Climate and Biomes - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Understanding Earth's Diverse Ecosystems and How Climate Shapes Them
What are Biomes?
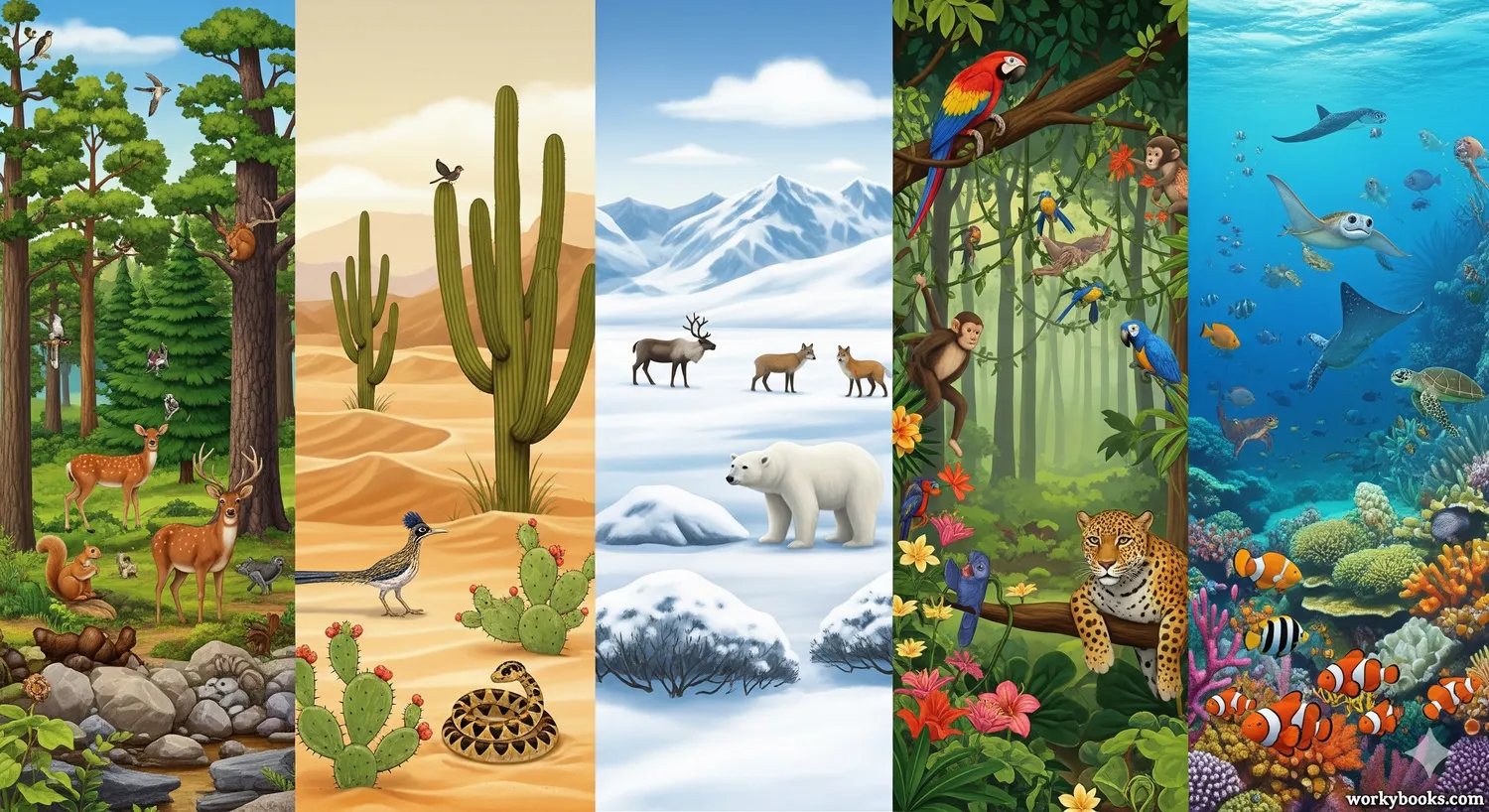

A biome is a large community of plants and animals that occupies a distinct region. Biomes are often defined by their climate, geography, and the types of organisms that live there.
