Alkali Metals - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the most reactive elements on the periodic table
What are Alkali Metals?
Alkali metals are a special group of elements found in the first column of the periodic table. They include:
Lithium (Li), Sodium (Na), Potassium (K), Rubidium (Rb), Cesium (Cs), and Francium (Fr).
These metals are called "alkali" because they form alkaline solutions when they react with water. What makes them special is that they all have just one electron in their outermost shell, which makes them highly reactive.
Science Fact!
All alkali metals are stored in oil to prevent them from reacting with oxygen and moisture in the air!
Properties of Alkali Metals
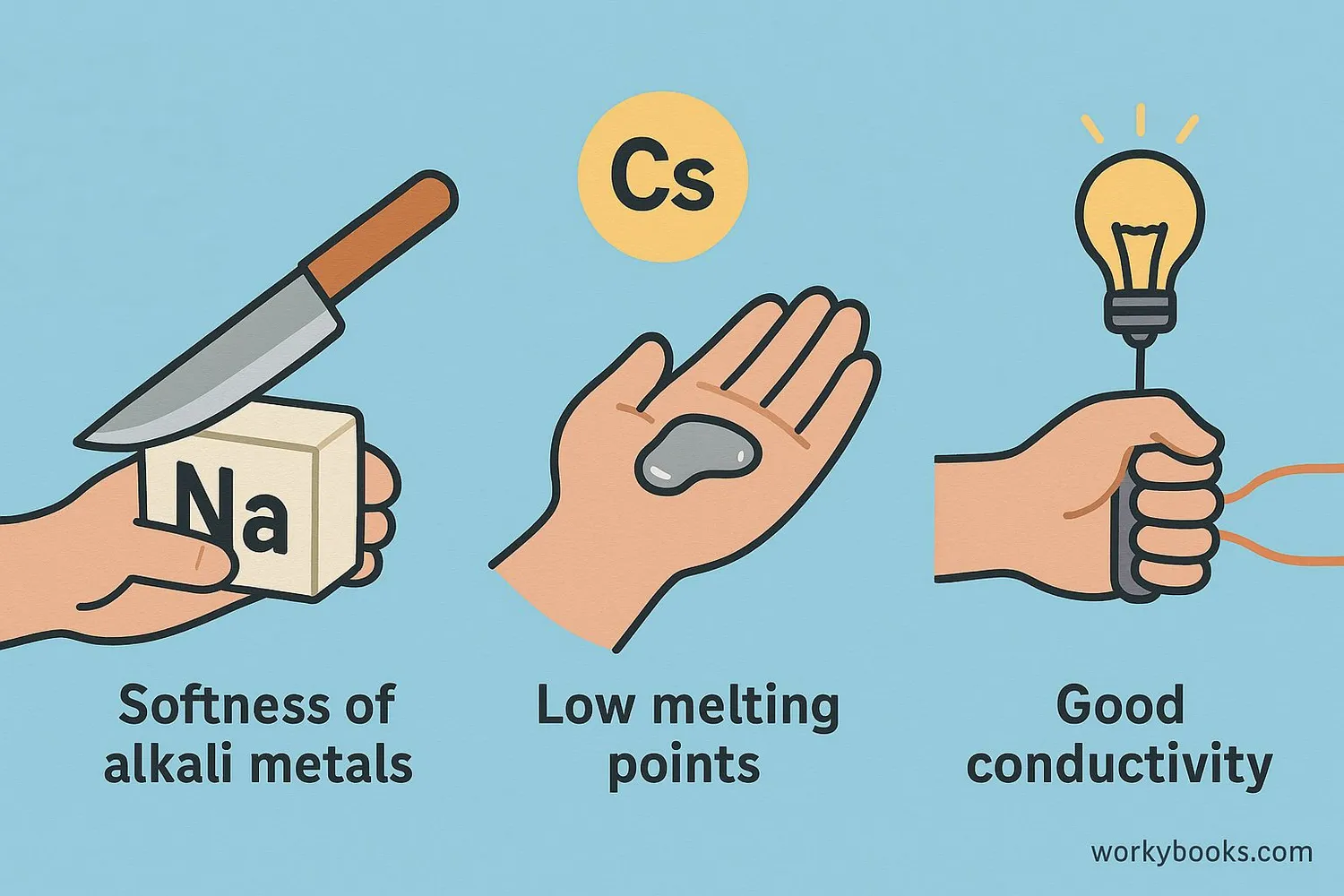
Alkali metals share several unique physical properties:
Softness
They are soft enough to cut with a knife
Low Density
Lithium, sodium and potassium float on water
Low Melting Points
Cesium melts at just 28°C (82°F)
Shiny Surfaces
When freshly cut, they have a metallic luster
Good Conductors
They conduct heat and electricity well
Alkali metals all have similar chemical properties because they each have one electron in their outermost shell. This makes them highly likely to lose that electron and form positive ions (+1 charge) when they react with other elements.
