Climate Zones - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Understanding Earth's Different Climate Regions and Their Characteristics
What Are Climate Zones?
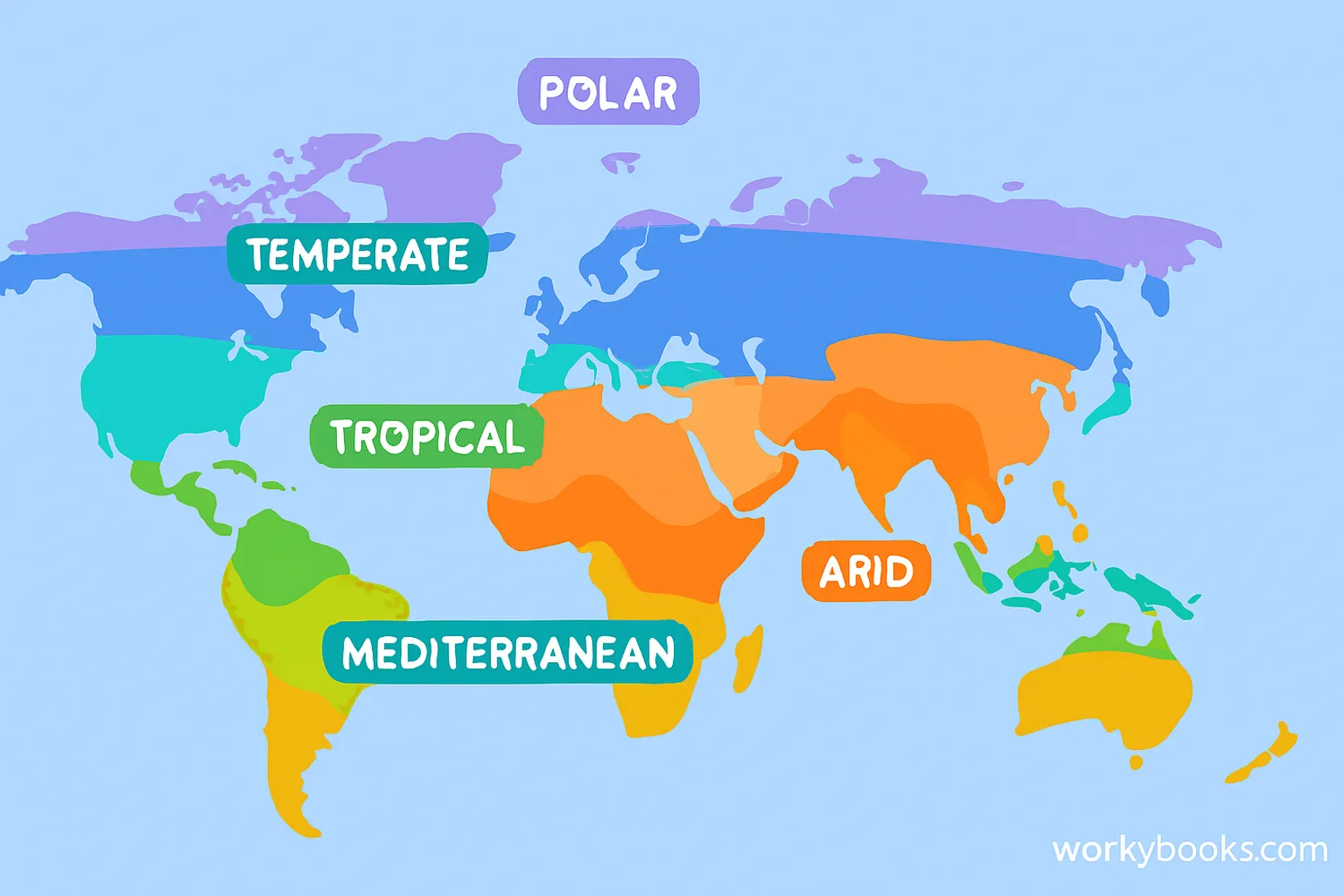
Climate zones are large regions of Earth that share similar weather patterns, temperatures, and amounts of rainfall throughout the year. Think of them as Earth's different "weather personalities"!
These zones help scientists and geographers understand how weather works in different parts of our planet and how plants, animals, and people have adapted to live in these varied environments.
Science Fact!
Earth's climate zones exist primarily because of how sunlight hits different parts of our planet. The equator receives direct sunlight year-round, while the poles receive indirect sunlight, creating temperature differences that drive climate patterns.
Koppen Climate Classification
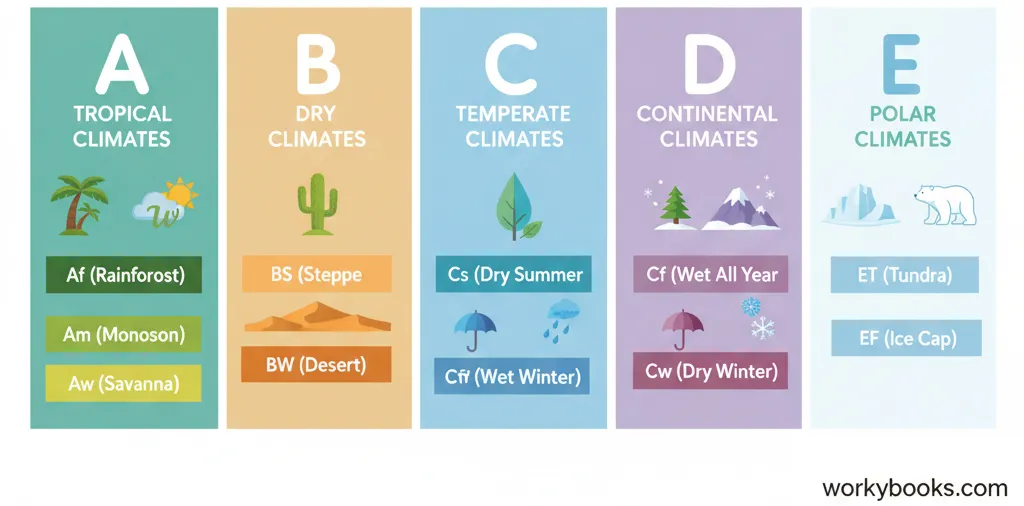
The most widely used system for classifying climate zones is called the Koppen Climate Classification, developed by German scientist Wladimir Koppen in the early 1900s. This system divides climates into five main types based on temperature, precipitation, and seasonal patterns:
Tropical
Warm temperatures year-round with high rainfall
Dry/Arid
Little rainfall with potential for high evaporation
Temperate
Mild climates with distinct seasons
Continental
Large temperature differences between seasons
Polar
Extremely cold temperatures year-round
Each main category is further divided into more specific subcategories based on precipitation patterns and temperature variations. This system helps scientists communicate about climate patterns consistently around the world.
Tropical Climate Zone

