Trough in Meteorology - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how troughs shape our weather patterns and influence daily forecasts
What is a Trough in Weather?
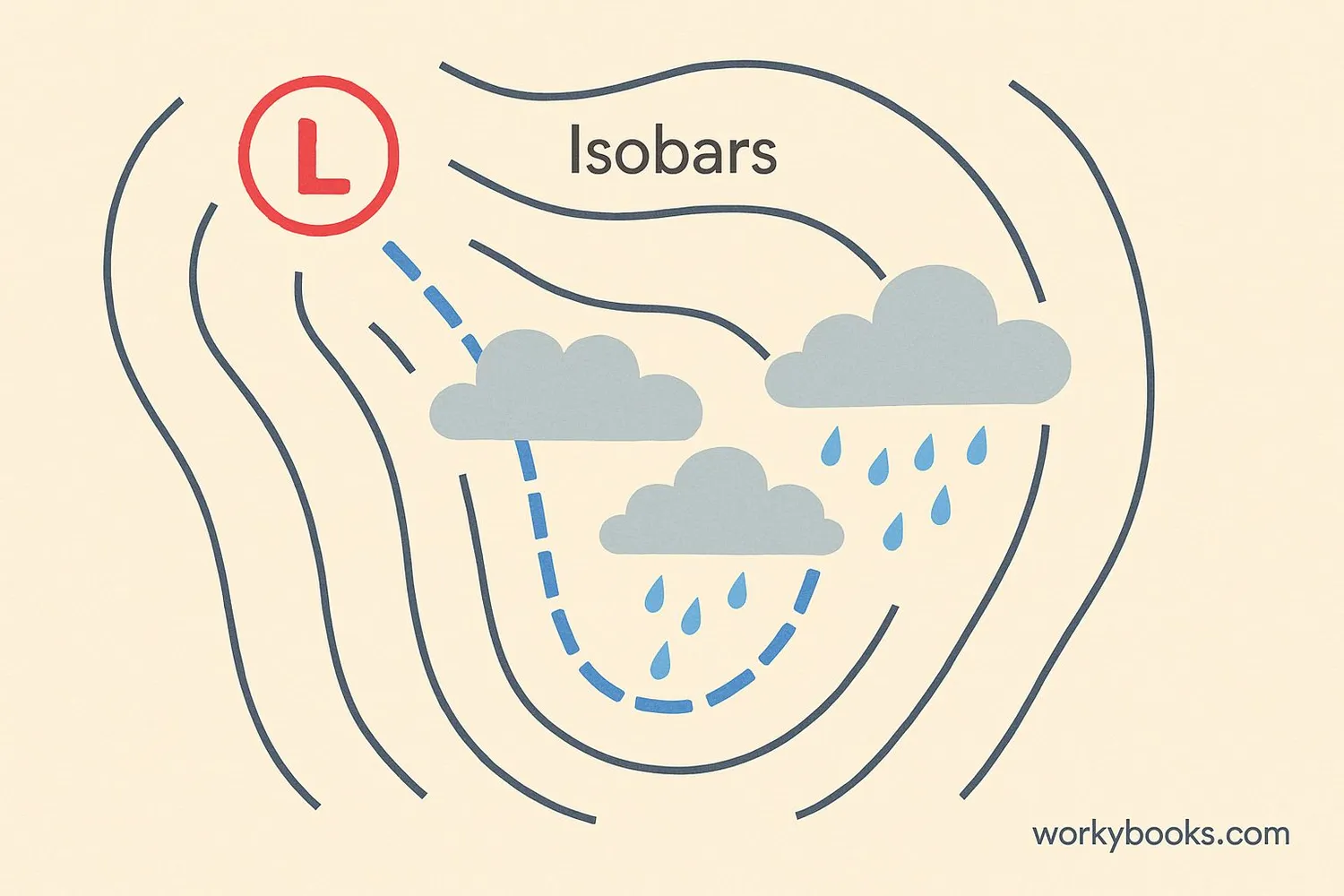
A trough is an elongated area of low atmospheric pressure that extends outward from a center of low pressure. On weather maps, troughs appear as U-shaped or V-shaped lines that bulge toward warmer air. Think of it like a valley in the atmosphere where the air pressure is lower than in surrounding areas.
Troughs are important in weather forecasting because they often bring clouds, precipitation, and changing weather conditions. When you see a trough on a weather map, it usually means the weather might become stormy or unsettled in that area.
Weather Fact!
Troughs can be hundreds of miles long and are a key feature meteorologists track when predicting weather patterns.
