Energy Conservation - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how energy changes forms but is never created or destroyed!
What is Energy Conservation?
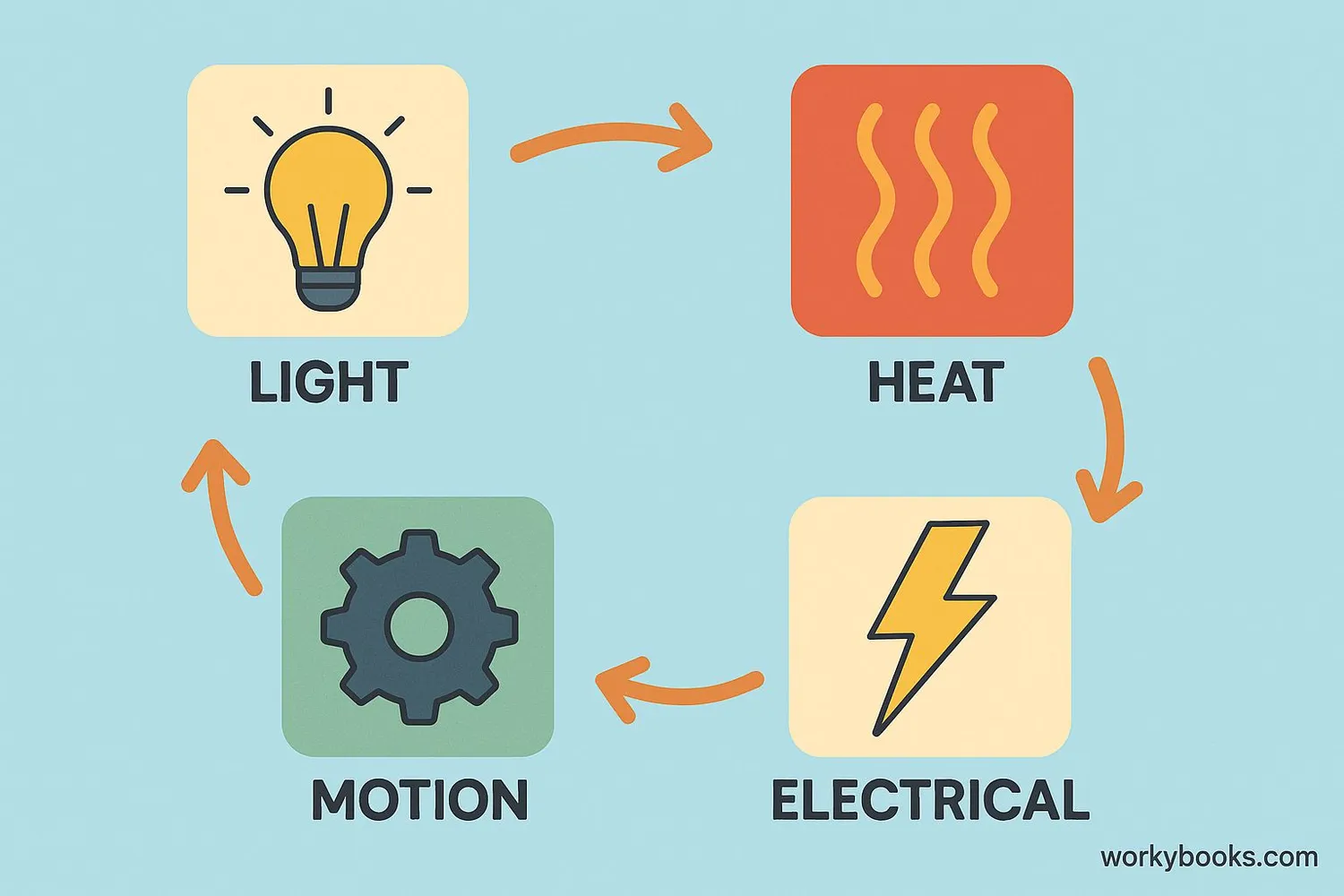
Energy conservation is a fundamental scientific principle that tells us energy cannot be created or destroyed - it can only change from one form to another. This means the total amount of energy in the universe always stays the same!
Think of energy like water. You can freeze water to make ice, or heat it to make steam, but the amount of H₂O molecules stays the same. Similarly, energy can change from light to heat, from motion to electricity, or from chemical energy to motion, but the total amount of energy remains constant.
Remember This!
Energy conservation doesn't mean using less energy (though that's important too)! In science, it means energy is never lost - it just changes forms.
