Covalent Bonds - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how atoms share electrons to form molecules!
What is a Covalent Bond?
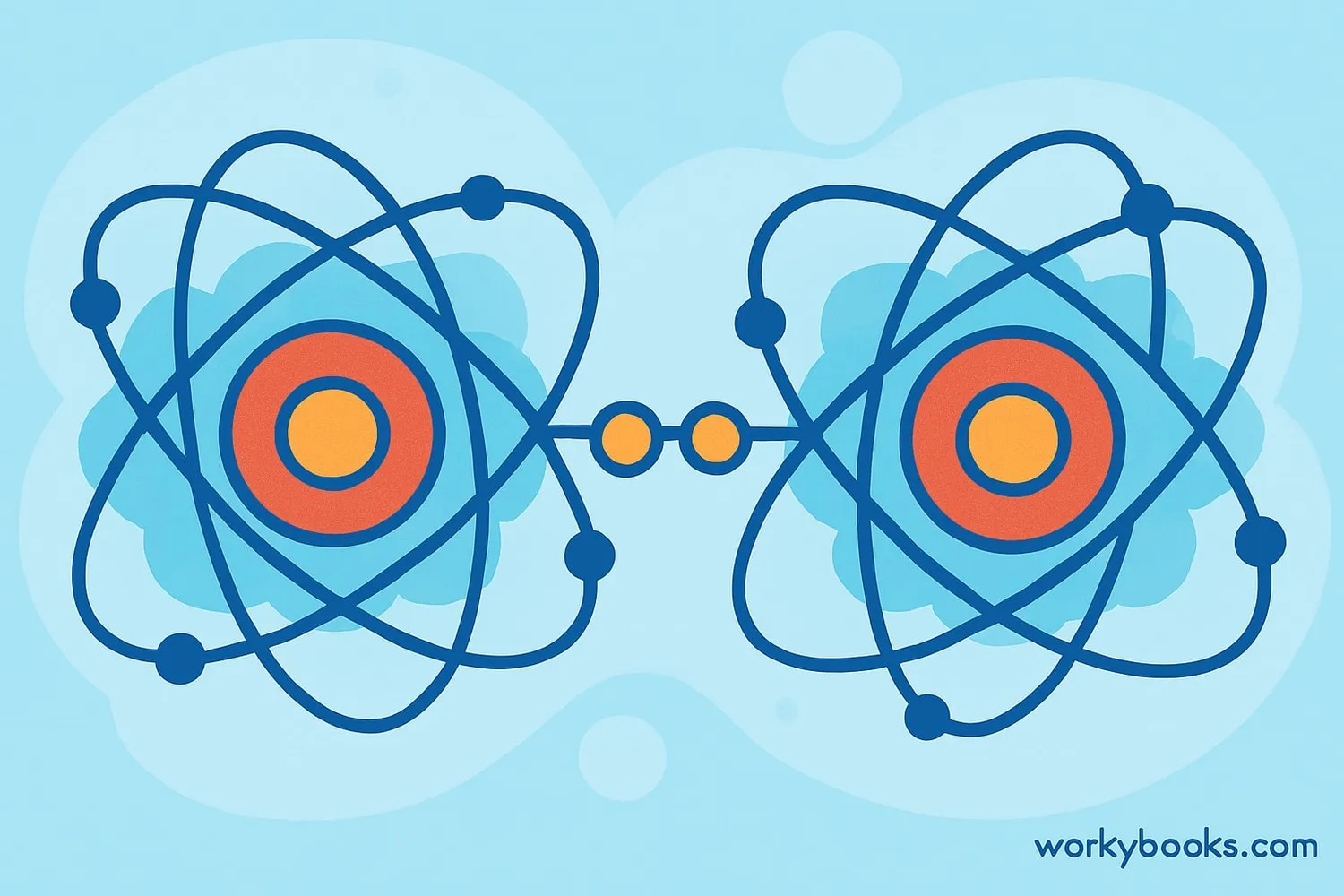
A covalent bond is a special connection between atoms where they share electrons to become stable. Atoms are like tiny building blocks that make up everything around us. They have electrons that orbit around their center (nucleus).
When atoms share one or more pairs of electrons, they form a covalent bond. This sharing helps both atoms complete their outer electron shells, making them more stable. Covalent bonds are like a friendship where two friends share toys so both can have fun!