How Troughs Form and Work
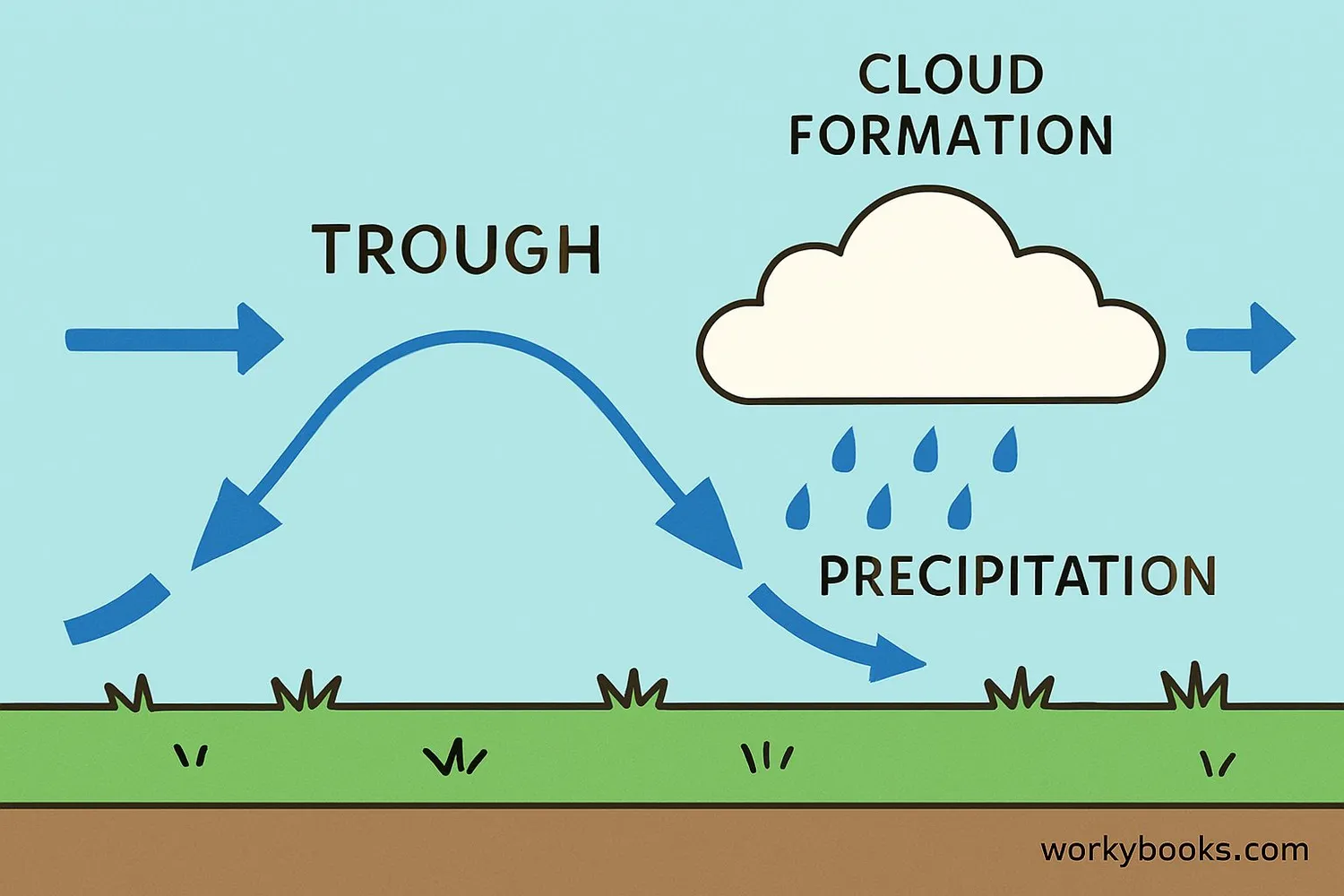
Troughs form due to differences in air temperature and pressure in the atmosphere. Here's how this important weather feature develops:
Temperature Contrast
Warm and cold air masses meet, creating pressure differences
Jet Stream Influence
The jet stream dips southward, dragging cooler air with it
Air Rising
Lower pressure causes air to rise and cool
Cloud Formation
Rising air leads to condensation and cloud development
Weather Changes
Precipitation and storms often form along the trough
In a trough, air tends to converge and rise, which leads to cloud formation and potentially precipitation. This is why we often associate troughs with more unsettled weather patterns. The rising air cools as it expands, causing water vapor to condense into clouds and possibly rain or snow.
Atmospheric Science!
Troughs are often associated with cyclonic circulation, meaning winds rotate counterclockwise around them in the Northern Hemisphere, bringing together different air masses.
