Atmospheric Pressure - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how air pressure affects our weather and daily life!
What is Atmospheric Pressure?
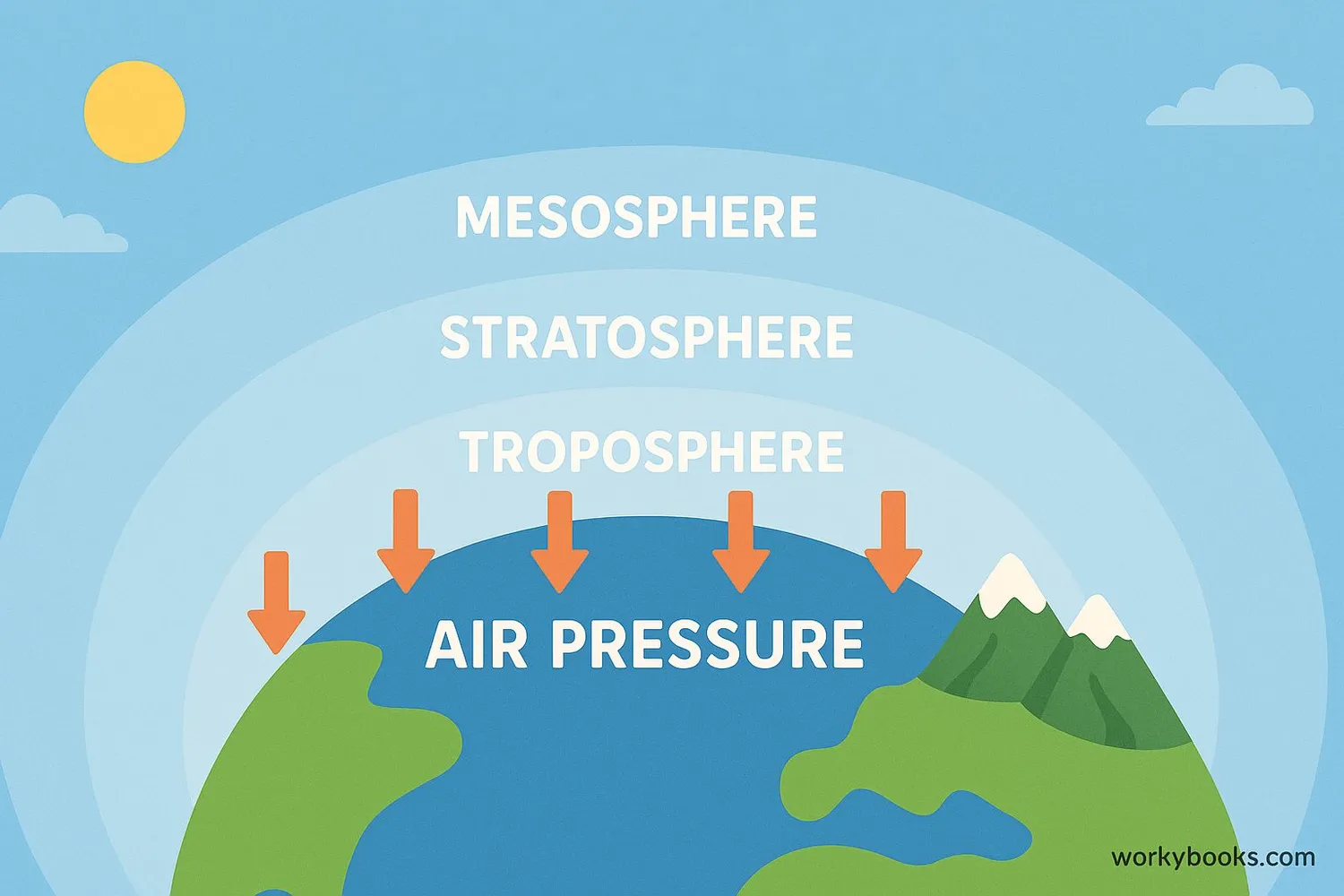
Atmospheric pressure is the weight of the air pressing down on Earth's surface. Imagine the atmosphere as a giant ocean of air above us. Just like water in the ocean presses down with its weight, the air above us does the same thing!
Our atmosphere is made of gases like nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. Gravity pulls these gases toward Earth, creating pressure. At sea level, this pressure is about 14.7 pounds per square inch - that's like having a small bowling ball pressing on every square inch of your body!
Air Pressure Fact!
The entire atmosphere weighs about 5.5 quadrillion tons! That's 5,500,000,000,000,000 tons!