Covalent bonds create molecules - groups of atoms held together by these shared electrons. Water (H₂O) and oxygen (O₂) are examples of molecules formed by covalent bonds.
Science Fact!
Your body contains trillions of covalent bonds holding together the molecules that make up your cells, tissues, and organs!
How Covalent Bonds Work
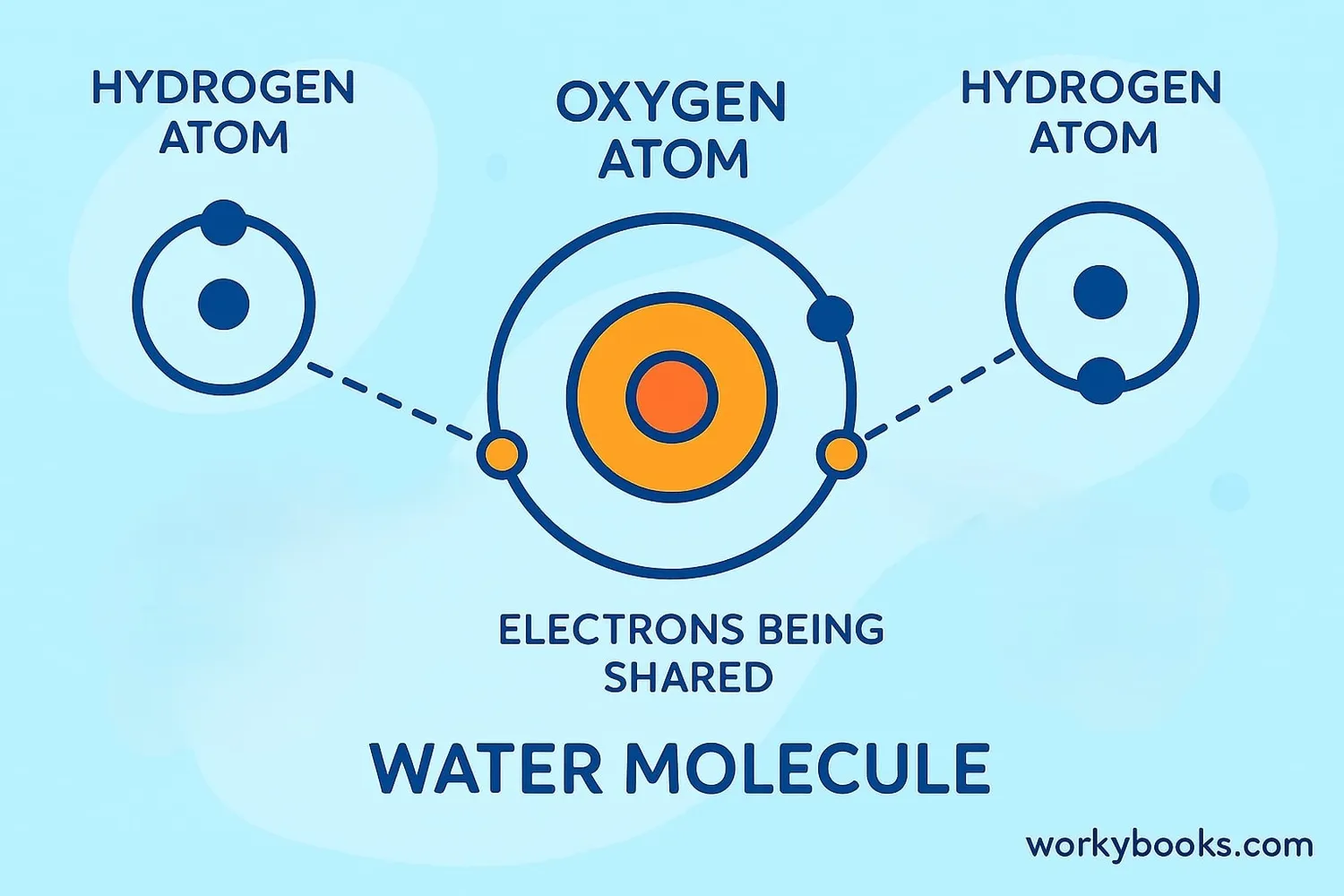
Covalent bonds form when atoms need to gain electrons to have a full outer shell. Here's how it works:
Atom Needs
Atoms want full outer electron shells
Electron Sharing
Atoms share electrons instead of transferring them
