Diatomic Molecules - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how atoms pair up to form the building blocks of gases
What are Diatomic Molecules?
Diatomic molecules are special molecules made of only two atoms. These atoms can be the same element or different elements. The word "diatomic" comes from "di-" meaning two and "atomic" meaning atoms.
Think of diatomic molecules as best friends who always stick together! Some elements, like oxygen and nitrogen, prefer to exist as pairs rather than single atoms. This pairing happens through chemical bonds that hold the atoms together.
Molecular Fact!
About 99% of Earth's atmosphere is made of diatomic molecules - mostly nitrogen (N₂) and oxygen (O₂)!
Types of Diatomic Molecules
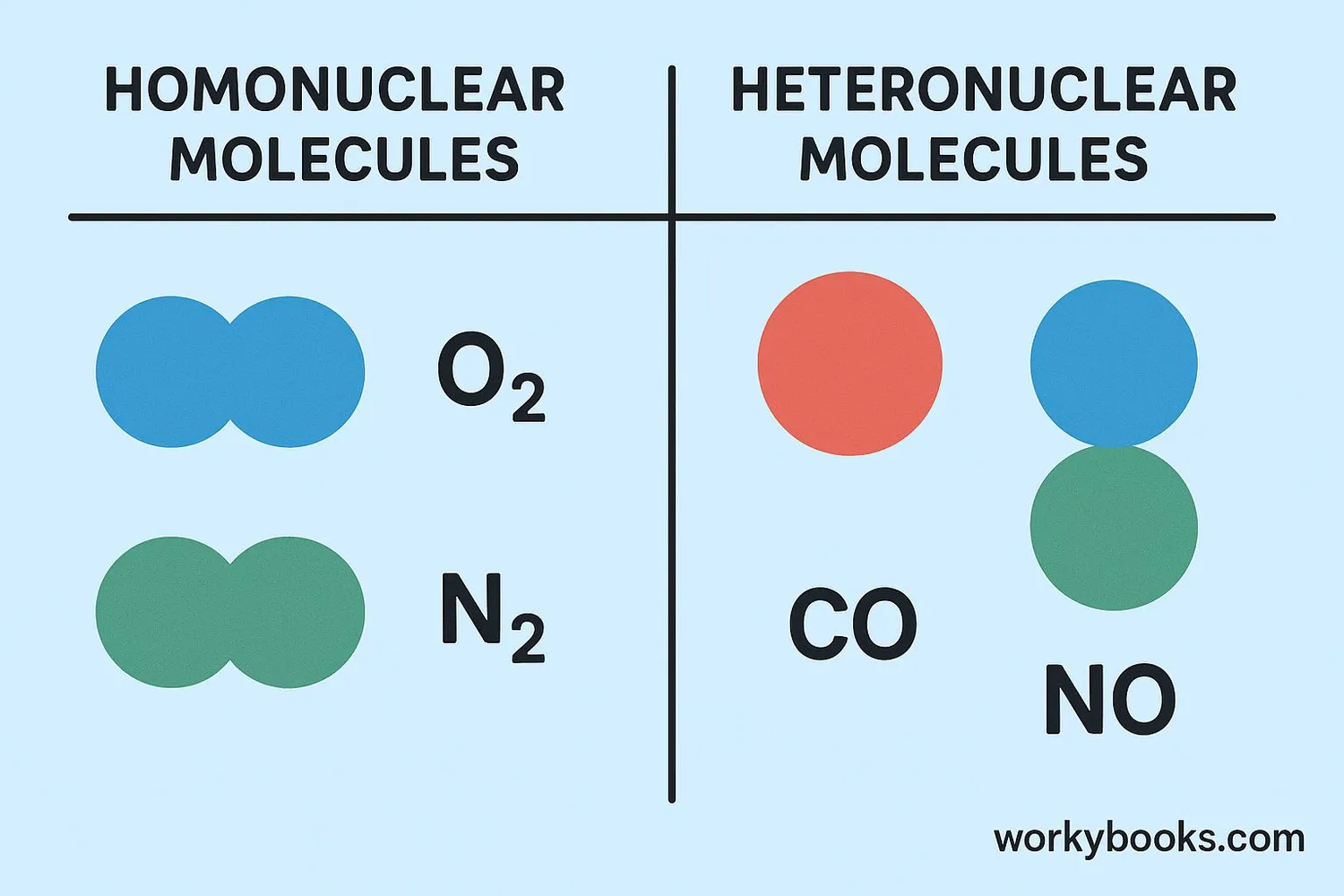
There are two main types of diatomic molecules:
Homonuclear
Made of two identical atoms (like O₂, N₂, H₂)
Heteronuclear
Made of two different atoms (like CO, NO, HCl)
The seven elements that always form diatomic molecules in their pure form are remembered with the acronym BrINClHOF:
Bromine, Iodine, Nitrogen, Cllorine, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Fluorine
These elements form covalent bonds by sharing electrons between the two atoms. This sharing creates a stable molecule that's more comfortable than single atoms.
Bonding Fact!
In a covalent bond, atoms share electrons like best friends sharing toys - this makes both atoms happy and stable!