Think of biomes as Earth's different neighborhoods! Each biome has its own special characteristics, like the plants that grow there, the animals that call it home, and the weather patterns it experiences.
Science Fact!
There are two main types of biomes: terrestrial (land-based) and aquatic (water-based). Each type has several smaller categories with unique features.
How Climate Affects Biomes
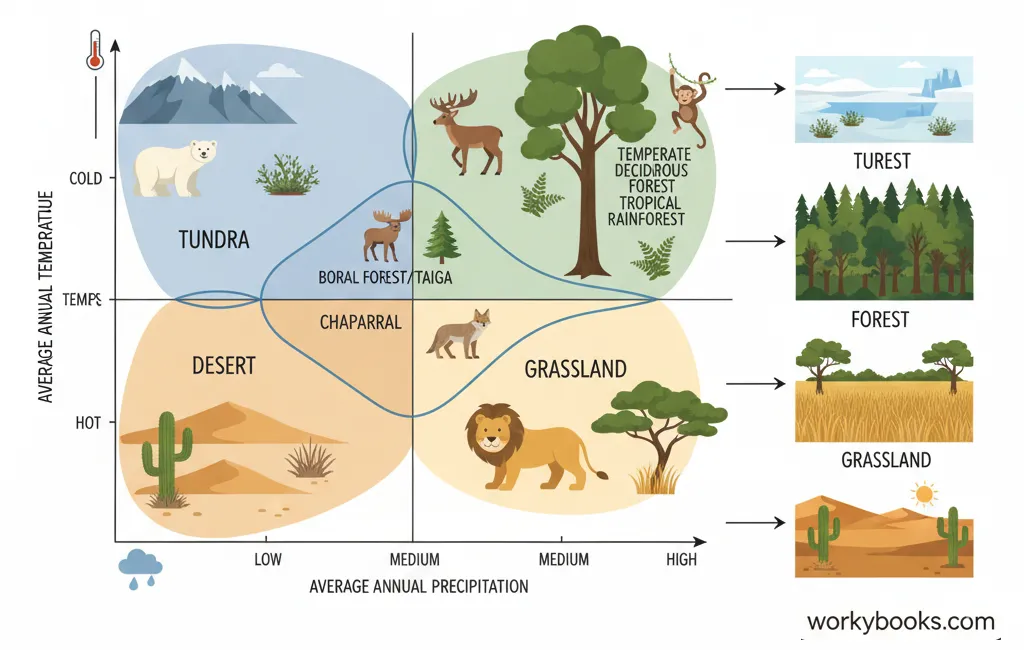
Climate is the long-term pattern of weather in a particular area. It includes factors like temperature, precipitation, humidity, and wind patterns. Climate plays a huge role in determining what types of plants and animals can survive in a region.
Temperature
Determines what plants can grow and what animals can survive
Precipitation
Amount of rain or snow affects water availability
Seasons
Seasonal changes affect plant growth and animal behavior
Sunlight
Amount of sunlight affects photosynthesis and temperature
Adaptations
Plants and animals develop special features to survive their climate
For example, cacti have adapted to desert biomes by developing thick stems to store water and spines to protect themselves. In contrast, trees in rainforests have broad leaves to capture sunlight in the dense forest canopy.