How Air Pressure Works
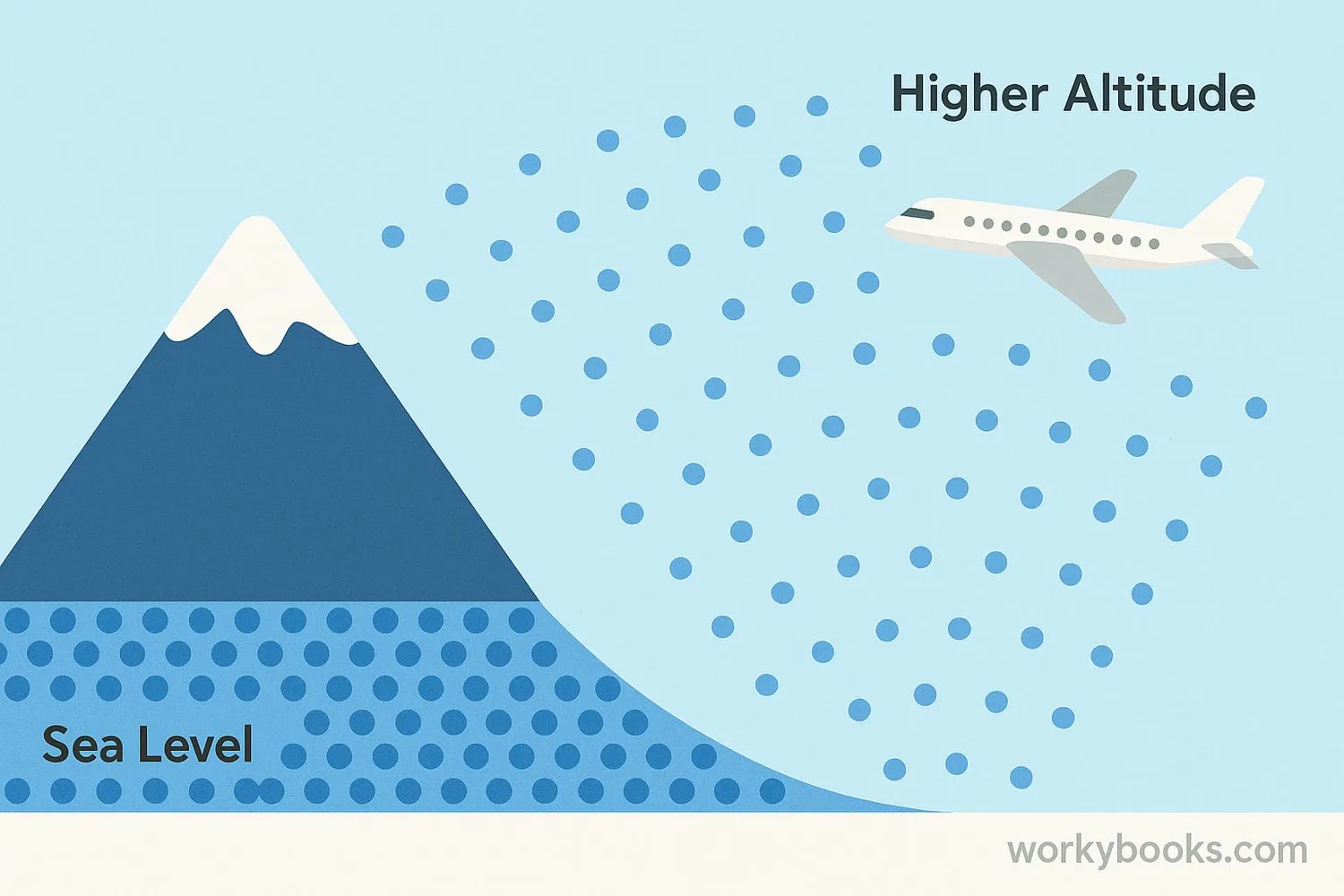
Air pressure works because air has weight and is pulled toward Earth by gravity. Here are the key things to understand:
Air Has Weight
Air molecules have mass and are pulled down by gravity
Altitude Effect
Pressure decreases as you go higher because there's less air above you
Temperature Effect
Warm air rises (low pressure), cold air sinks (high pressure)
Weather Systems
High pressure brings sunny weather, low pressure brings clouds and storms
At higher altitudes like mountaintops, air pressure is much lower than at sea level. That's why it's harder to breathe on mountains - there are fewer air molecules in each breath you take!
Mountain Fact!
At the top of Mount Everest, air pressure is only one-third of what it is at sea level!
