Direction of Force - Definition, Facts, Example, Quiz, Trivia
Discover how forces work and the importance of direction in making objects move!
What is Force?
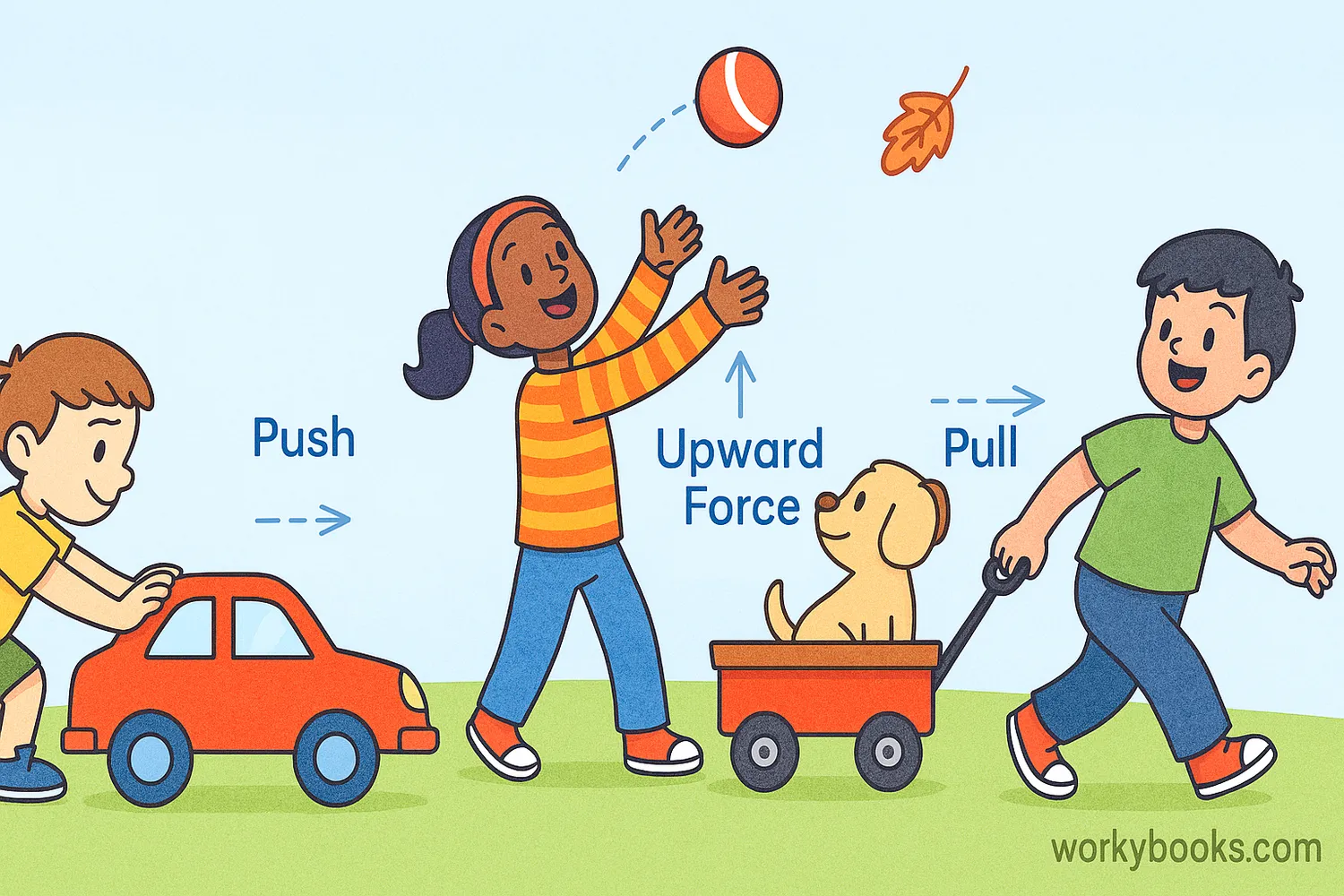
A force is a push or a pull that can make objects move, stop moving, or change direction. Forces are all around us! When you push a door open, pull a wagon, or even just stand on the ground, you're experiencing forces.
Forces can't be seen, but we can see what they do. They can make things speed up, slow down, or change direction. Every time something moves or stops moving, a force is responsible!
Science Fact!
Forces are measured in units called Newtons (N), named after Sir Isaac Newton who studied how forces work.
