Subduction Zones - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how Earth's tectonic plates collide to create mountains, volcanoes, and earthquakes!
What is a Subduction Zone?
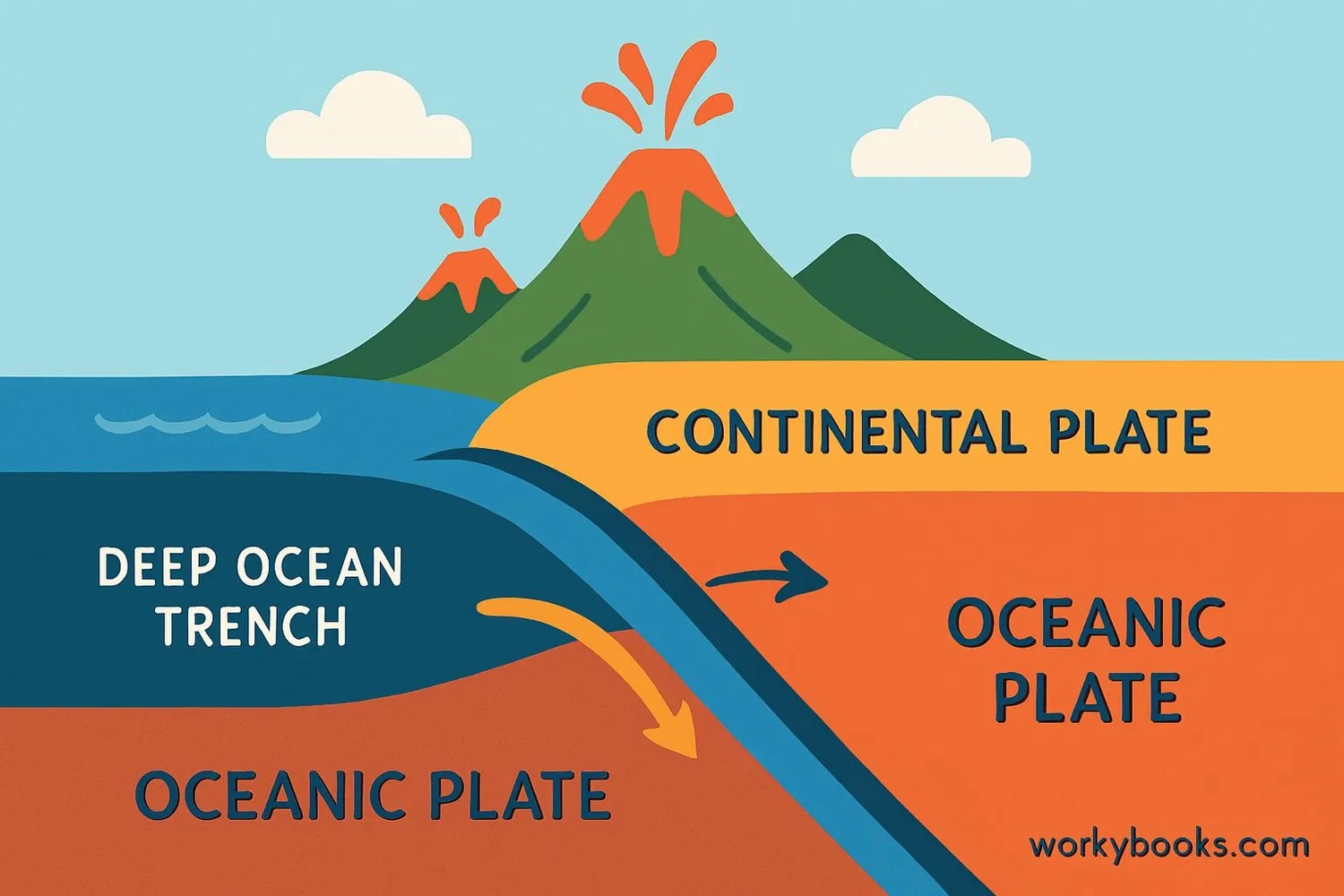
A subduction zone is a place where two of Earth's tectonic plates collide, and one plate slides beneath the other into the Earth's interior. This happens at convergent boundaries where plates are moving toward each other.
Imagine Earth's crust is like a giant jigsaw puzzle made of huge rock plates. When two plates meet, sometimes one plate is forced down into the hot mantle below. This process is called subduction, and it creates some of Earth's most dramatic geological features!
Earth Science Fact!
The deepest place on Earth, the Mariana Trench, is formed by a subduction zone and is nearly 11 kilometers (7 miles) deep!