Measuring Air Pressure
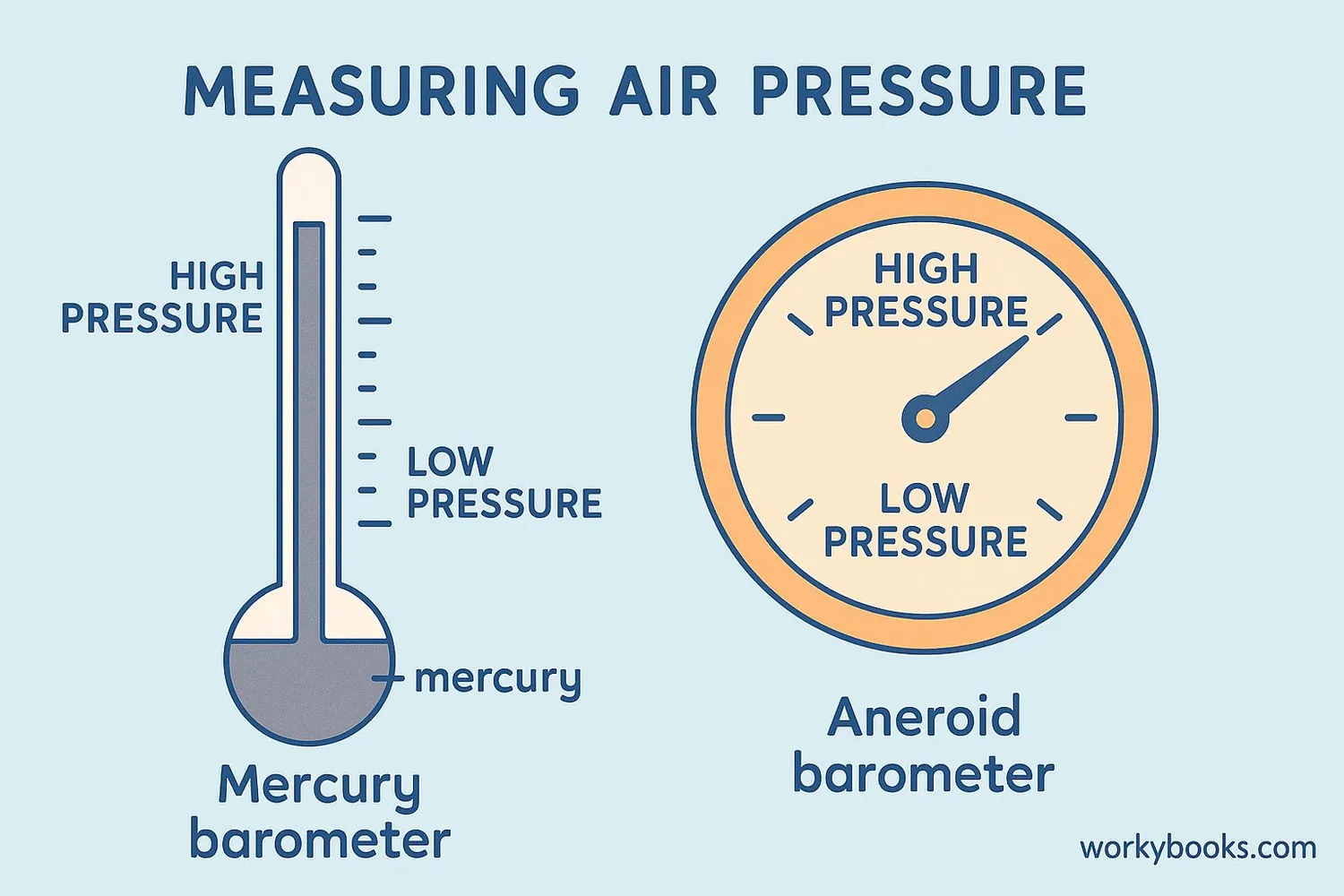
Scientists measure air pressure with an instrument called a barometer. There are two main types:
Mercury Barometer
Uses a glass tube filled with mercury. Air pressure pushes on the mercury, causing it to rise or fall in the tube.
Aneroid Barometer
Uses a small metal box that expands or contracts with pressure changes, moving a needle on a dial.
Air pressure is measured in different units:
• Millibars (mb) - used by scientists and meteorologists
• Inches of mercury (inHg) - often used in weather reports
• Pounds per square inch (psi) - used for some technical measurements
Normal sea-level pressure is about 1013 mb or 29.92 inHg. When pressure drops below this, it often means stormy weather is coming!
