Photosynthesis Equation - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Understanding How Plants Make Food from Sunlight
What is Photosynthesis?
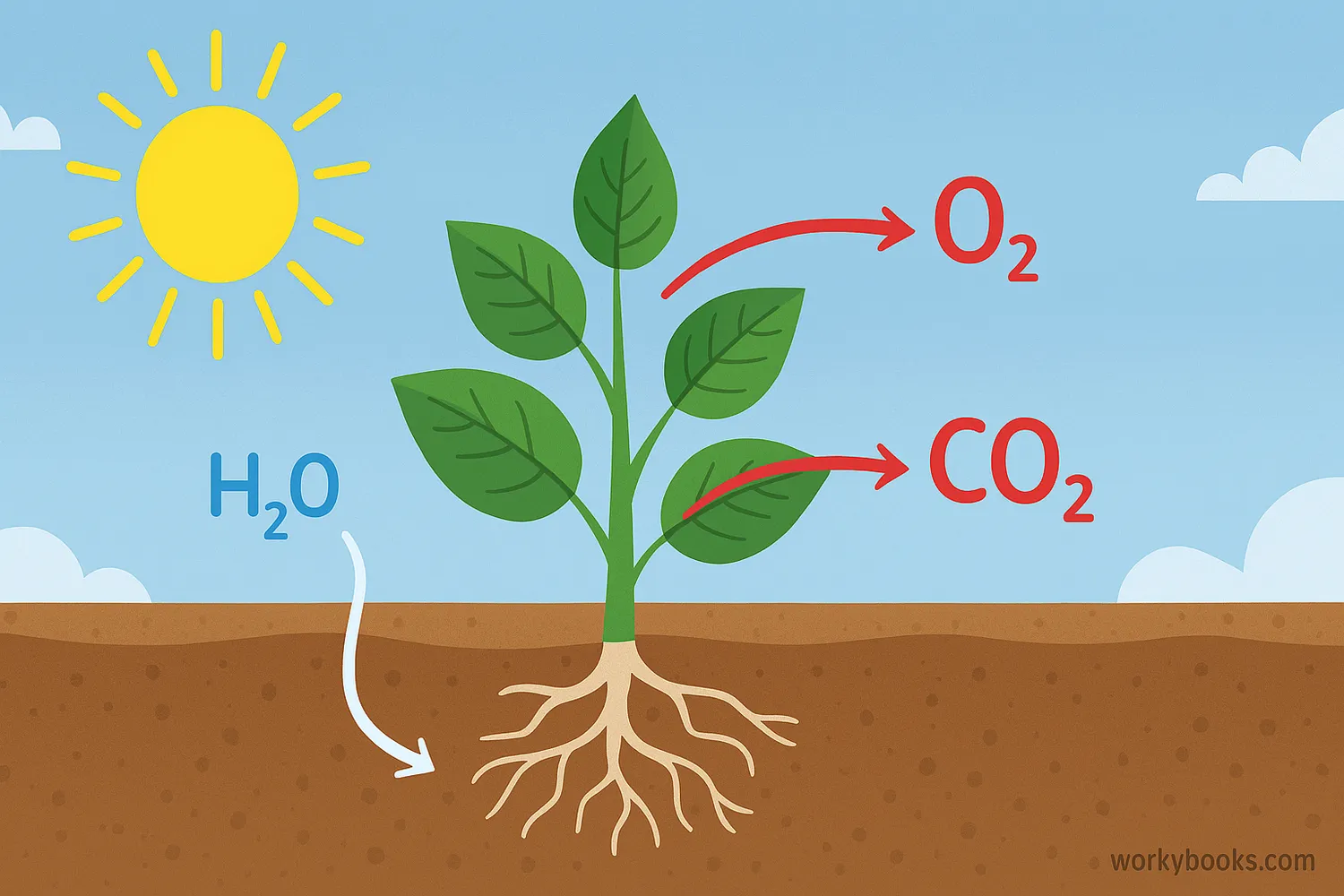
Photosynthesis is the amazing process that plants use to make their own food using sunlight! The word "photosynthesis" comes from Greek words meaning "putting together with light."
Think of plants as tiny food factories that use sunlight as their power source. They take simple ingredients - water from the soil and carbon dioxide from the air - and transform them into glucose (sugar) that they use for energy, while releasing oxygen as a byproduct.
Science Fact!