Bond Formation
Shared electrons hold atoms together
Molecule Created
Atoms become a stable molecule
Water (H₂O)
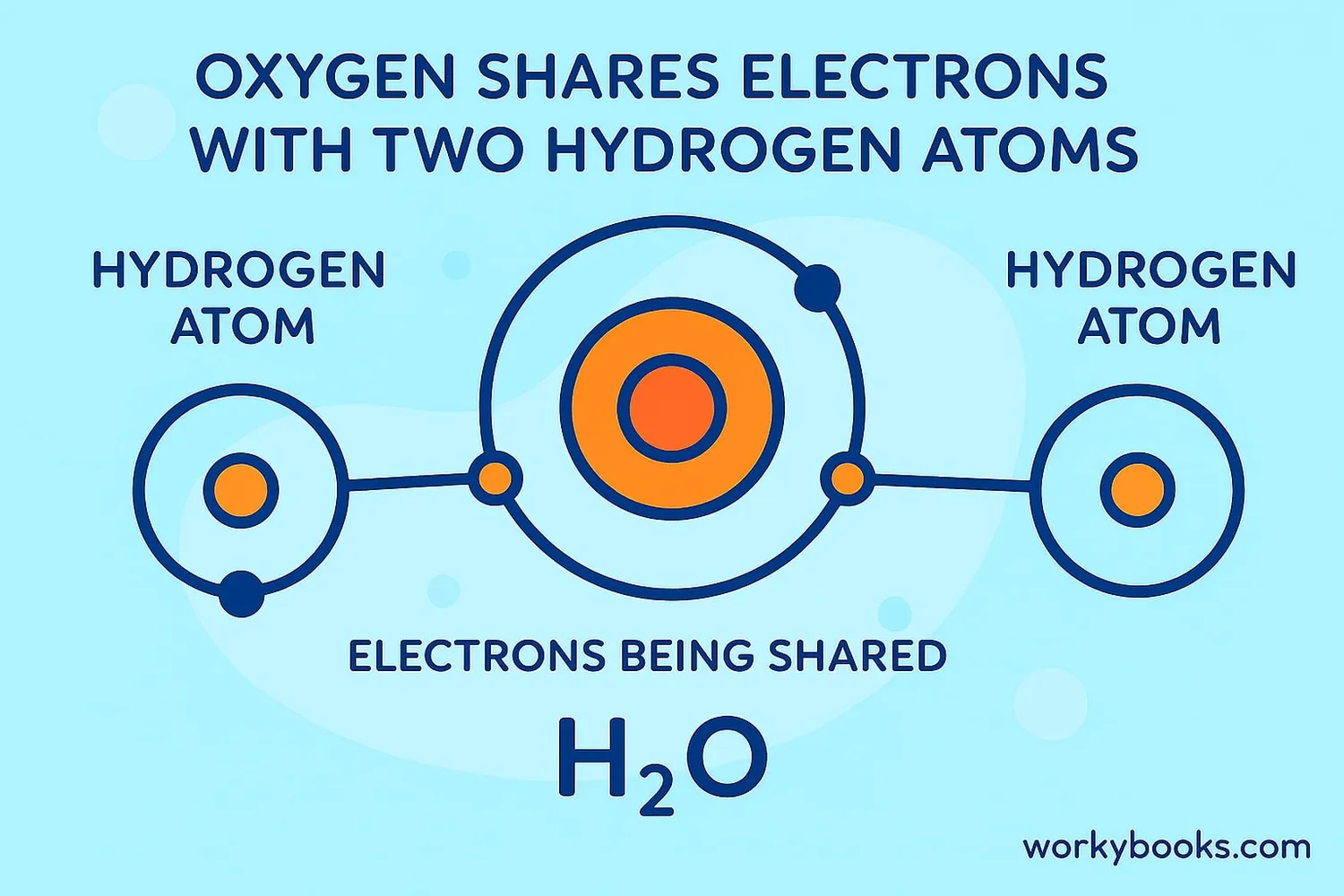
Oxygen shares electrons with two hydrogen atoms
Oxygen (O₂)
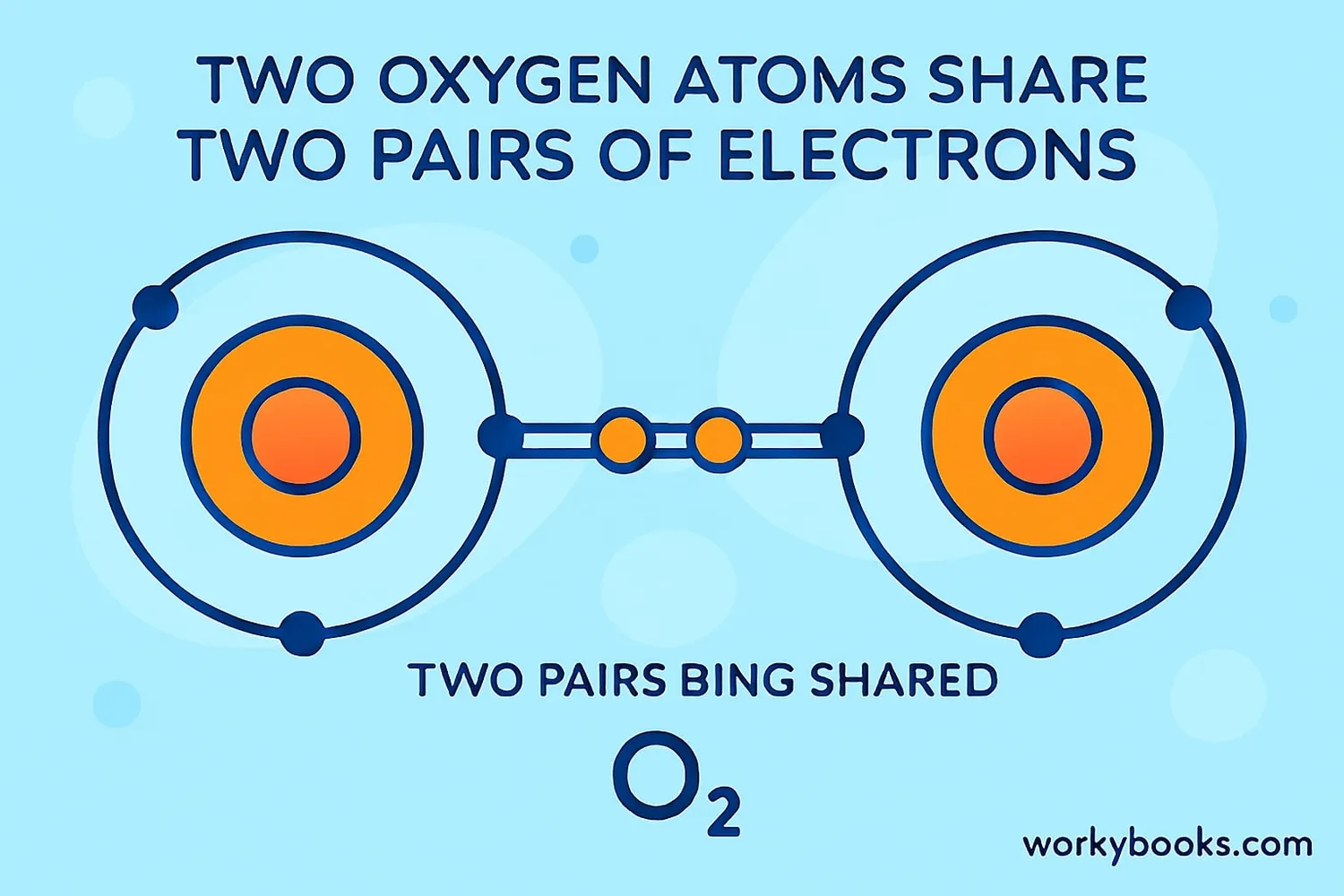