Why Air Pressure Matters
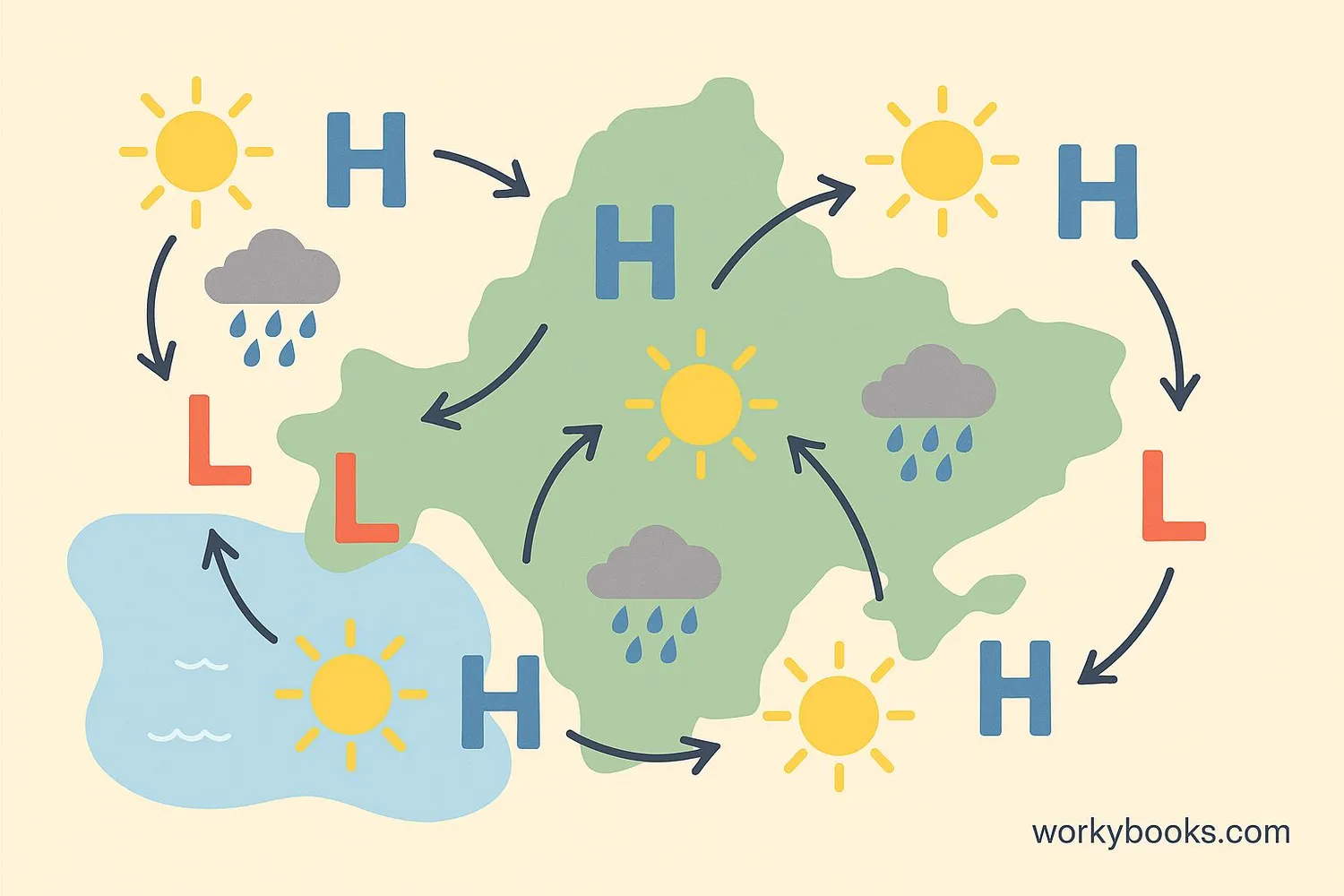
Atmospheric pressure is incredibly important for understanding and predicting weather:
Weather Prediction
Rising pressure usually means improving weather, falling pressure often means storms are coming
Wind Creation
Wind is air moving from high pressure areas to low pressure areas
Altitude Effects
Pressure changes affect how we breathe at high altitudes
High pressure systems:
• Bring clear, sunny skies
• Have air sinking toward the ground
• Usually have light winds
Low pressure systems:
• Bring cloudy, stormy weather
• Have air rising from the ground
• Often have stronger winds
The difference in pressure between areas creates pressure gradients, which determine how strong the winds will be.
Atmospheric Pressure Quiz
Test your knowledge with this air pressure quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about atmospheric pressure:
Fun Air Pressure Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about atmospheric pressure!
Deep Ocean Pressure
At the deepest point in the ocean (Challenger Deep), water pressure is over 1,000 times greater than at sea level - equivalent to having 50 jumbo jets stacked on top of you!
Space Suit Pressure
Space suits maintain air pressure equivalent to being at 30,000 feet altitude. Without them, the near-vacuum of space would cause body fluids to boil at room temperature!
Bird Breathing
Birds have special air sacs that help them breathe at high altitudes where pressure is low. Bar-headed geese fly over the Himalayas at 29,000 feet where oxygen is scarce!
Record Low Pressure
The lowest sea-level pressure ever recorded was 870 mb during Typhoon Tip in 1979. Normal pressure is 1013 mb - this was like removing 14% of the atmosphere's weight!