Photosynthesis is one of the most important biological processes on Earth. Without it, most life wouldn't exist because it provides both food and oxygen!
The Photosynthesis Equation
Scientists represent photosynthesis with a balanced chemical equation that shows all the ingredients (reactants) and results (products):
Let's break down what this means:
Reactants (Inputs):
• 6CO2 = Six molecules of carbon dioxide
• 6H2O = Six molecules of water
• Light energy = Energy from sunlight
Products (Outputs):
• C6H12O6 = One molecule of glucose (sugar)
• 6O2 = Six molecules of oxygen
Reactants & Products of Photosynthesis
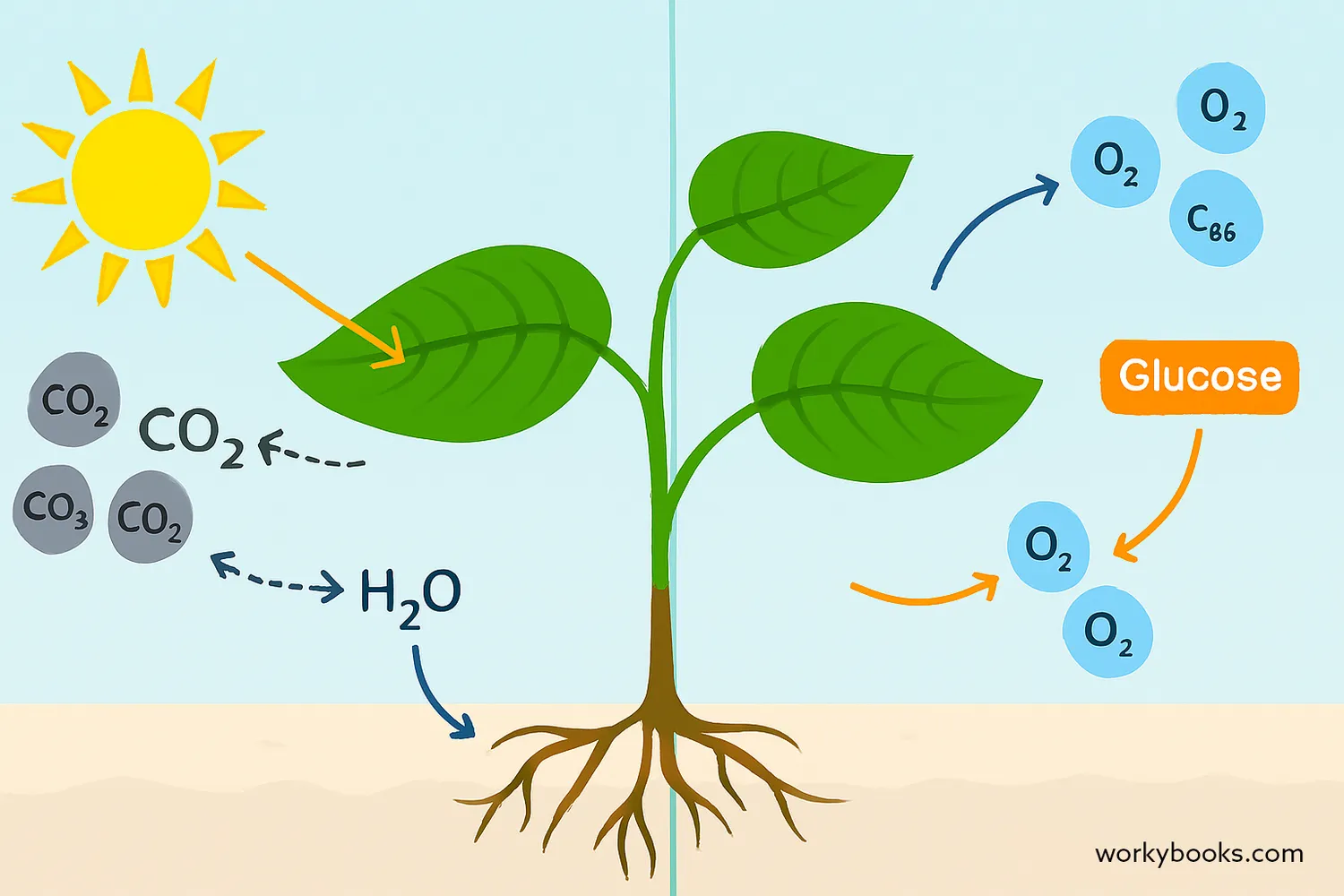
Let's look more closely at each part of the photosynthesis equation:
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Plants take in CO2 from the air through tiny pores in their leaves called stomata
Water (H2O)
Plants absorb water from the soil through their roots, which travels up to the leaves
Sunlight
Light energy is captured by chlorophyll, the green pigment in plant leaves
Glucose (C6H12O6)
The sugar plants make for food and energy to grow
Oxygen (O2)
Released into the air as a waste product - essential for animals to breathe!
