Metallic Bonding - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how metal atoms bond together to create amazing materials!
What is Metallic Bonding?
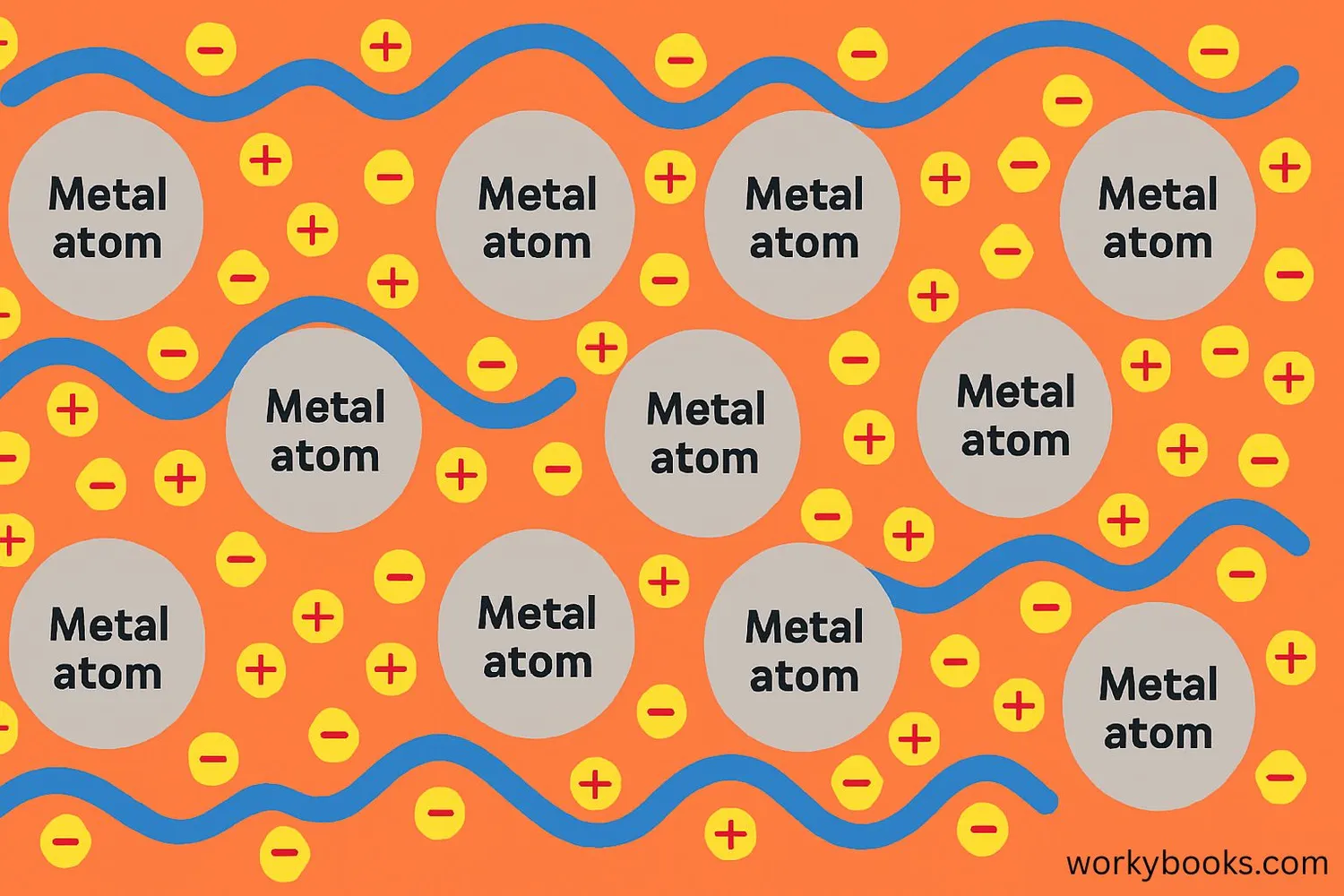
Metallic bonding is the special way that metal atoms stick together. Unlike other types of chemical bonds, metallic bonding creates a special "sea of electrons" that moves freely around the metal atoms.
Think of metallic bonding like a group of positive metal ions (atoms that have lost electrons) floating in a sea of negative electrons. These free-moving electrons are what give metals their special properties like conductivity and malleability.
Did You Know?
About 75% of all known elements are metals! That's why metallic bonding is so important in our world.