Did You Know?
Francium is the rarest naturally occurring alkali metal. Only about 20-30 grams exist in the Earth's crust at any time!
Reactivity of Alkali Metals
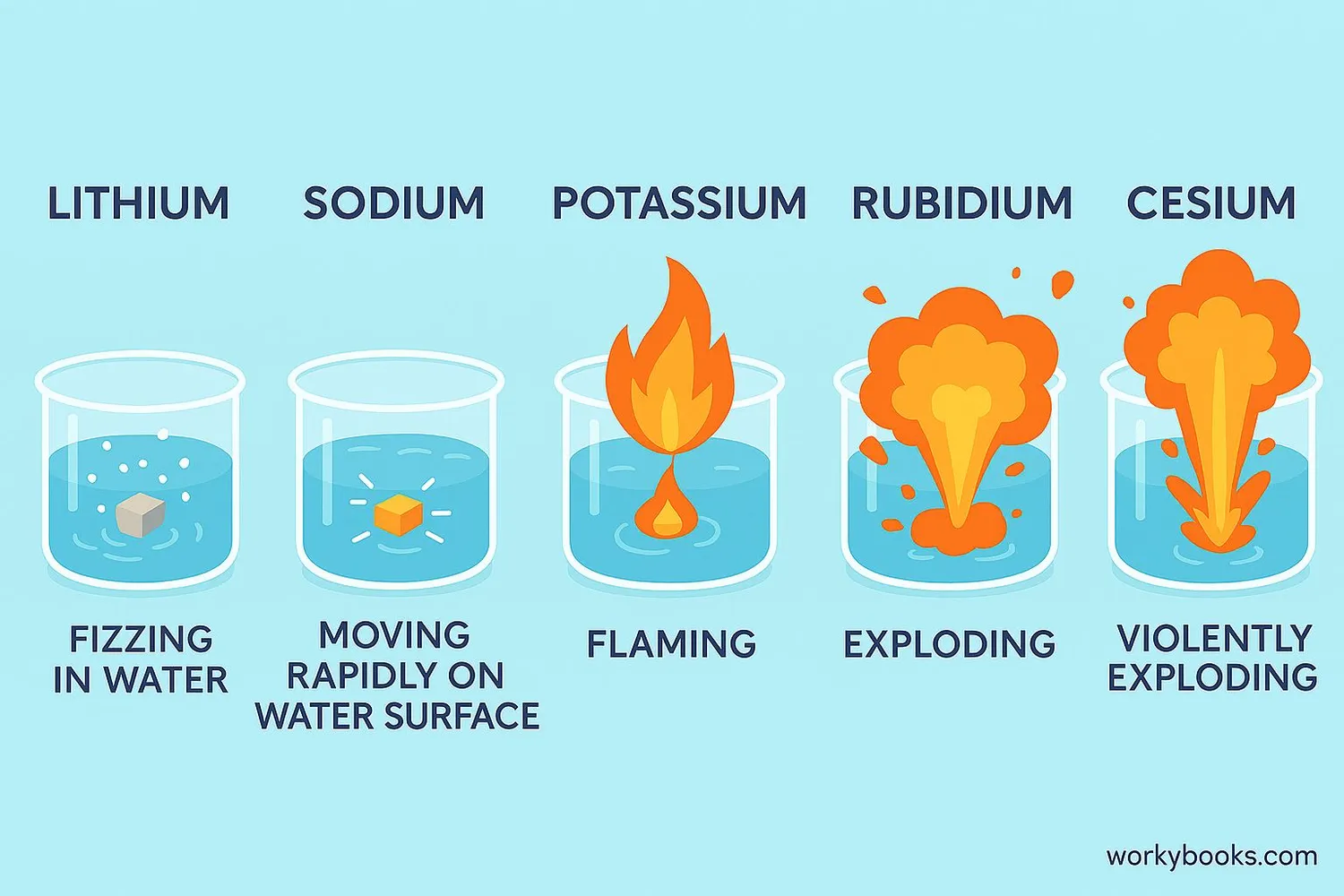
Alkali metals are famous for their reactivity, especially with water. This reactivity increases as you go down the group in the periodic table:
Lithium
Fizzes steadily on water
Sodium
Melts into a ball, moves rapidly
Potassium
Ignites with a lilac flame
Rubidium
Violent explosion
Cesium
Extremely violent explosion
The reason for this increasing reactivity is that as atoms get larger going down the group, the single outer electron is farther from the nucleus and easier to remove. This makes it easier for the metal to form positive ions and react with other substances.
Safety First!
Never handle alkali metals directly! They can cause severe chemical burns and react violently with moisture on your skin.