Law of Conservation of Energy
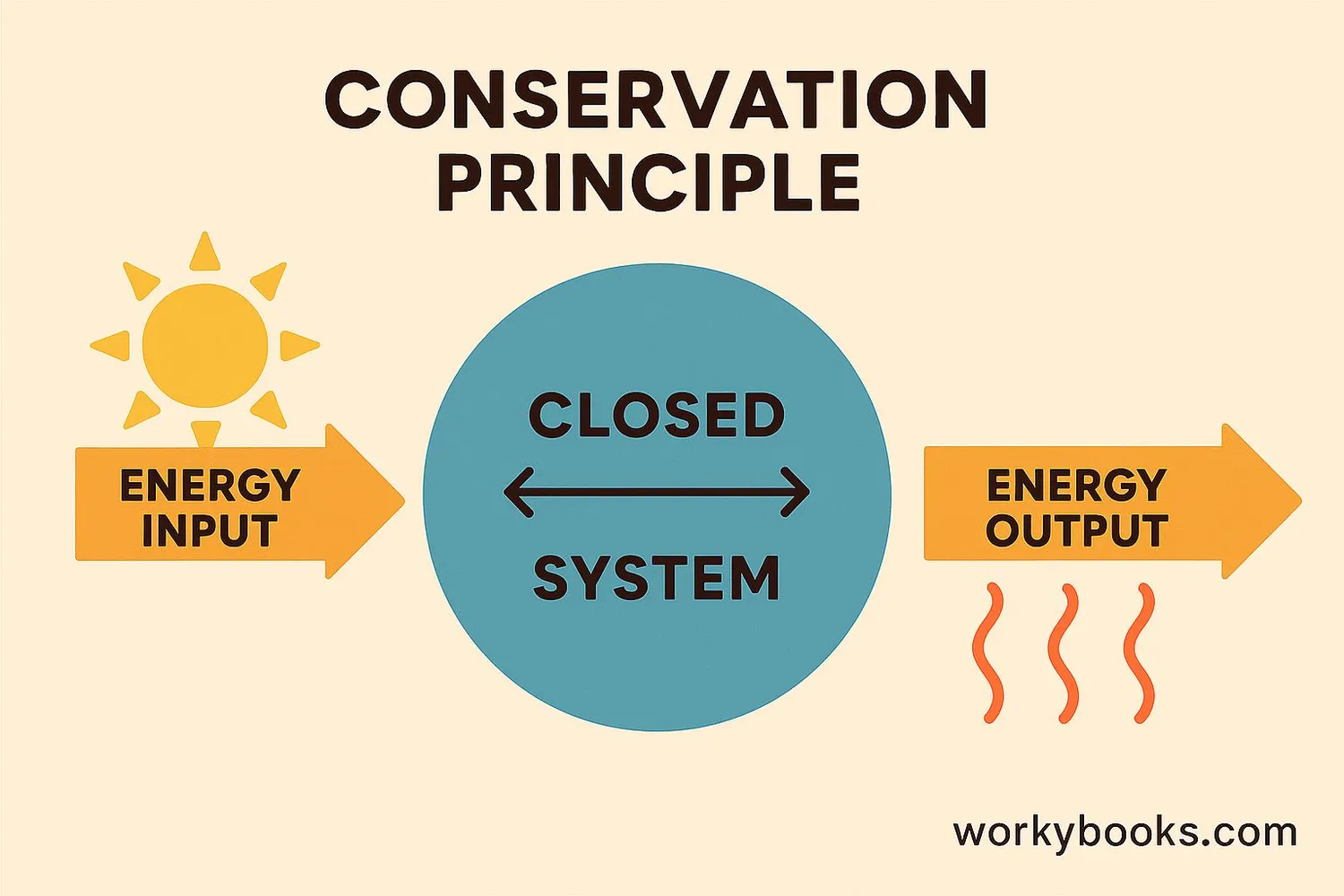
The Law of Conservation of Energy is one of the most important laws in all of physics. It states that:
"The total energy in an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time."
This means that while energy can change forms (like from potential to kinetic), the total amount of energy never changes. Scientists have tested this law countless times and it always holds true!
Closed System
A system where no energy enters or escapes
Energy Transformation
Energy changes from one form to another
Total Energy
The total amount of energy remains the same
Historical Note
This law was first proposed by Julius Robert Mayer in 1842. Many scientists including James Prescott Joule and Hermann von Helmholtz contributed to developing this fundamental principle.