Direction of Force
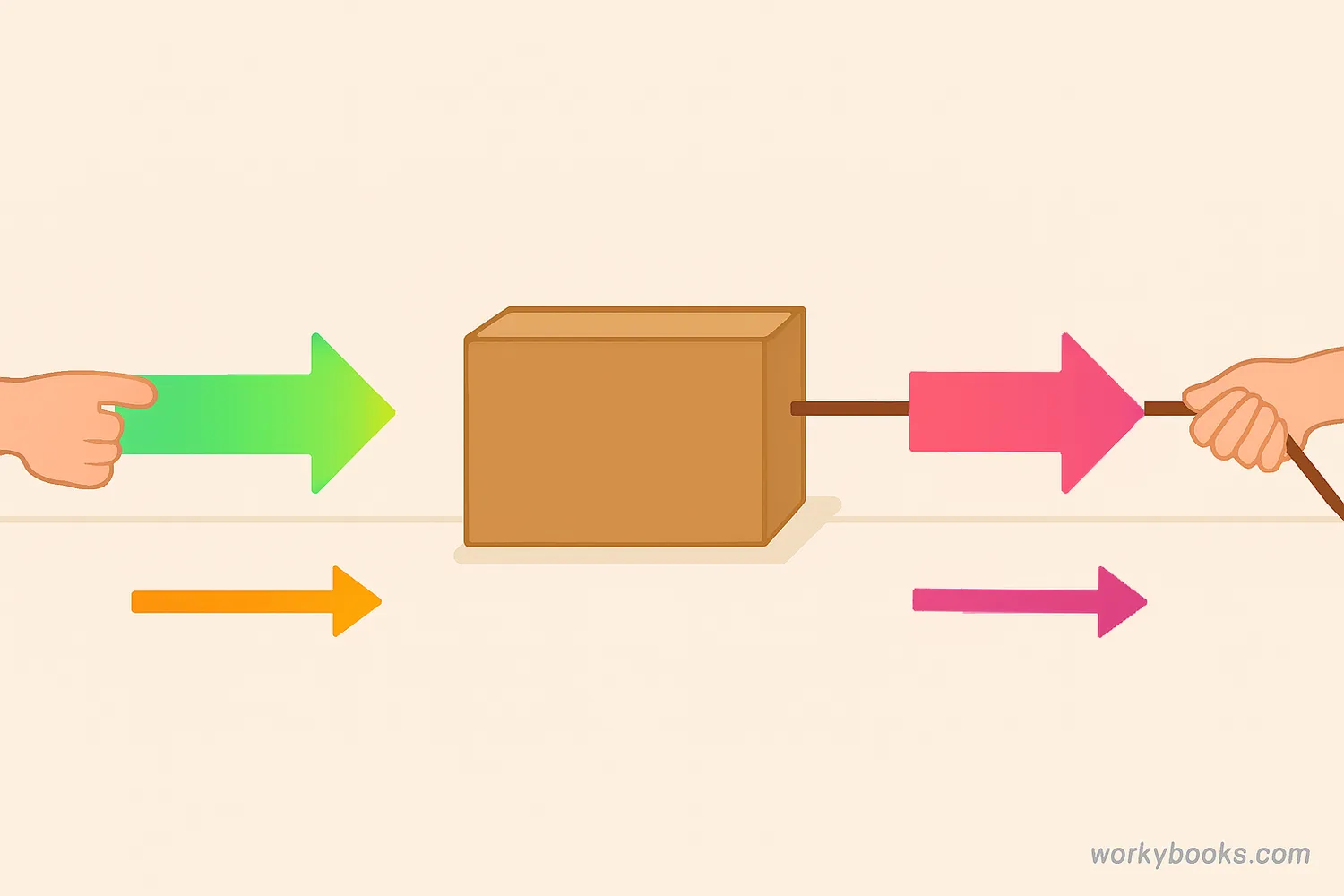
The direction of a force is just as important as how strong the force is. The direction tells us which way the force is pushing or pulling. This determines how an object will move or change its motion.
For example, if you push a box to the right, it moves to the right. If you pull it to the left, it moves to the left. The direction of the force always matches the direction the object starts moving.