Two oxygen atoms share two pairs of electrons
Methane (CH₄)
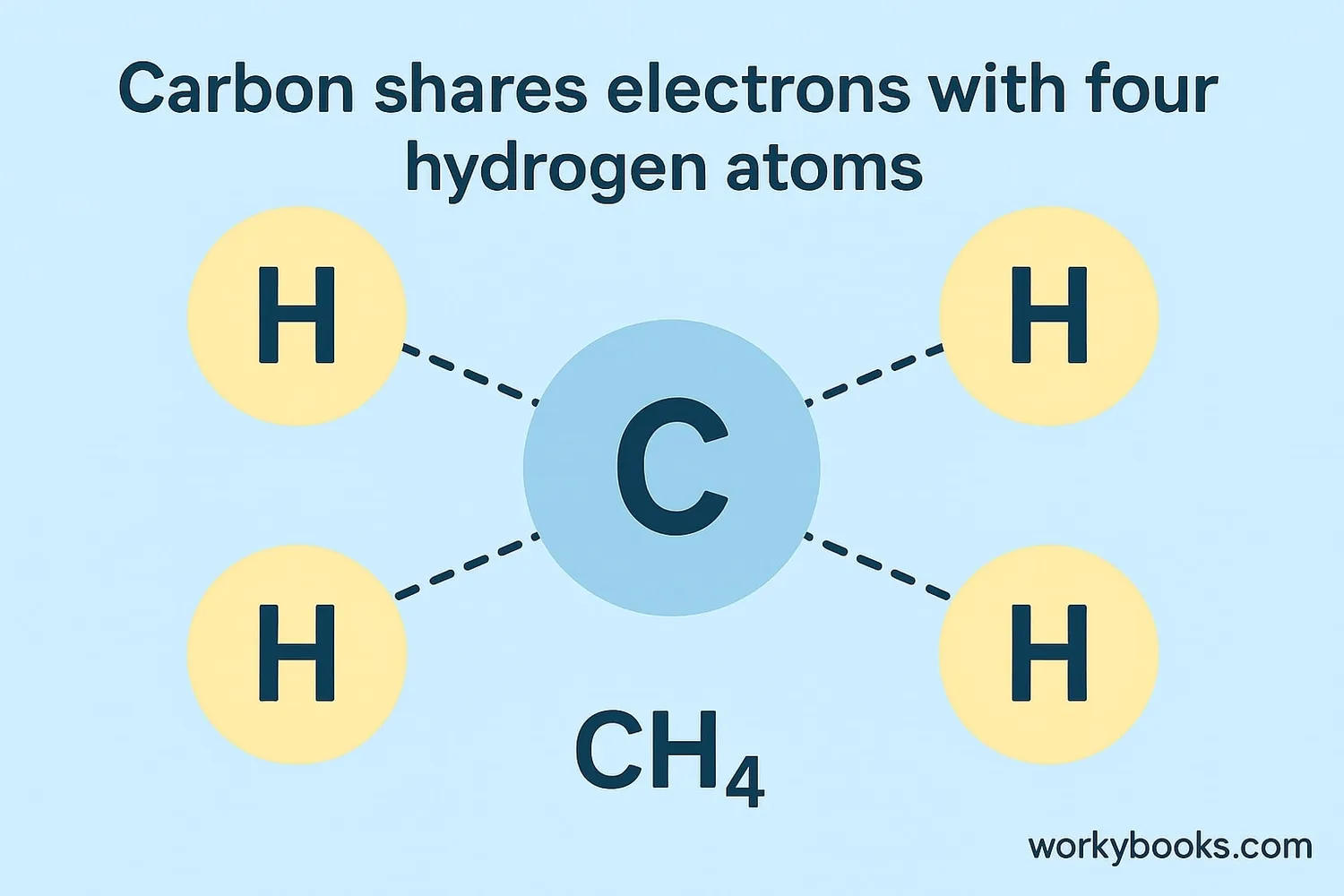
Carbon shares electrons with four hydrogen atoms
Single bonds share one pair of electrons, double bonds share two pairs, and triple bonds share three pairs. The more electrons shared, the stronger the bond!