How Subduction Zones Work
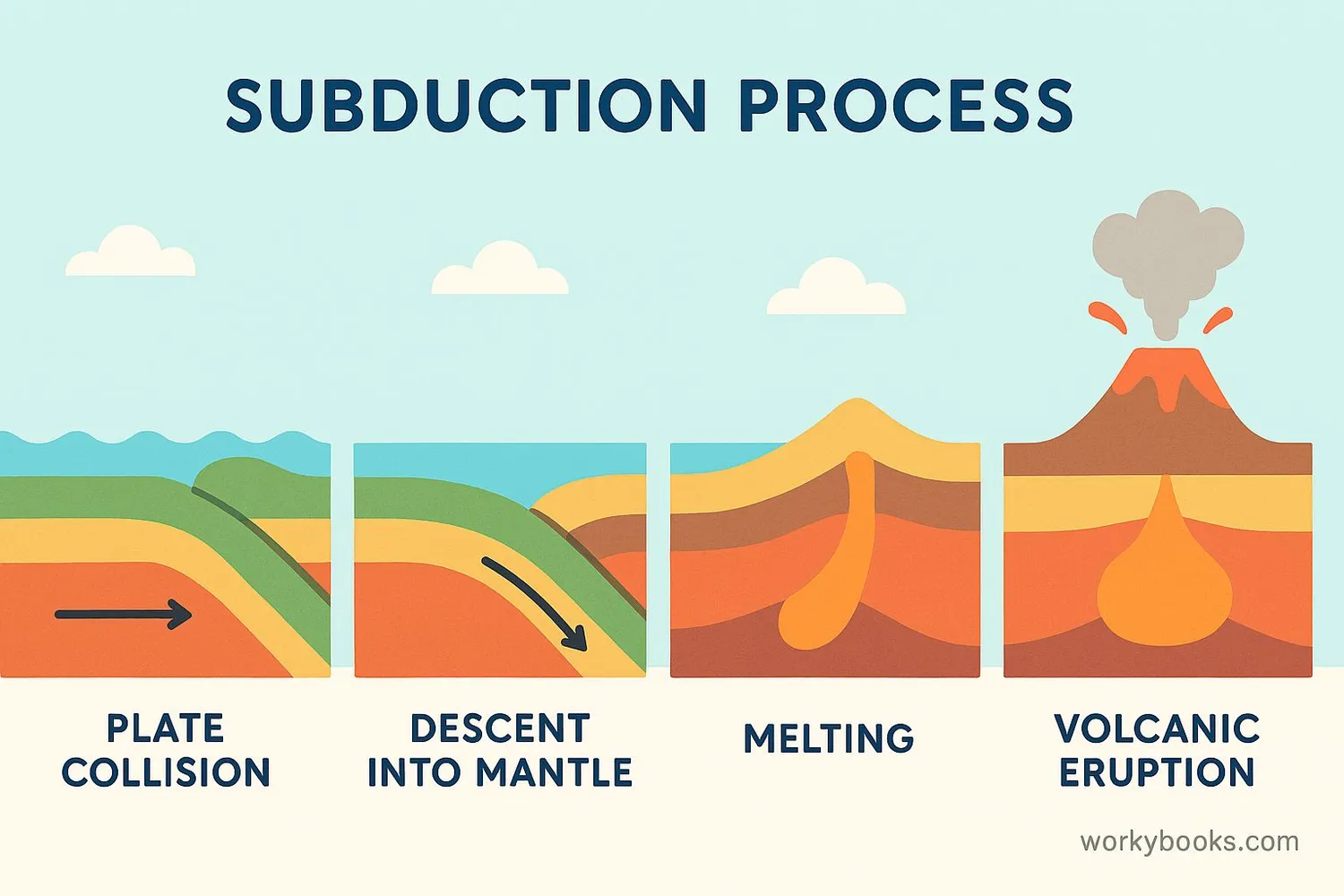
Subduction zones are Earth's recycling centers where old crust is destroyed and recycled back into the mantle. Here's how this amazing geological process works:
Plate Collision
Two tectonic plates move toward each other at a convergent boundary
Denser Plate Sinks
The denser oceanic plate slides beneath the less dense continental plate
Trench Formation
A deep oceanic trench forms where the plate bends downward
Melting Begins
The sinking plate heats up and releases water, causing rock above to melt
Magma Rises
Molten rock (magma) rises toward the surface, creating volcanoes
The entire process is driven by Earth's internal heat and the slow movement of tectonic plates. Subduction zones are where Earth's crust is recycled back into the mantle over millions of years.
Plate Speed Fact!
Tectonic plates move at about the same speed your fingernails grow - 2-5 centimeters per year!