Push Forces
Moving something away from you
Pull Forces
Moving something toward you
Up/Down Forces
Like lifting or dropping objects
Newton's Laws of Motion
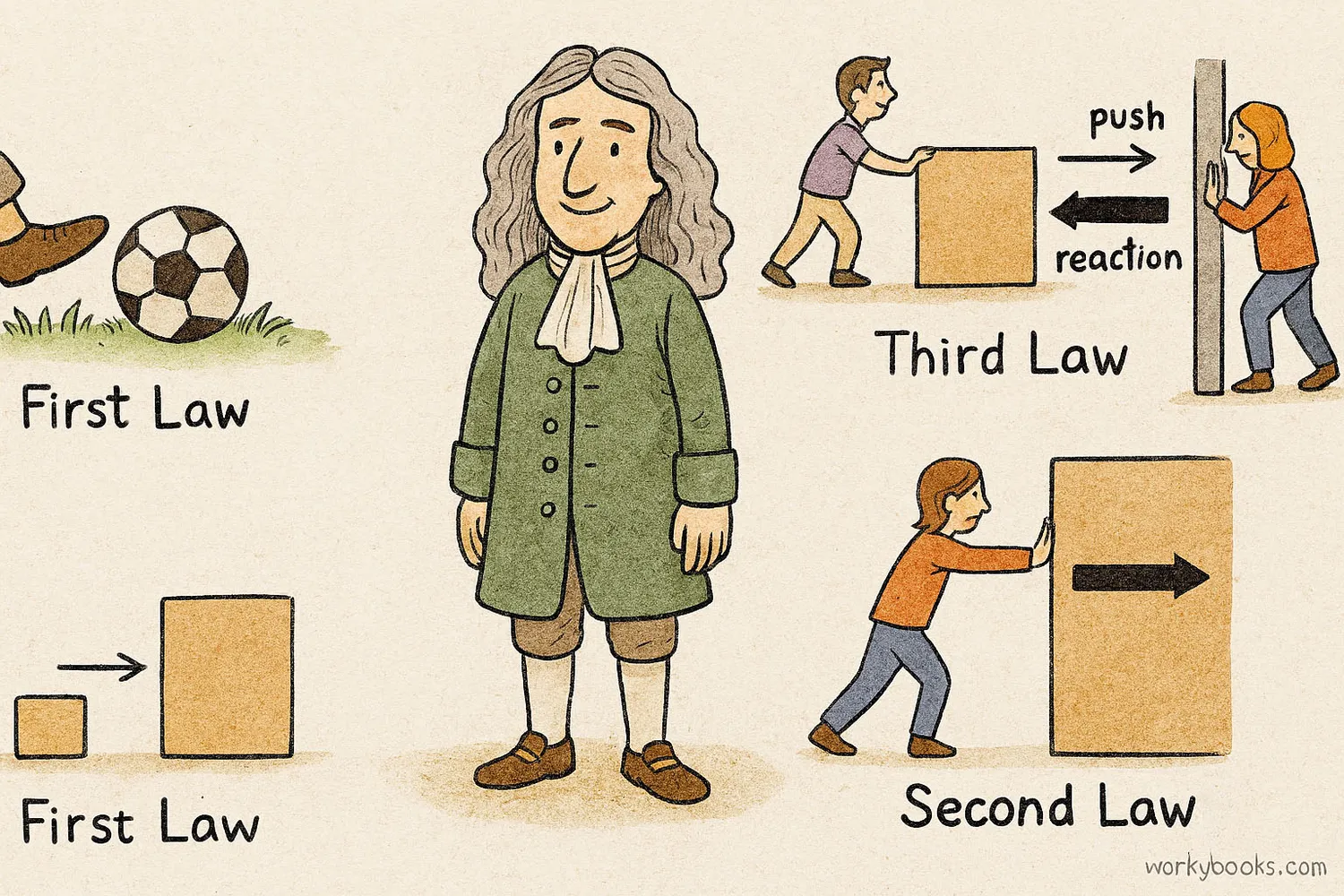
Sir Isaac Newton was a scientist who discovered three important laws about how forces work. These laws help us understand why objects move the way they do:
First Law: Law of Inertia
Objects at rest stay at rest, and objects in motion stay in motion unless a force acts on them.
Example: A soccer ball stays still until you kick it.
Second Law: F = m × a
Force equals mass times acceleration. Stronger forces make objects accelerate faster.
Example: It takes more force to push a heavy box than a light one.
Third Law: Action-Reaction
For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Example: When you push on a wall, the wall pushes back on you.
These laws work together to explain how all objects move when forces act upon them. The direction of the force is important in all three laws!