Types of Covalent Bonds
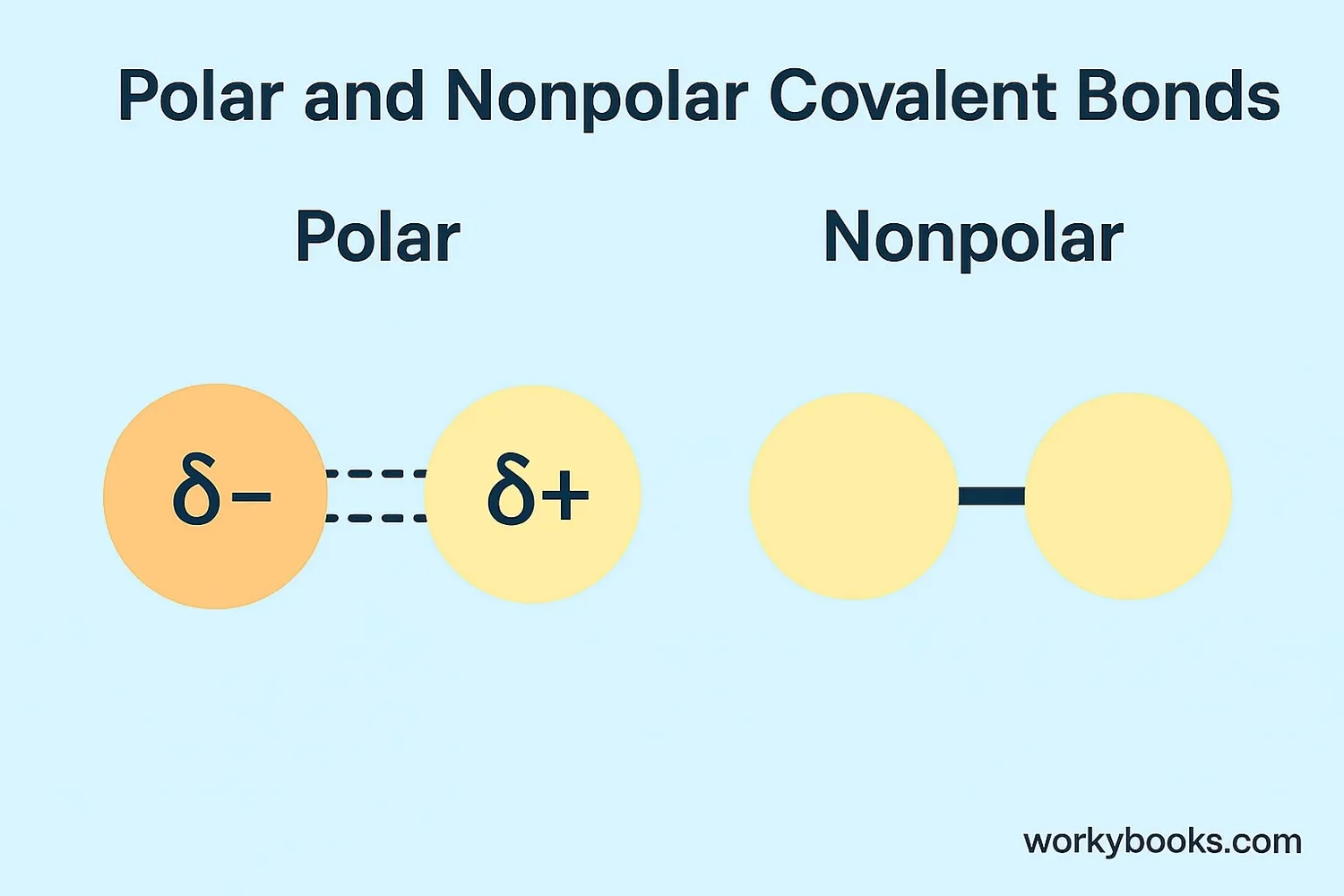
There are two main types of covalent bonds:
Polar Covalent Bonds
Electrons are shared unequally between atoms. One atom pulls electrons more strongly, creating slight charges.
Example: Water (H₂O)
Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
Electrons are shared equally between identical atoms or atoms with similar electron attraction.
Example: Oxygen (O₂)
Bond Strength Fact!
The strongest covalent bond is the triple bond in nitrogen gas (N₂), which requires lots of energy to break!
The difference between polar and nonpolar bonds explains why oil and water don't mix. Water molecules are polar, while oil molecules are nonpolar!