Examples of Energy Conservation
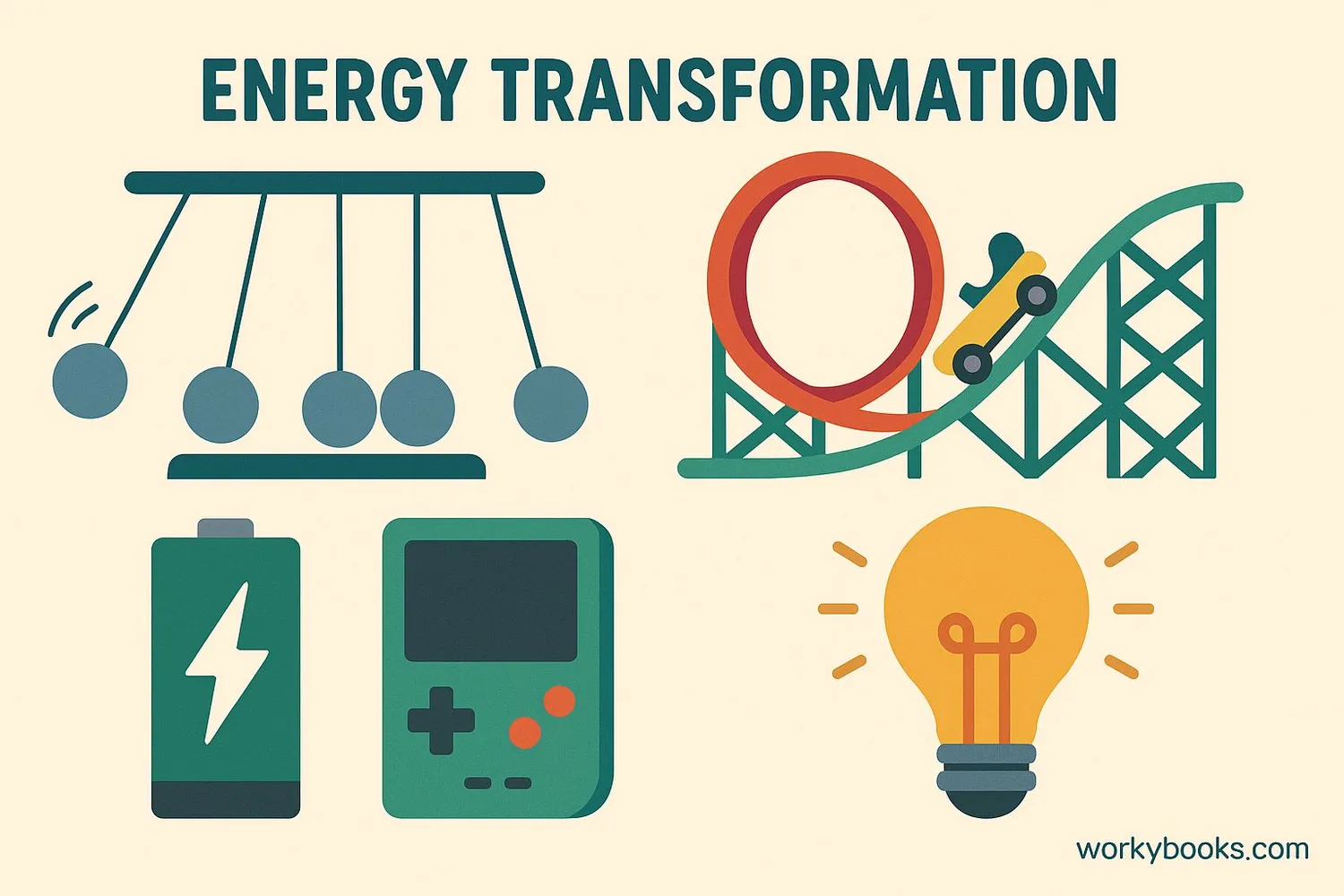
Energy conservation happens all around us every day! Here are some common examples:
Campfire
Chemical energy → Heat energy + Light energy
Battery
Chemical energy → Electrical energy → Light energy
Wind Turbine
Kinetic energy → Mechanical energy → Electrical energy
Other examples include:
• Pendulum: Potential energy ↔ Kinetic energy
• Eating food: Chemical energy → Kinetic energy (movement)
• Solar panel: Light energy → Electrical energy
• Hydroelectric dam: Potential energy → Kinetic energy → Electrical energy
Energy Conservation Formula
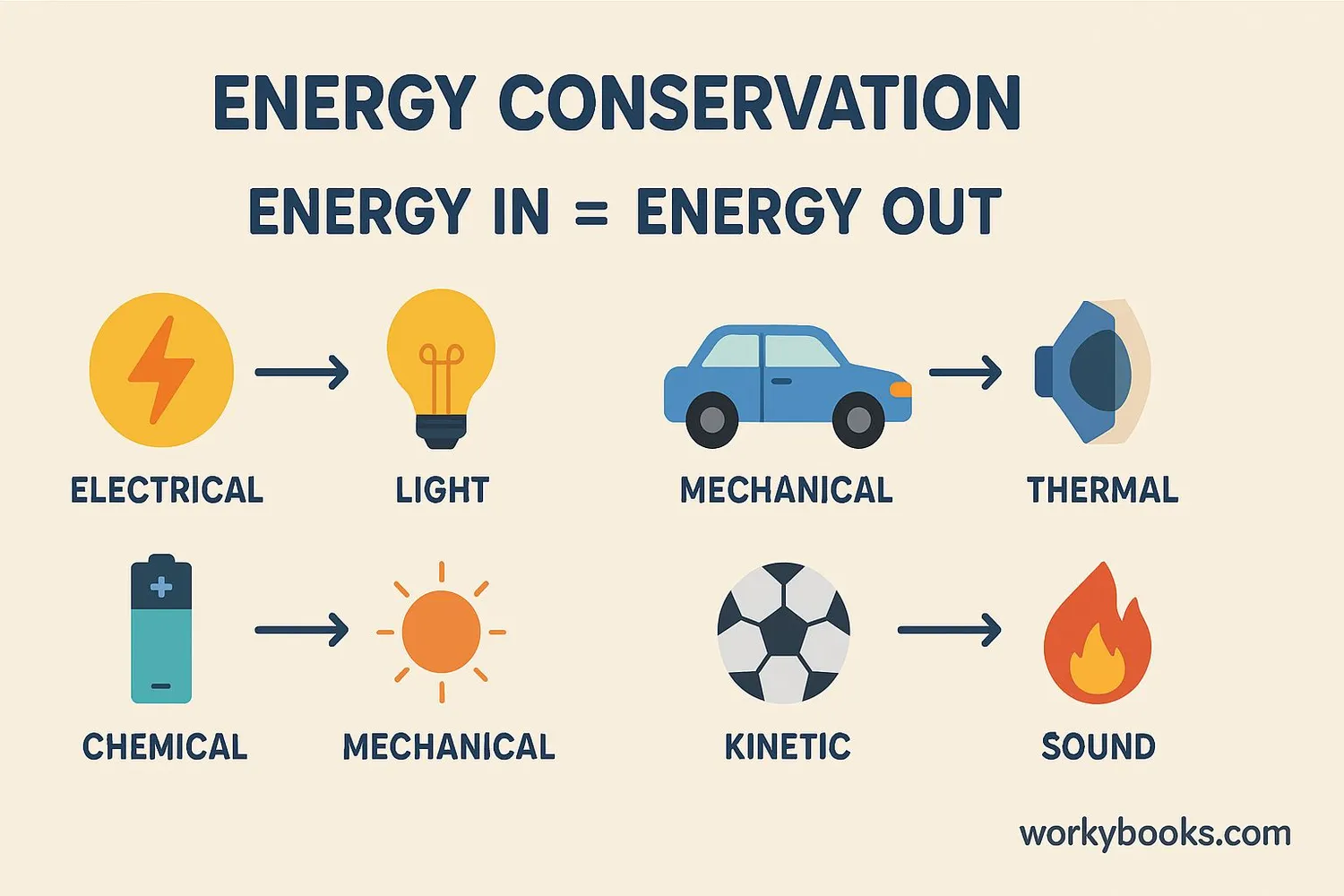
The principle of energy conservation can be expressed mathematically. For any closed system:
Initial Total Energy = Final Total Energy
This means that if we add up all the energy at the beginning (potential, kinetic, thermal, etc.), it will equal the total energy at the end, even though the forms of energy may have changed.
Simple Example
For a falling object: Potential Energy + Kinetic Energy = Constant
As the object falls, potential energy decreases while kinetic energy increases, but their sum remains the same.
The most common formula you'll see is:
PE₁ + KE₁ = PE₂ + KE₂
Where PE is potential energy and KE is kinetic energy. This formula helps scientists and engineers solve problems about motion, electricity, heat transfer, and more!
Energy Conservation Quiz
Test your knowledge with this energy conservation quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about energy conservation:
Science Facts About Energy
Discover some amazing facts about energy conservation!
Universal Constant
The total amount of energy in the universe has remained exactly the same since the Big Bang nearly 14 billion years ago! It has just been changing forms ever since.
Human Power
The average person at rest generates about 100 watts of energy—enough to power a bright light bulb. When exercising, this can increase to 1,000 watts or more!
Solar Power
In just one hour, the Earth receives more energy from the sun than all humanity uses in an entire year! This energy is conserved as it transforms into other forms.
Time Symmetry
The law of energy conservation is related to the fact that the laws of physics don't change over time. This connection is called Noether's Theorem, discovered by mathematician Emmy Noether.





