences in temperature create winds and storms
Ocean Currents
Temperature gradients drive ocean circulation
Home Insulation
We use materials to reduce temperature gradients
Temperature gradients help explain:
• Why you feel cold when stepping out of a warm shower
• How refrigerators keep food cold
• Why metal feels colder than wood at room temperature
• How our planet maintains livable temperatures
Understanding temperature gradients helps scientists predict weather, design energy-efficient buildings, and even develop new technologies!
Temperature Gradient Quiz
Test your knowledge with this temperature gradient quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about temperature gradients:
Amazing Heat Facts
Discover some fascinating facts about temperature gradients and heat transfer:
Extreme Gradients
The steepest natural temperature gradient on Earth occurs in geysers like Old Faithful, where superheated water (over 200°C) meets cool air (20°C) in seconds!
Animal Adaptations
Arctic foxes use temperature gradients to their advantage! Their noses stay warm while their bodies are insulated, creating a gradient that helps prevent heat loss.
Solar Secrets
The sun's corona (outer atmosphere) is millions of degrees hotter than its surface! Scientists are still studying this mysterious temperature gradient reversal.
Super Materials
Aerogel, one of the best insulators ever made, can block extreme temperature gradients. A thin sheet can protect your hand from a blowtorch flame!





