California Drought - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Understanding water shortage, conservation, and impacts in California
What is a Drought?

A drought is a period of unusually dry weather that lasts long enough to cause water shortage. It happens when there's less rain or snow than normal over an extended period. Think of it like a water budget - when we use more water than nature provides, we have a water shortage.
California's climate is naturally dry, with most rain falling in just a few winter months. When those rainy months bring less precipitation than usual, it can lead to drought conditions that affect our water supply, agriculture, and environment.
Water Year Fact!
California's "water year" runs from October 1 to September 30. This helps water managers track precipitation and plan for dry periods.
Current California Drought Status
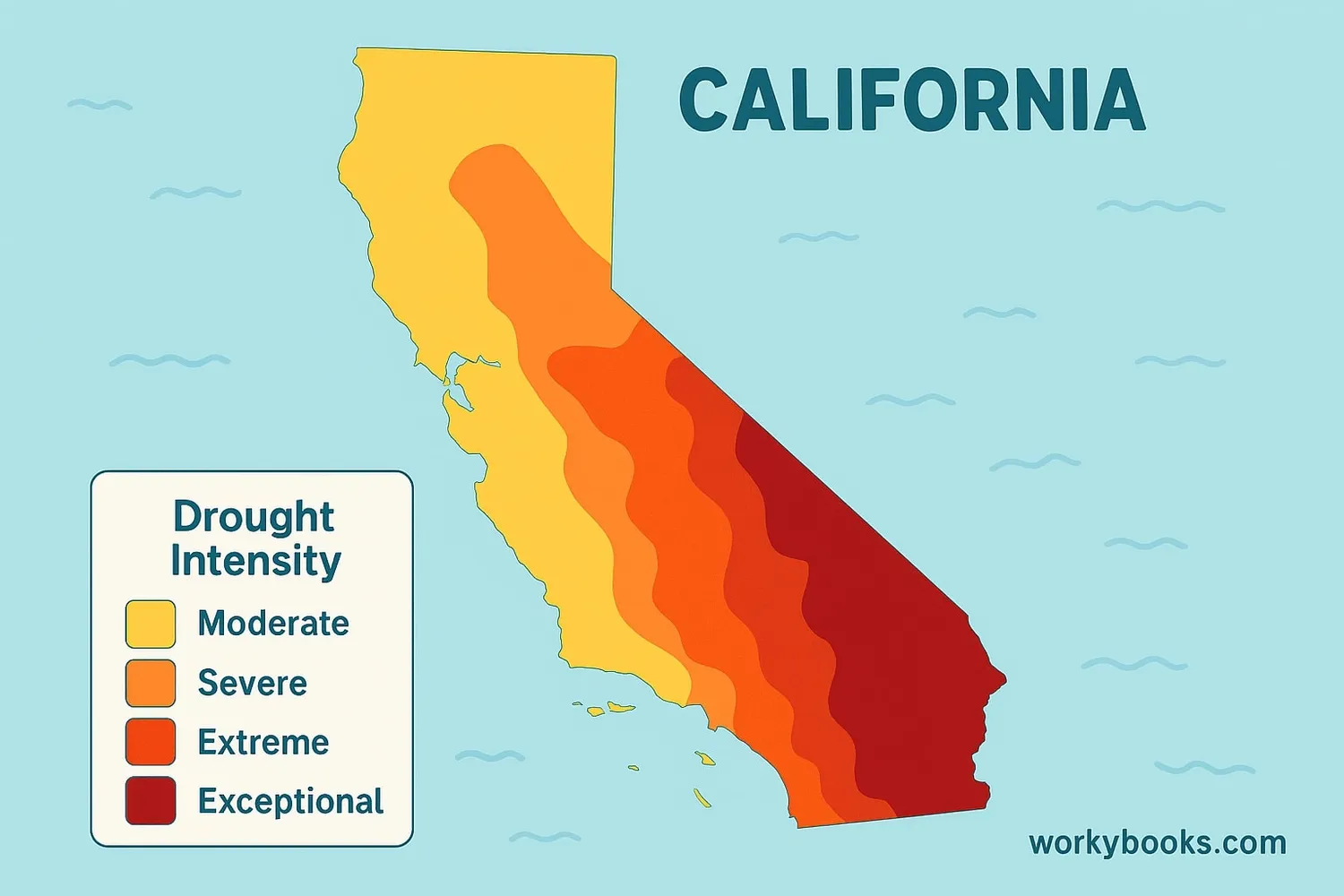
Scientists use special tools called "drought monitors" to track drought conditions across California. These maps show which areas are experiencing drought and how severe it is. The drought intensity is measured in categories:
Abnormally Dry
Some water shortage developing
Moderate Drought
Some damage to crops, water shortages
Severe Drought
Crop loss likely, water restrictions
Extreme Drought
Major crop losses, widespread water shortages
Exceptional Drought
Exceptional water shortages, emergency conditions
California's reservoir levels and groundwater supplies are carefully monitored during drought periods. Reservoirs are large human-made lakes that store water for dry times. Groundwater is water found underground in spaces between rocks and soil.
Reservoir Watch!
Major California reservoirs like Shasta, Oroville, and San Luis can hold millions of acre-feet of water. During drought, these levels drop significantly.
Drought Impacts

Drought affects many parts of our lives and environment. Here are some key impacts:
Agriculture
Farmers have less water for crops, which can lead to smaller harvests and higher food prices
Communities
Water restrictions may be implemented, limiting outdoor watering and encouraging conservation
Environment
Plants and wildlife suffer from lack of water, and wildfire risk increases
Extended droughts can also affect our economy and recreation. With less water in rivers and lakes, activities like fishing, boating, and swimming may be limited. Hydroelectric power generation can decrease, potentially affecting electricity supplies.
Water Conservation
Water conservation means using water wisely and avoiding waste. During droughts, conservation becomes especially important. Here are ways we can all help conserve water:
Indoor Savings
Take shorter showers, fix leaks, run full dishwasher and laundry loads
Outdoor Savings
Water plants early or late in the day, use drought-resistant plants, use mulch
Community Efforts
Support water recycling projects, report water waste, learn about local restrictions
Every drop counts! Small changes in our daily habits can add up to significant water savings. For example, turning off the tap while brushing your teeth can save up to 4 gallons of water each time.
Did You Know?
Outdoor watering accounts for about 50% of water use in many California homes. Reducing outdoor watering is one of the most effective conservation strategies.
California Drought Knowledge Check
Test your understanding of California's drought with this quiz. Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about California's drought:
Water Facts
Discover some interesting facts about water and droughts!
Water Use
The average Californian uses about 85 gallons of water per day at home. Outdoor watering accounts for nearly half of all residential water use!
Historical Drought
Tree ring studies show that California experienced a "megadrought" that lasted more than 200 years during the Middle Ages, from the 9th to 12th centuries!
Sierra Snowpack
The Sierra Nevada snowpack provides about 30% of California's water supply as it melts slowly through spring and summer. Measuring snowpack helps predict water availability.
Conservation Success
During the 2012-2016 drought, Californians reduced urban water use by nearly 25%, saving enough water to supply 6.5 million people for a year!