The magic of photosynthesis happens in special parts of plant cells called chloroplasts, which contain chlorophyll that gives plants their green color and captures sunlight.
How Photosynthesis Works
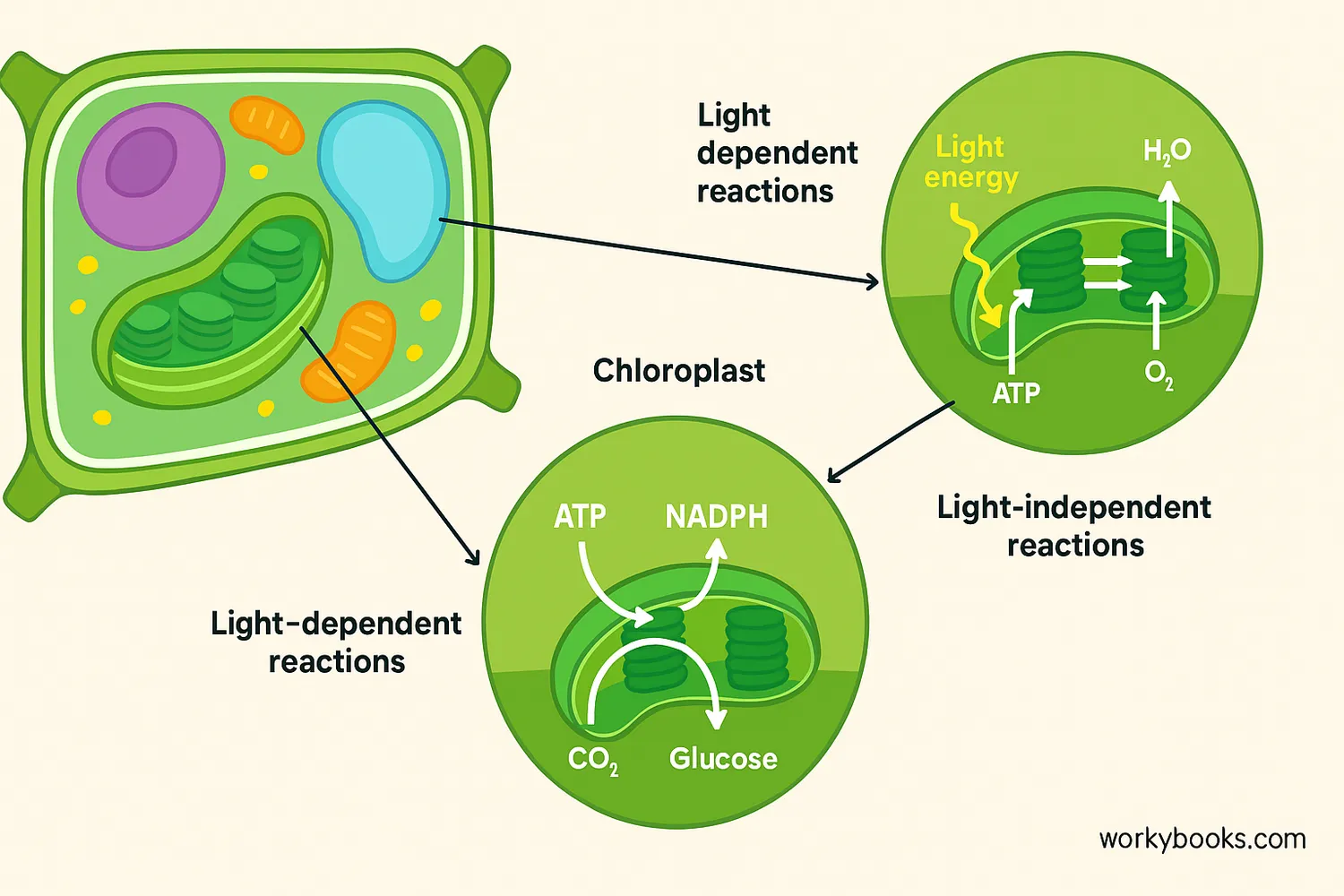
Photosynthesis happens in two main stages inside the chloroplasts:
Light-Dependent Reactions
Sunlight is captured by chlorophyll and converted to chemical energy
Light-Independent Reactions
Chemical energy is used to convert CO2 into glucose
In the light-dependent reactions, sunlight energy is used to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. The oxygen is released, and the hydrogen is used to create energy-carrier molecules (ATP and NADPH).