Uses of Alkali Metals
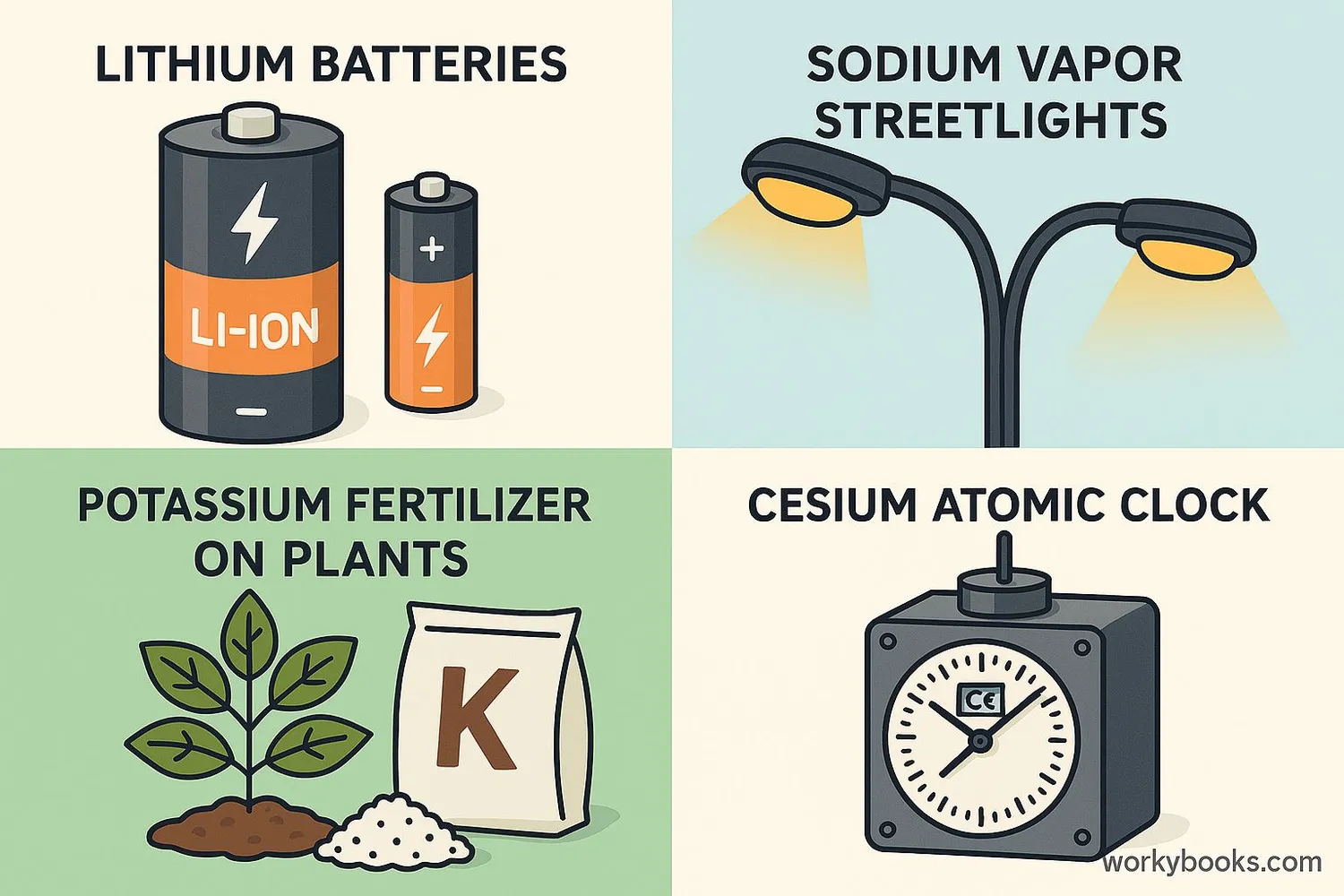
Despite their reactivity, alkali metals have many important uses:
Lithium
Rechargeable batteries in phones and electric cars
Sodium
Street lighting (vapor lamps), table salt (sodium chloride)
Potassium
Fertilizers, vital for plant growth
Cesium
Atomic clocks (most accurate timekeeping)
Alkali metals also form important compounds:
• Sodium chloride - table salt
• Potassium nitrate - fertilizer and gunpowder
• Lithium carbonate - medication for bipolar disorder
• Sodium bicarbonate - baking soda
• Potassium hydroxide - soap making
Alkali Metals Quiz
Test your knowledge about alkali metals with this interactive quiz!
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about alkali metals:
Alkali Metals Trivia
Discover some fascinating facts about alkali metals:
Space Elements
Astronomers have detected lithium in the atmospheres of certain stars. The presence of alkali metals helps scientists determine a star's temperature and composition!
Historic Discovery
Potassium was the first metal to be discovered by electrolysis. Sir Humphry Davy isolated it in 1807 using a powerful battery he invented!
Precise Timekeeping
Cesium atomic clocks are so accurate they would lose less than one second in 300 million years! These clocks define the international standard for time.
Essential for Life
Sodium and potassium ions are crucial for nerve function in your body. Your nervous system uses them to transmit electrical signals throughout your body!