How Metallic Bonding Works
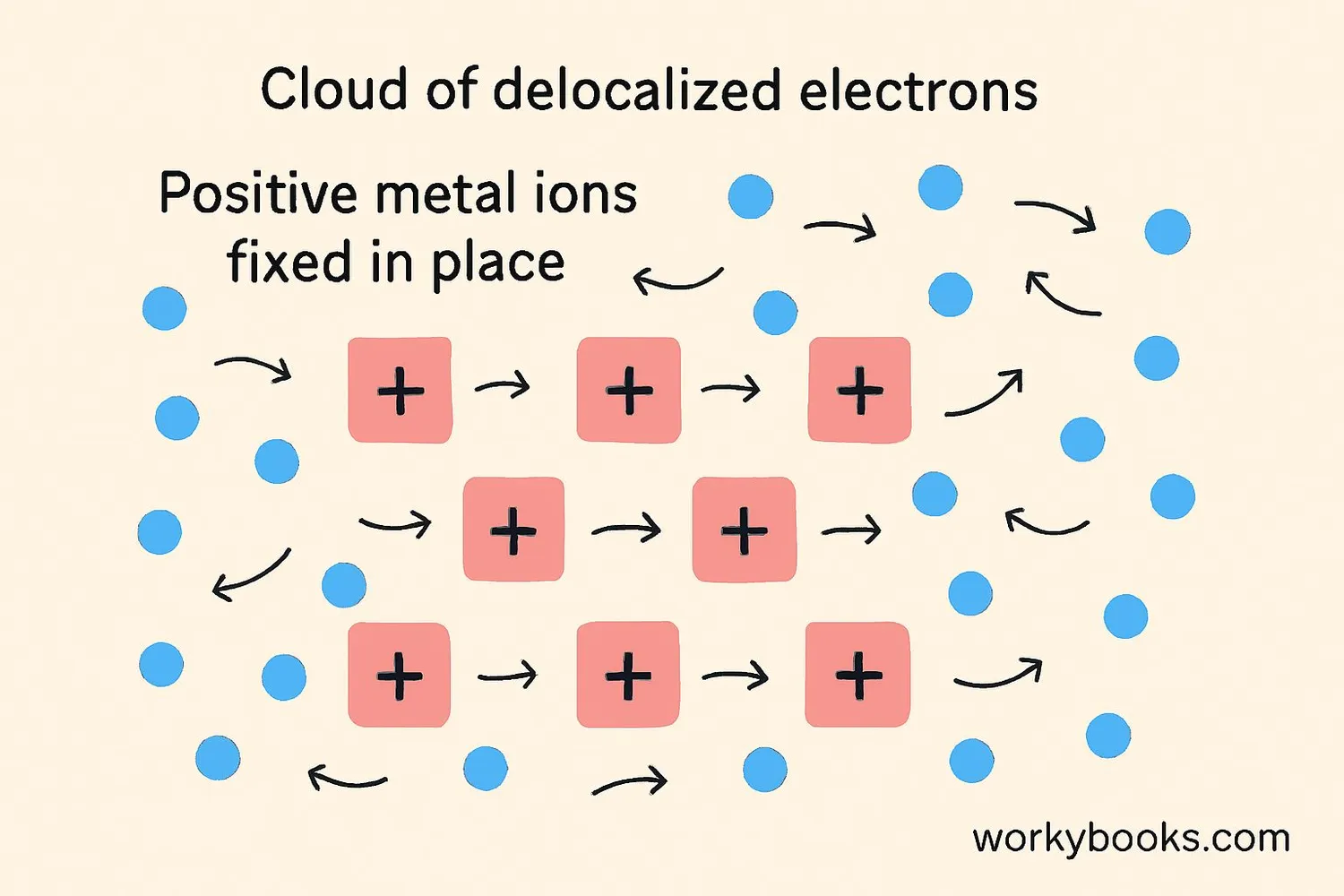
Metallic bonding works through the "electron sea model." Here's how this amazing bonding process works:
Metal Atoms
Metal atoms have loosely held outer electrons
Electron Donation
Atoms donate electrons to form positive ions
Electron Sea
The donated electrons form a "sea" that moves freely
Attraction
Positive metal ions are attracted to the electron sea
Bond Formation
This attraction creates the metallic bond
The free-moving electrons in metallic bonding are called "delocalized electrons" because they aren't attached to any particular atom. This sea of electrons acts like glue that holds the positive metal ions together in a strong but flexible structure.
Bonding Strength
The strength of metallic bonding depends on the number of delocalized electrons. That's why transition metals with more electrons to contribute form stronger bonds.