In the light-independent reactions (also called the Calvin Cycle), the energy from those carrier molecules is used to combine carbon dioxide with hydrogen to make glucose.
Connection to Cellular Respiration
The glucose made in photosynthesis is used by plants (and animals that eat plants) in cellular respiration: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy. Notice how it's essentially the reverse of photosynthesis!
Importance of Photosynthesis
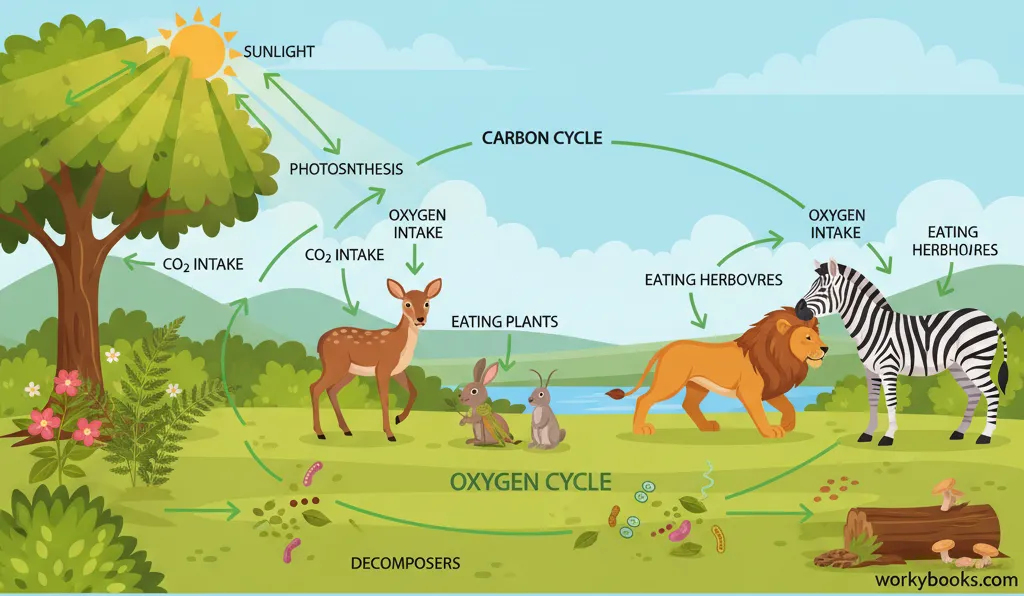
Photosynthesis is incredibly important for three main reasons:
Food Production
Photosynthesis produces the energy that plants use to grow, and plants are the base of most food chains
Oxygen Production
Photosynthesis provides the oxygen that most living things need to breathe
Carbon Cycle
Photosynthesis helps balance Earth's atmosphere by removing CO2 and producing O2
Without photosynthesis, Earth would be a very different planet! There would be no plants, no animals that eat plants, no oxygen to breathe, and much more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Photosynthesis Quiz
Test your knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned about photosynthesis.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about photosynthesis:
Science Facts About Photosynthesis
Discover some fascinating facts about photosynthesis and plants!
Ocean Photosynthesis
About 70% of the oxygen in our atmosphere comes from photosynthesis by phytoplankton and algae in the oceans, not from land plants!
Efficiency Rate
Photosynthesis is surprisingly inefficient - plants typically convert only about 1% of the sunlight that hits them into chemical energy. Scientists are working to improve this for better biofuel production.
Historical Discovery
The basic equation of photosynthesis was discovered in the 1800s, but Dutch scientist Jan Ingenhousz demonstrated in 1779 that plants need sunlight to produce oxygen.
Rainforest Importance
Although rainforests cover only about 6% of Earth's surface, they produce about 20% of our oxygen! This is why they're often called the "lungs of the planet."