Tropical climate zones are found near the equator, between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn. These regions experience warm temperatures year-round, with average temperatures staying above 18°C (64°F) every month.
Characteristics:
- High temperatures throughout the year
- High humidity and abundant rainfall
- Little temperature variation between seasons
- Home to rainforests and diverse ecosystems
Where to find tropical climates:
- The Amazon Basin in South America
- Central Africa (Congo Basin)
- Southeast Asia (Indonesia, Malaysia)
- Northern Australia
- Central America and the Caribbean
Tropical zones are known for their incredible biodiversity. The constant warm temperatures and abundant rainfall create perfect conditions for plants to grow year-round, supporting diverse animal life.
Temperate Climate Zone

Temperate climate zones are found between the tropical and polar zones, roughly between 30° and 60° latitude in both hemispheres. These regions experience four distinct seasons with moderate temperatures that change throughout the year.
Characteristics:
- Four distinct seasons: spring, summer, autumn, winter
- Moderate rainfall distributed throughout the year
- Temperature variations between seasons
- Deciduous forests that lose leaves in winter
Where to find temperate climates:
- Most of Europe
- Eastern North America
- Eastern Asia (China, Korea, Japan)
- Southern Australia
- Southern South America
The Mediterranean climate is a special type of temperate climate characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. This climate is found in regions like Southern California, the Mediterranean region, parts of Australia, and South Africa.
Polar Climate Zone

Polar climate zones are found near the North and South Poles, within the Arctic and Antarctic Circles. These regions experience extremely cold temperatures year-round, with long, harsh winters and short, cool summers.
Characteristics:
- Very cold temperatures throughout the year
- Permanently frozen ground (permafrost)
- Long, dark winters with periods of 24-hour darkness
- Short summers with periods of 24-hour daylight
- Low precipitation, mostly in the form of snow
Where to find polar climates:
- Antarctica
- Greenland
- Northern parts of Canada, Alaska, and Russia
- Arctic Ocean regions
Despite the challenging conditions, polar regions are home to specially adapted plants and animals. These include polar bears, Arctic foxes, penguins, seals, and various types of mosses and lichens that can survive the extreme cold.
Arid Climate Zone

Arid climate zones, also known as desert climates, are characterized by extremely low rainfall—less than 250 mm (10 inches) per year. These regions can be either hot or cold, but all share the common feature of very little precipitation.
Characteristics:
- Very low rainfall
- High evaporation rates
- Large temperature differences between day and night
- Sparse vegetation adapted to dry conditions
- Specialized animal life
Where to find arid climates:
- Sahara Desert in Africa
- Arabian Desert in the Middle East
- Gobi Desert in Asia
- Great Basin Desert in North America
- Atacama Desert in South America
Plants and animals in arid zones have special adaptations to conserve water. Cacti store water in their stems, many animals are nocturnal to avoid the heat of the day, and some creatures can obtain all the water they need from their food.
Did You Know?
The Atacama Desert in Chile is the driest place on Earth. Some areas of this desert have not received rainfall for over 400 years!
Climate Zones Quiz
Test your knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned about climate zones.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about climate zones:
Science Facts About Climate Zones
Discover some fascinating facts about climate zones and Earth's diverse regions!
Microclimates
Within larger climate zones, small areas can have their own "microclimates" with different weather patterns. Cities often create urban heat islands that are warmer than surrounding rural areas, while valleys might be cooler than nearby hillsides.
Altitude Effects
In tropical regions, you can experience multiple climate zones by traveling up a mountain. The base might be hot and humid like a tropical rainforest, but the peak could be as cold as a polar region, even though you're near the equator!
Ocean Current Influence
Ocean currents dramatically affect climate zones. The Gulf Stream carries warm water from the tropics to Northern Europe, making countries like the UK much warmer than other places at similar latitudes, like Labrador in Canada.
Climate Zone Shift
Due to climate change, climate zones are shifting poleward at an average rate of about 1.25 miles per year. This means plants and animals are having to adapt to changing conditions or move to new areas to survive.