Terrestrial Biomes
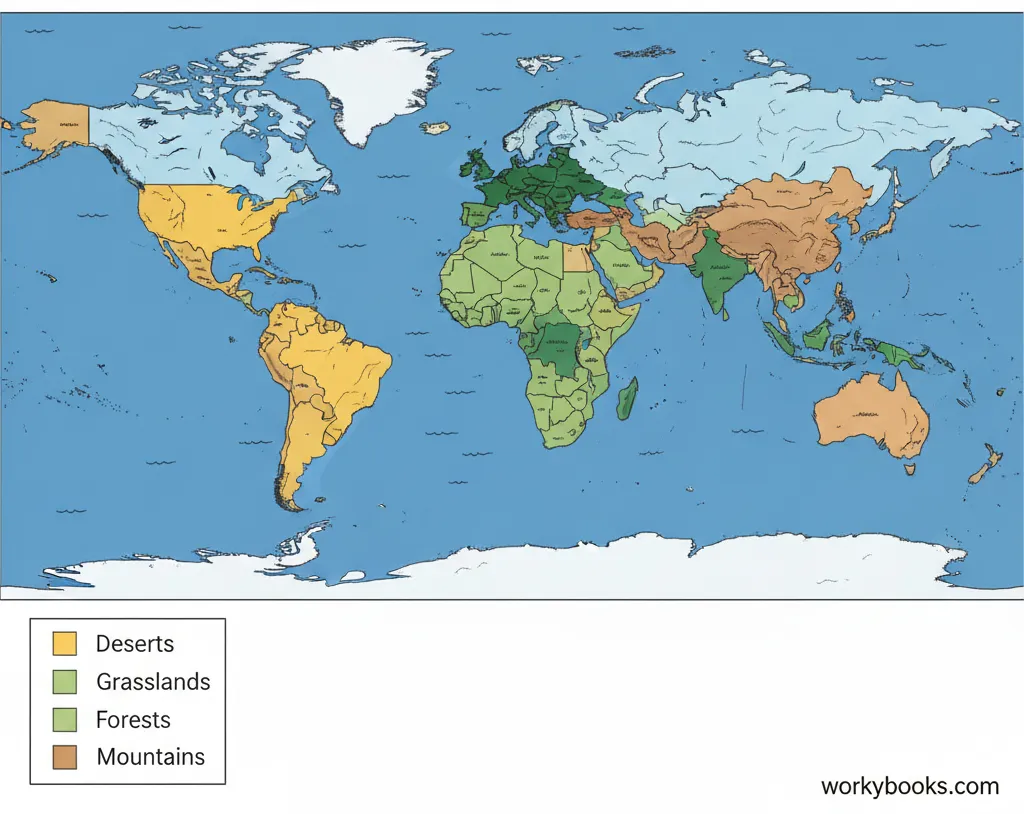
Terrestrial biomes are land-based ecosystems. There are several major types of terrestrial biomes, each with distinct climate conditions and life forms:
Desert
Very dry with less than 25 cm of rain per year. Plants include cacti and shrubs. Animals are often nocturnal to avoid heat.
Forest
Includes tropical, temperate, and boreal forests. High rainfall supports many trees and diverse animal life.
Grassland
Open areas dominated by grasses. Includes prairies and savannas. Home to grazing animals and their predators.
Tundra
Cold, treeless biome with permafrost. Short growing season. Animals have thick fur and fat for insulation.
Alpine
Found in mountainous regions worldwide. Conditions become more extreme with higher elevation.
Each terrestrial biome has plants and animals specially adapted to its particular climate conditions. These adaptations help organisms survive and thrive in their environment.
Aquatic Biomes

Aquatic biomes are water-based ecosystems. They are divided into two main categories: freshwater and marine (saltwater) biomes. Water temperature, sunlight penetration, and nutrient availability determine what life forms can survive in these biomes.
Freshwater Biomes
Includes lakes, rivers, streams, and ponds. Have low salt concentration (less than 1%).
Marine Biomes
Oceans and seas with high salt concentration (about 3.5%). Cover about 71% of Earth's surface.
Estuaries
Where freshwater meets saltwater. Rich in nutrients and support diverse life forms.
Aquatic biomes are incredibly important to life on Earth. They regulate climate, provide food, and are home to countless species. Coral reefs, found in marine biomes, are among the most biodiverse ecosystems on the planet.
Did You Know?
The ocean is the largest biome on Earth, covering about 71% of the planet's surface. It's home to the largest animal that has ever lived—the blue whale!
Climate and Biomes Quiz
Test your knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned about climate and biomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about climate and biomes:
Science Facts About Climate and Biomes
Discover some fascinating facts about climate and biomes!
Rainforest Diversity
Tropical rainforests cover only about 6% of Earth's surface but contain more than half of the world's plant and animal species! This makes them the most biodiverse terrestrial biome.
Extreme Temperatures
Desert biomes can experience extreme temperature changes between day and night. The Sahara Desert can reach 50°C (122°F) during the day but drop to near freezing at night!
Ocean Dominance
The ocean is the largest biome on Earth, covering about 71% of the planet's surface. It's divided into many zones based on depth and light availability, each with unique life forms.
Permafrost
The tundra biome has a layer of permanently frozen soil called permafrost. This frozen layer prevents trees from growing and affects how water drains through the soil.