Types of Troughs
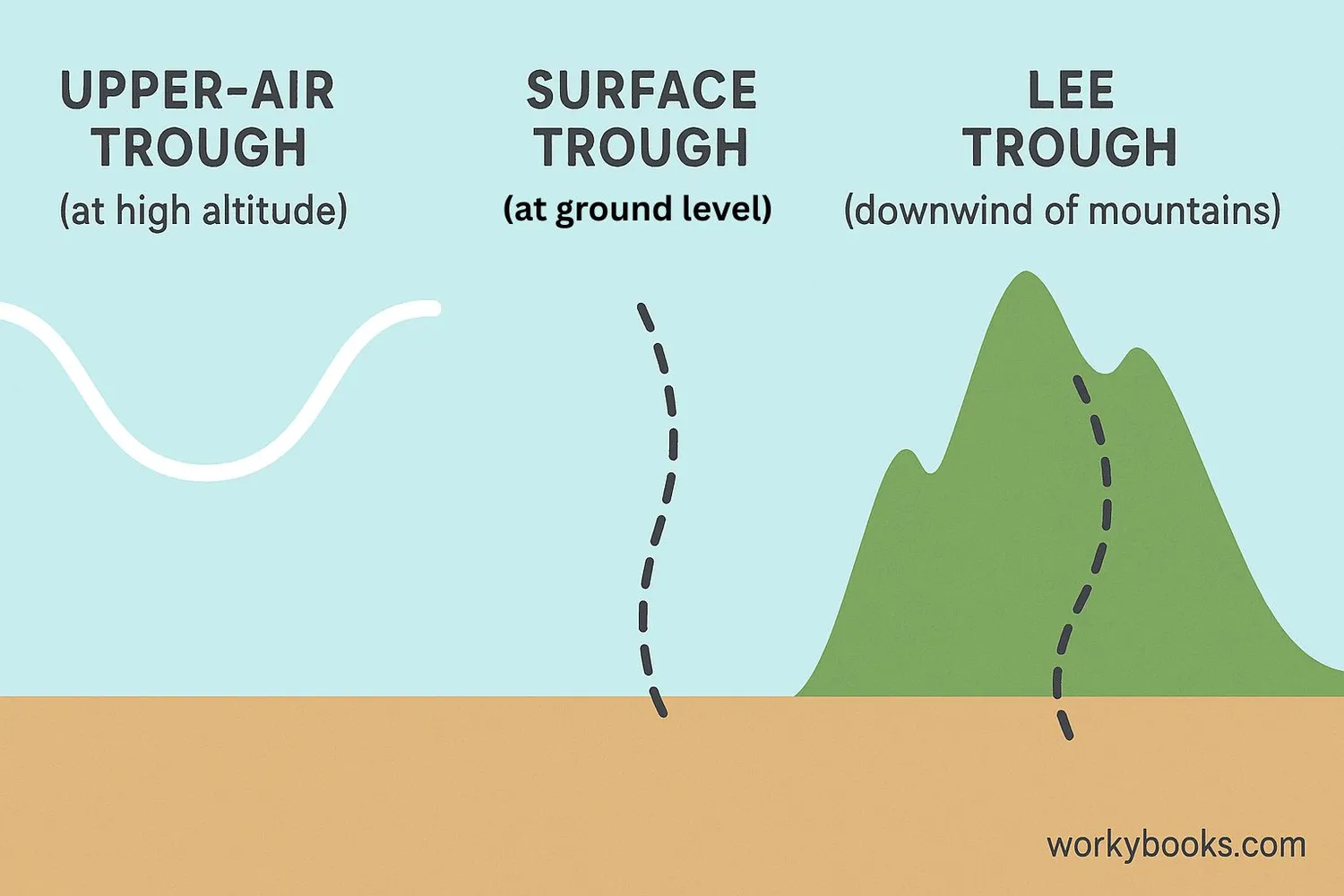
Meteorologists identify several types of troughs based on where they form and how they behave:
Lee Trough
Forms downwind of mountain ranges as air descends and warms
Surface Trough
Occurs at ground level, often bringing noticeable weather changes
Upper-Air Trough
Exists at high altitudes and influences surface weather patterns
Tropical Waves
Weak troughs in the tropics that can develop into tropical storms
Each type of trough has different characteristics and impacts on our weather. Upper-air troughs are especially important for meteorologists because they often signal larger weather pattern changes. Surface troughs might bring immediate changes like rain showers or thunderstorms, while lee troughs form specifically in the "shadow" of mountain ranges.