Examples of Force Direction
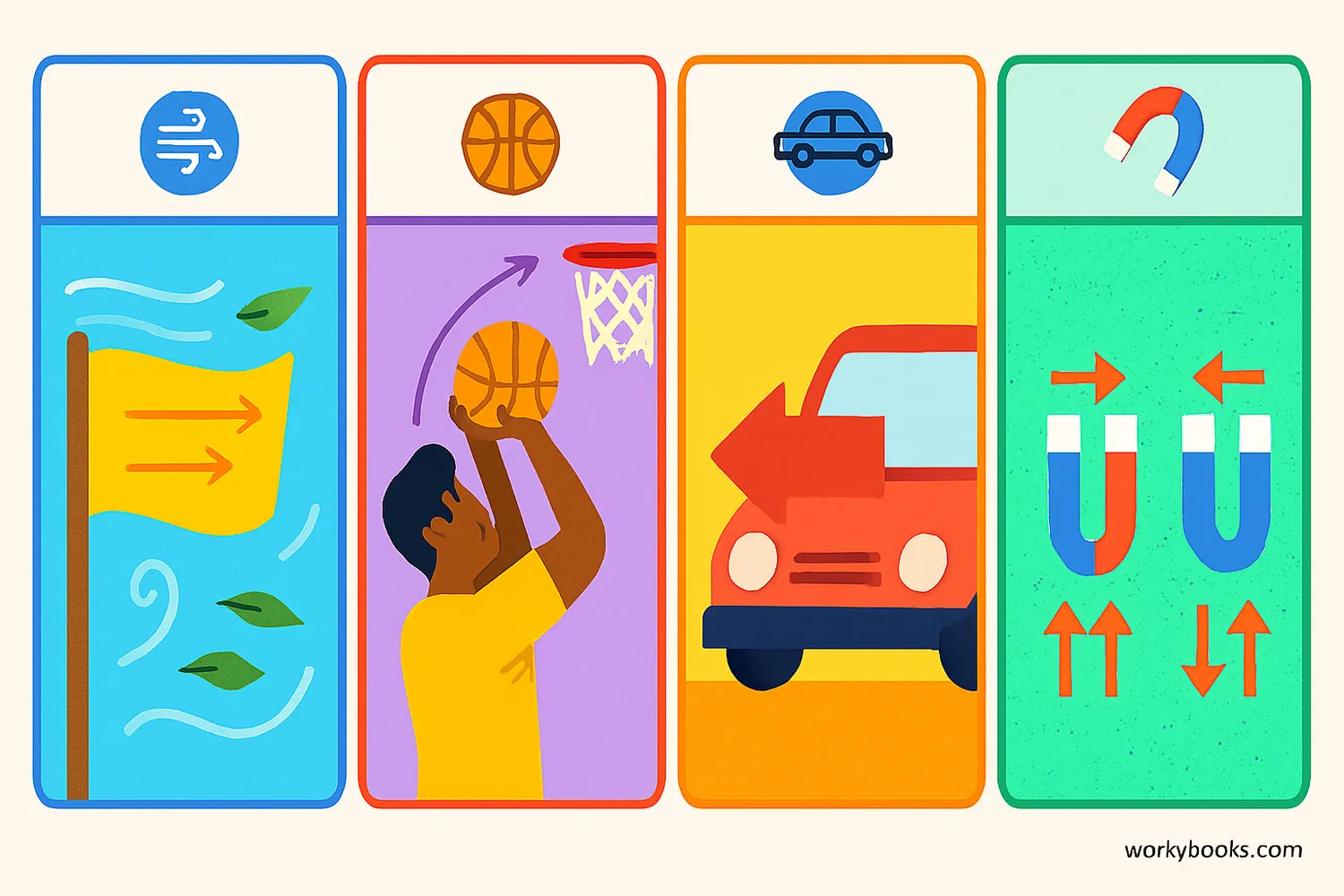

Let's look at some everyday examples of forces and their directions:
Wind Blowing
The wind applies force in the direction it's blowing, making leaves and flags move that way.
Shooting a Basket
You apply upward and forward force to the basketball to make it arc toward the basket.
Braking a Car
Brakes apply force opposite to the car's direction, making it slow down and stop.
Magnets
Magnets can pull (attract) or push (repel) other magnets, depending on their orientation.
Understanding force direction helps us predict how objects will move. This is important for engineers, athletes, drivers, and anyone who works with moving objects!
Force Quiz
Test your knowledge about forces with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about forces:
Science Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about forces!
Gravity's Pull
Earth's gravity pulls everything toward its center at 9.8 meters per second squared. This means falling objects speed up by 9.8 m/s every second they fall!
Rocket Power
Rockets work by pushing gases downward with tremendous force. According to Newton's third law, this creates an equal and opposite force that pushes the rocket upward.
Force Measurement
One Newton of force is about the weight of a small apple. It's the force needed to accelerate a 1 kilogram mass at 1 meter per second squared.
Human Strength
The human body can generate different amounts of force depending on the muscles used. Your jaw muscles can create about 90 kg of force, while your leg muscles can push with over 450 kg of force!