Effects & Importance of Subduction Zones
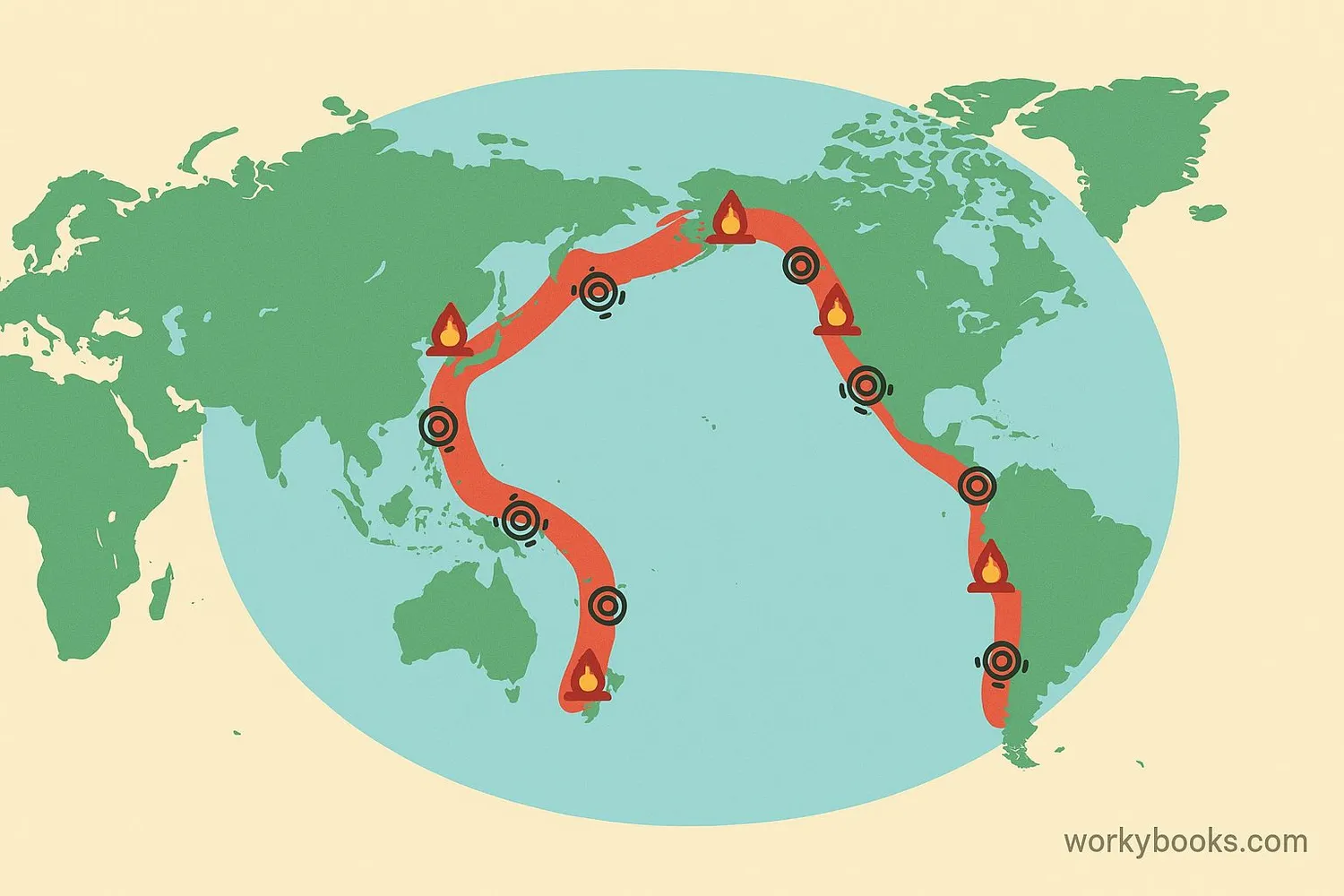
Subduction zones create some of Earth's most spectacular and dangerous geological features. They're incredibly important in shaping our planet:
Volcanic Activity
Most of Earth's active volcanoes form above subduction zones
Earthquakes
Powerful earthquakes occur as plates grind against each other
Mountain Building
Continental collisions create massive mountain ranges
The Pacific Ring of Fire is the most famous subduction zone area, surrounding the Pacific Ocean. This region contains:
• 75% of the world's active volcanoes
• 90% of Earth's earthquakes
• Deep ocean trenches
• Volcanic island arcs like Japan and the Philippines
Subduction zones are also where Earth recycles its crust - old oceanic crust is carried back into the mantle where it melts and can eventually form new crust.
Subduction Zone Quiz
Test your knowledge about subduction zones with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about subduction zones:
Earth Science Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about subduction zones and plate tectonics!
Deepest Point
The Challenger Deep in the Mariana Trench is the deepest known point in Earth's oceans, created by subduction. It's so deep that Mount Everest would fit inside with over a mile to spare!
Ring of Fire
The Pacific Ring of Fire is a 40,000 km (25,000 mile) horseshoe-shaped zone with 452 volcanoes - that's 75% of the world's active and dormant volcanoes!
Powerful Quakes
The strongest earthquake ever recorded (9.5 magnitude in Chile, 1960) occurred at a subduction zone. Subduction zones produce the most powerful earthquakes on Earth.
Earth's Recycling
Subduction zones recycle Earth's crust! Oceanic crust created at mid-ocean ridges is eventually destroyed in subduction zones, completing a cycle that takes about 200 million years.