Why Diatomic Molecules are Important
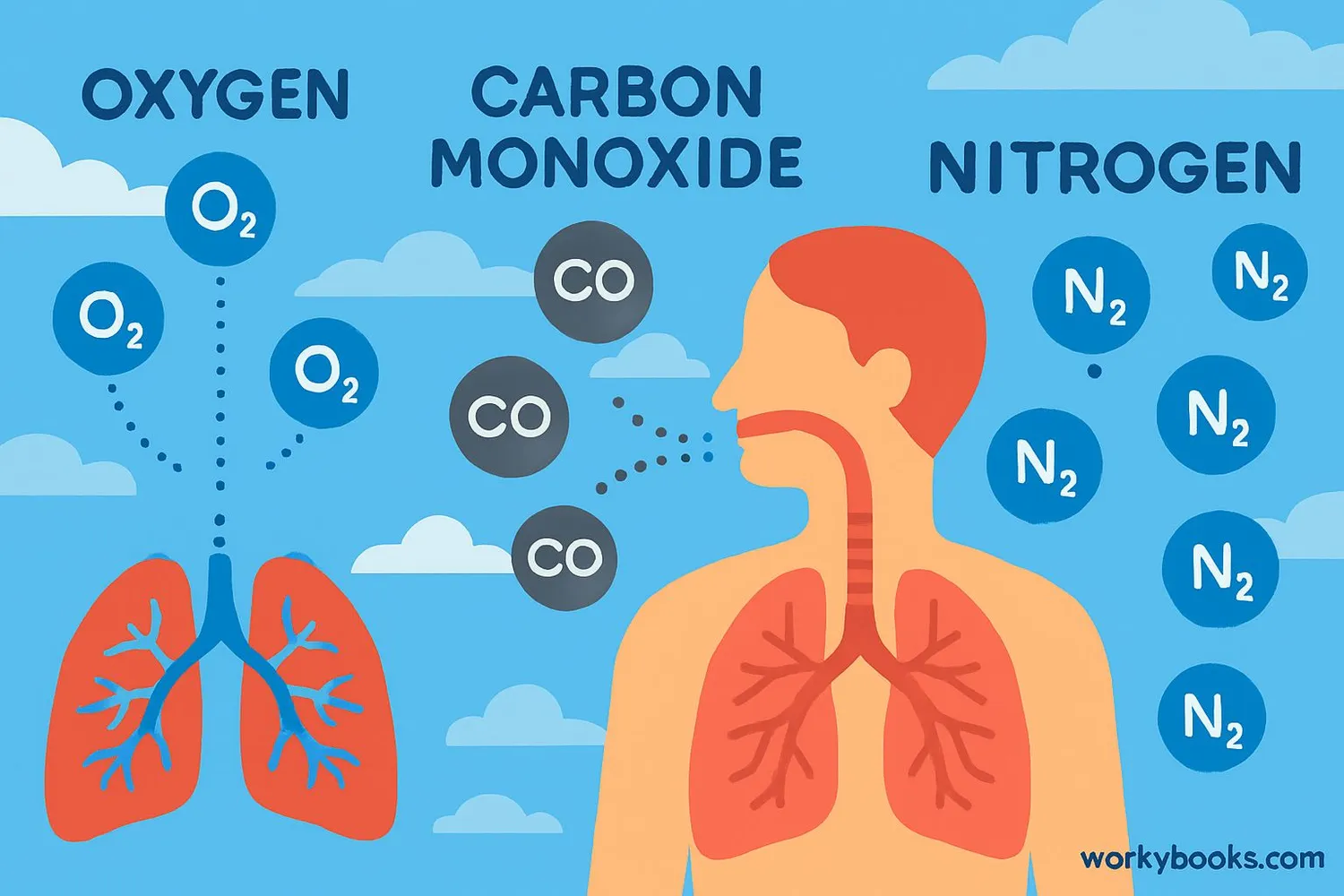
Diatomic molecules are essential for life on Earth! Here's why they're so important:
Breathing
Oxygen (O₂) is necessary for animals to breathe and create energy
Atmosphere
Nitrogen (N₂) makes up 78% of our atmosphere
Chemical Building Blocks
Diatomic molecules are starting points for many chemical reactions
Without diatomic molecules, there would be no:
• Oxygen for breathing and energy production
• Nitrogen to create a stable atmosphere
• Hydrogen for water and many organic compounds
• Protective ozone layer (O₃ is triatomic, made from O₂)
Diatomic molecules also play important roles in industry, medicine, and technology. For example, carbon monoxide (CO) is used in manufacturing, while nitric oxide (NO) is important in our bodies for signaling between cells.
Diatomic Molecules Quiz
Test your knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about diatomic molecules:
Interesting Facts About Diatomic Molecules
Discover some amazing facts about diatomic molecules!
Air Composition
99% of the air we breathe is made of diatomic molecules! About 78% is nitrogen (N₂) and 21% is oxygen (O₂), with the remaining 1% being other gases.
Space Molecules
Diatomic molecules exist in space too! Molecular hydrogen (H₂) is the most abundant molecule in the universe, found in giant molecular clouds where stars are born.
Strong Bonds
Nitrogen molecules (N₂) have one of the strongest chemical bonds in nature. It takes a lot of energy to break nitrogen molecules apart, which is why nitrogen gas is so stable.
Historical Discovery
The concept of diatomic molecules was first proposed by Amedeo Avogadro in 1811. His hypothesis helped scientists understand the difference between atoms and molecules.