Why Covalent Bonds are Important
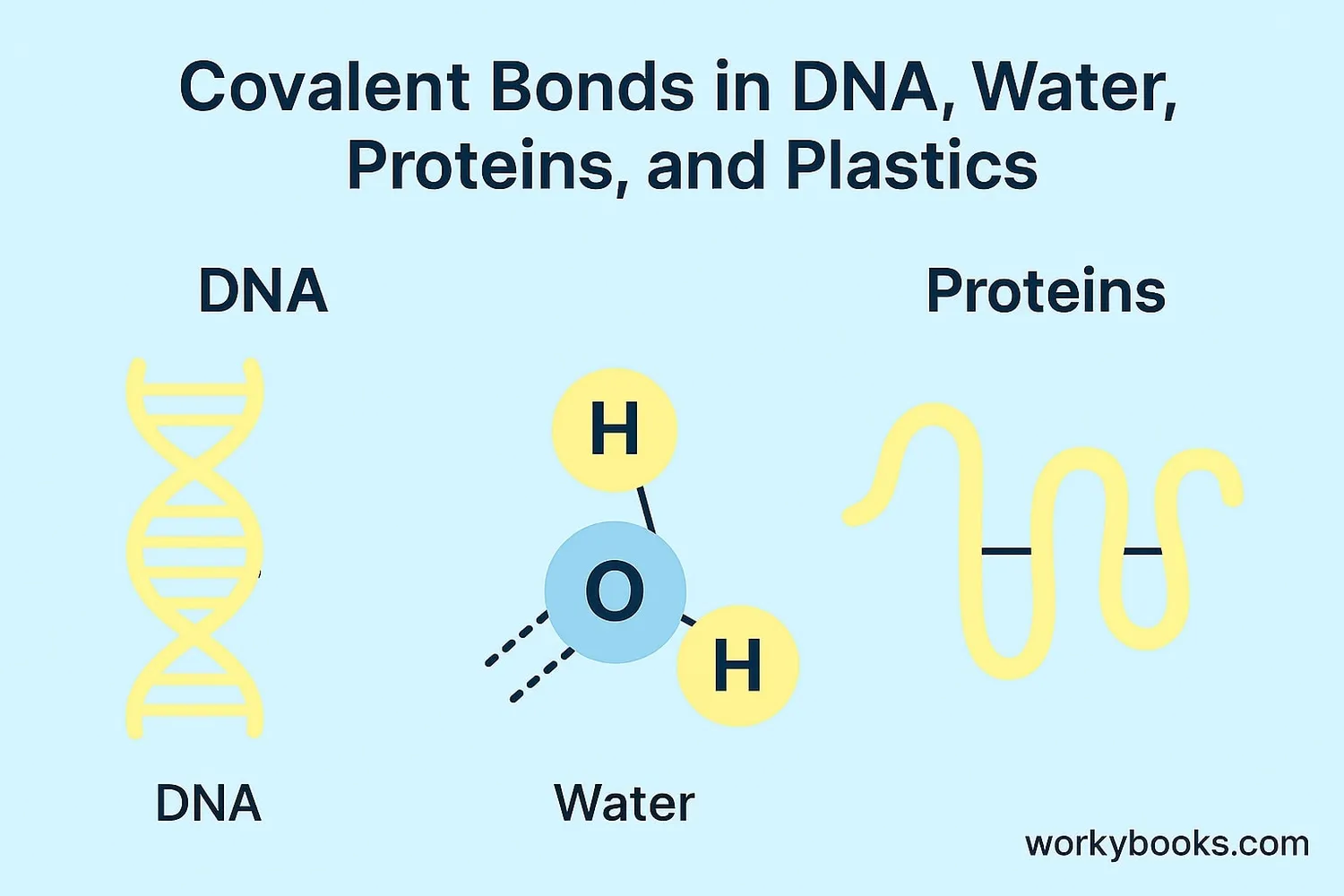
Covalent bonds are essential to life and our world:
Building Life
DNA and proteins are held together by covalent bonds
Water Properties
Covalent bonds give water its special properties
Medicines
Medicines work because of covalent bonds in molecules
Without covalent bonds, we wouldn't have:
• The water we drink and need to survive
• The air we breathe (oxygen and nitrogen molecules)
• The materials that make up our world (plastics, fabrics)
• The DNA that carries our genetic information
Covalent bonds are the "glue" that holds together the molecules that make up our world!
Covalent Bonds Quiz
Test your covalent bonds knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about covalent bonds:
Covalent Bonds Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about covalent bonds!
Diamond Strength
Diamonds are made of carbon atoms connected by strong covalent bonds in a 3D network. This makes diamonds the hardest natural material on Earth!
DNA Bonds
Your DNA contains about 3 billion atoms held together by covalent bonds! If stretched out, the DNA in one cell would be about 2 meters long.
Water's Special Bonds
Water's polar covalent bonds create surface tension, allowing insects to walk on water and water to form droplets. This is essential for life on Earth!
Tiny Bonds
Covalent bonds are incredibly small! A typical bond length is about 0.1-0.2 nanometers. You could fit about 500,000 carbon-carbon bonds across the width of a human hair!