How Troughs Affect Weather
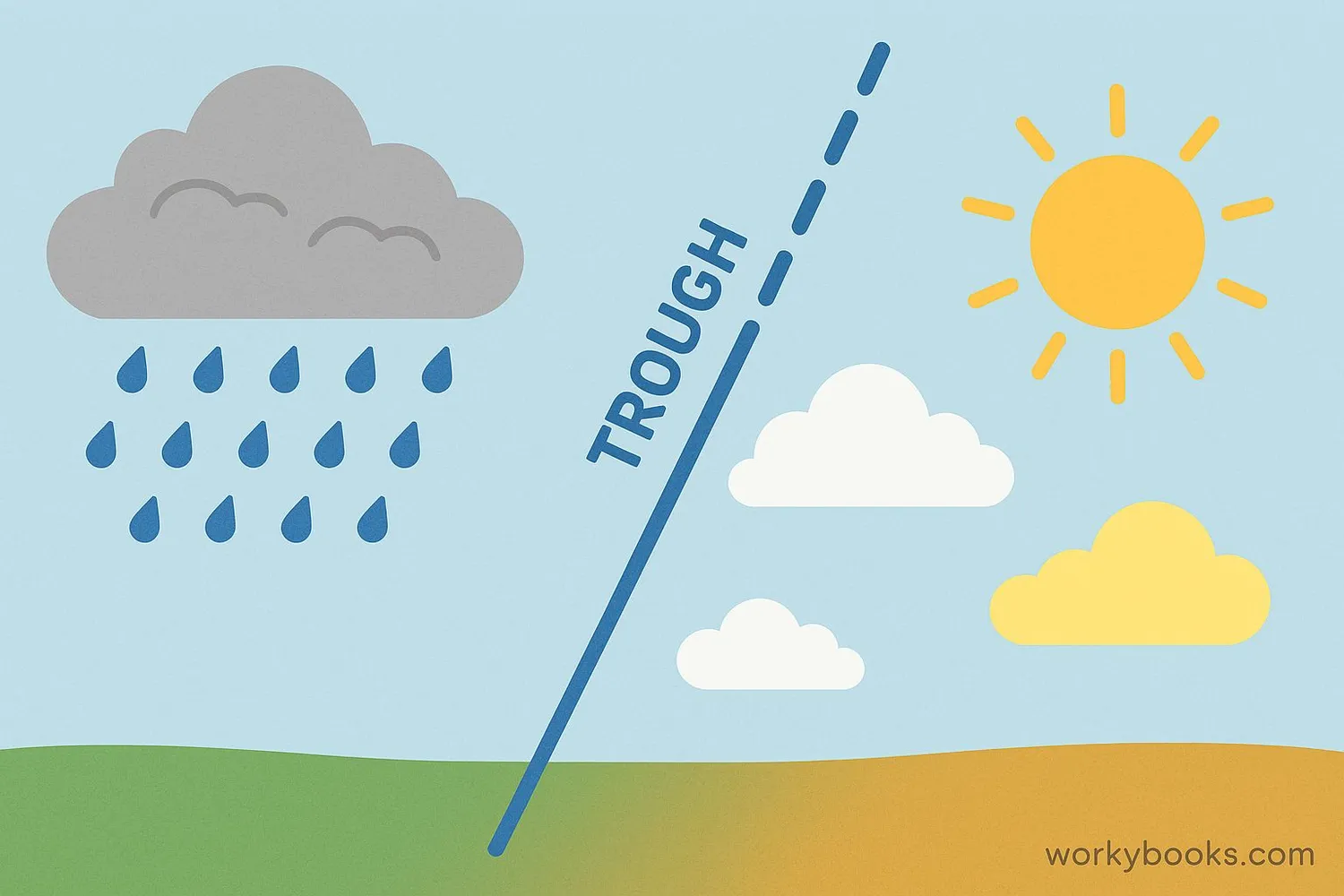
Troughs play a crucial role in our daily weather patterns. Understanding troughs helps meteorologists predict:
Precipitation
Troughs often bring rain, snow, or storms
Temperature Changes
Cooler air typically follows a trough passage
Wind Patterns
Winds change direction and speed around troughs
When a trough approaches, you might notice:
• Increasing clouds and possible precipitation
• Changes in wind direction and speed
• Dropping temperatures as the trough passes
• Potential for storm development
After a trough moves through, weather often becomes clearer and cooler as higher pressure builds behind it. This pattern of troughs and ridges (the opposite of troughs) creates the constantly changing weather we experience.
Forecasting Fact!
Meteorologists use computer models to predict how troughs will develop and move, helping them create more accurate weather forecasts days in advance.
Trough Meteorology Quiz
Test your knowledge about weather troughs with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about troughs in meteorology:
Weather Trivia
Discover some fascinating facts about troughs and weather patterns!
Size Matters
Some troughs can extend for thousands of miles! Long-wave troughs in the upper atmosphere can span continents and influence weather patterns for weeks.
Satellite Detection
Weather satellites can detect troughs by observing cloud patterns. The distinctive comma-shaped cloud pattern often reveals the presence of a trough in the atmosphere.
Historical Forecasting
Before modern technology, meteorologists identified troughs by tracking changes in barometric pressure and wind direction across weather stations.
Tropical Connection
Some tropical waves (a type of trough) that form off the coast of Africa can develop into hurricanes as they move across the Atlantic Ocean.