Properties of Metals from Bonding
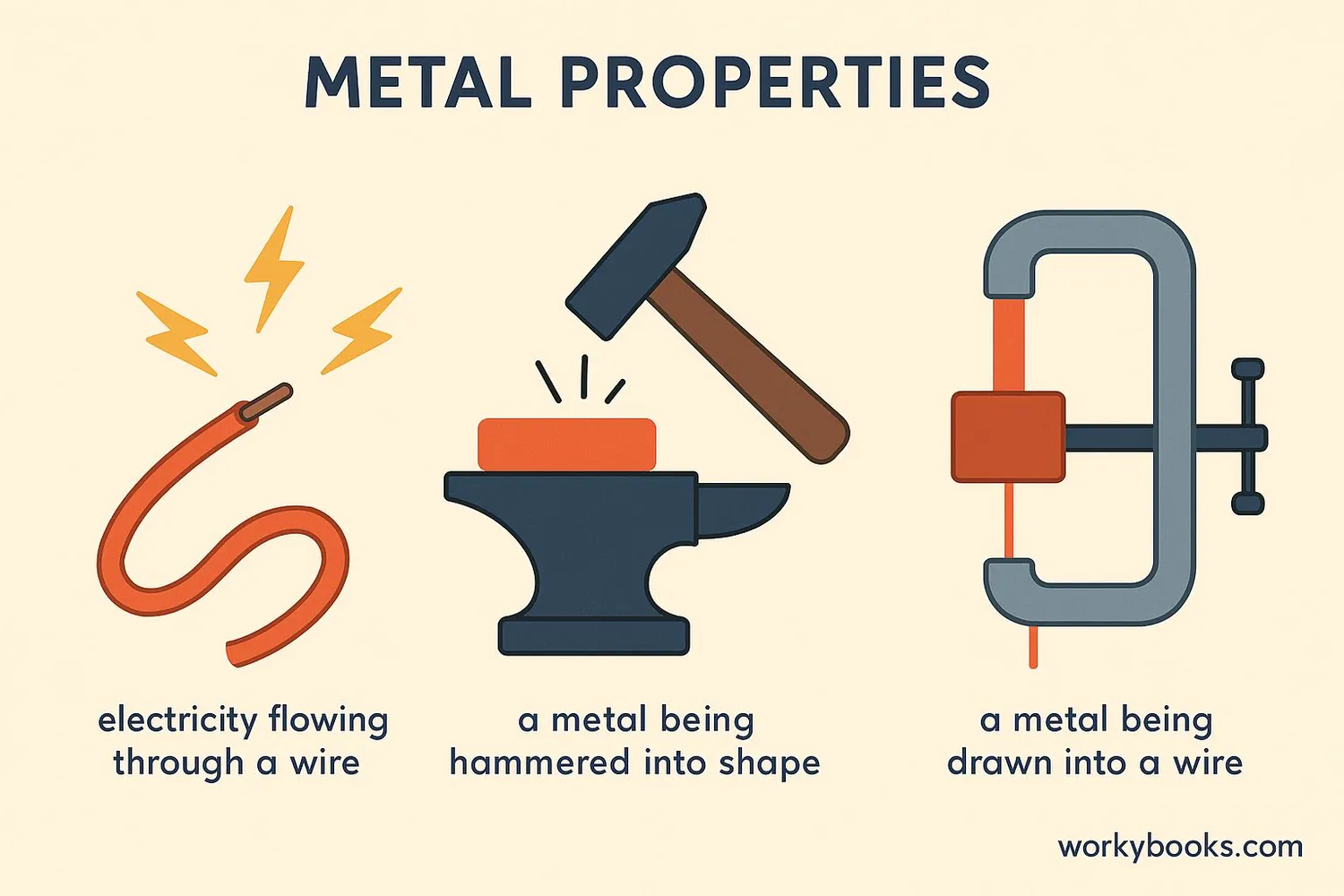
The unique structure of metallic bonding gives metals their special properties. Here are the key properties and how they relate to the electron sea model:
Electrical Conductivity
Free electrons can carry electrical current through the metal
Thermal Conductivity
Electrons transfer heat energy quickly through the metal
Malleability
Layers of atoms can slide past each other without breaking
Ductility
Metals can be drawn into wires without fracturing
Luster
Electrons reflect light, giving metals their shiny appearance
The strength of these properties varies between different metals based on:
• The number of delocalized electrons available
• The size of the metal ions
• How the metal atoms are arranged
This is why some metals like copper are excellent conductors, while others like tungsten have very high melting points.
Metallic Bonding Quiz
Test your metallic bonding knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about metallic bonding:
Fun Metallic Bonding Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about metallic bonding and metals!
Super Conductors
Silver is the best conductor of electricity among all metals because its electrons move more freely than in any other element.
Ancient Metalworking
Humans have been using metallic bonding properties for thousands of years! The earliest known metal jewelry dates back over 10,000 years.
Tiny Structures
In a single grain of metal, there can be billions of atoms arranged in a regular pattern called a crystal lattice, all held together by metallic bonds.
Space Age Metals
Special metal alloys with strong metallic bonds are used in spacecraft because they can withstand extreme temperatures and conditions in space.





