Elasticity - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how materials stretch and return to their original shape!
What is Elasticity?
Elasticity is the superpower that lets materials stretch, bend, or squeeze and then return to their original shape! Think of a rubber band - you can stretch it, but when you let go, it snaps back to its original size. That's elasticity in action!
Elastic materials can be deformed when force is applied but return to their original shape when the force is removed. This happens because of special bonds between atoms inside the material. These bonds act like tiny springs that pull the material back to its original shape.
Original Shape
Material is in its natural state
Force Applied
You stretch or squeeze the material
Deformation
Material changes shape temporarily
Force Removed
You stop stretching or squeezing
Return to Shape
Material bounces back to original form
Everyday Elasticity!
When you bounce a basketball, sit on a sofa, or wear stretchy clothes, you're experiencing elasticity in action!
Hooke's Law
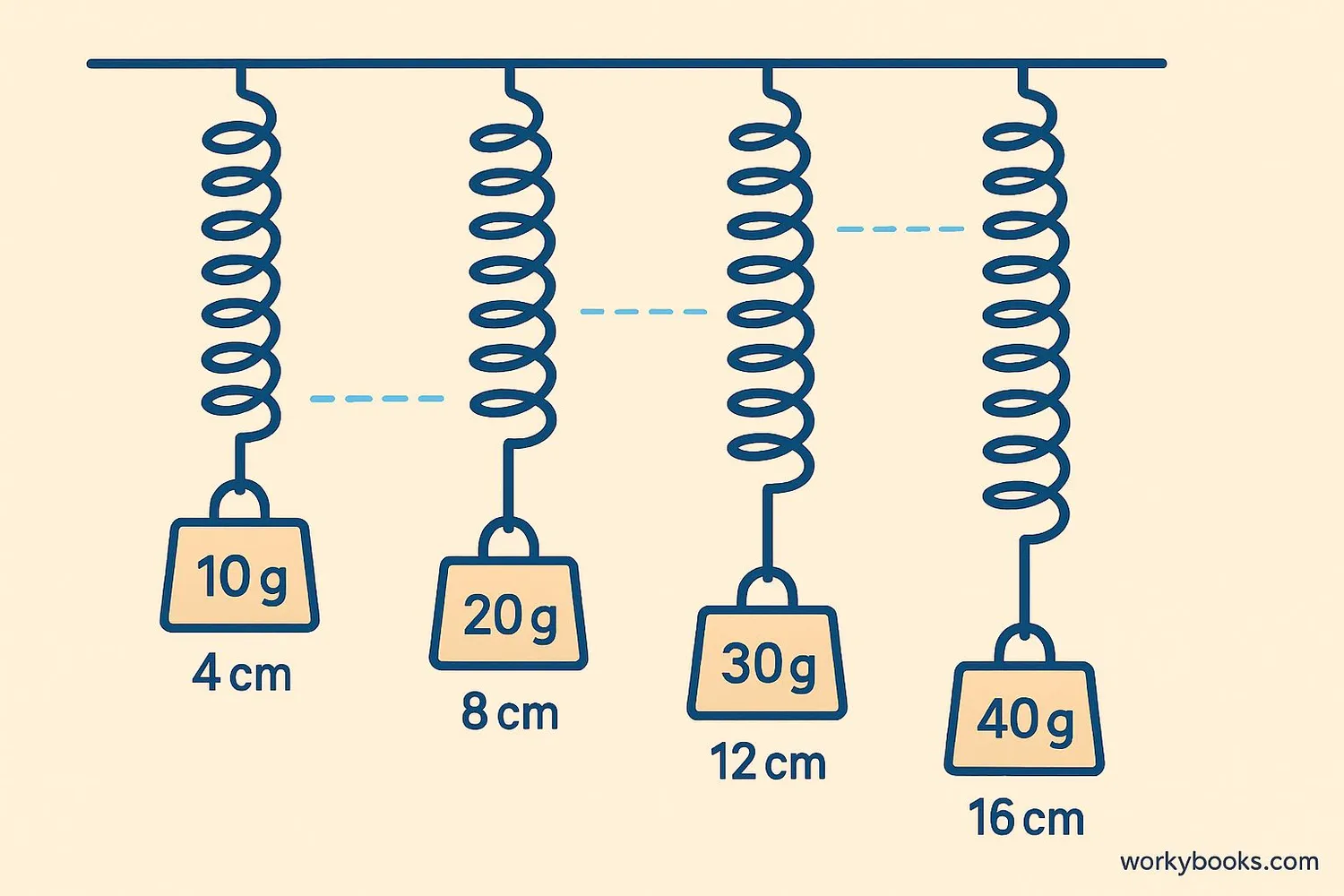
Hooke's Law is a simple rule that tells us how elastic materials behave. Discovered by scientist Robert Hooke in 1660, it states:
The amount a material stretches is proportional to the force applied to it.
This means if you double the force, the material stretches twice as much. The formula for Hooke's Law is:
F = kx
Where:
• F = Force applied (in Newtons)
• k = Spring constant (how stiff the material is)
• x = Extension (how much it stretches)
Spring Constant
The spring constant (k) tells us how stiff a material is. A high k value means the material is stiff (like steel) while a low k value means it's stretchy (like rubber).
Stress and Strain
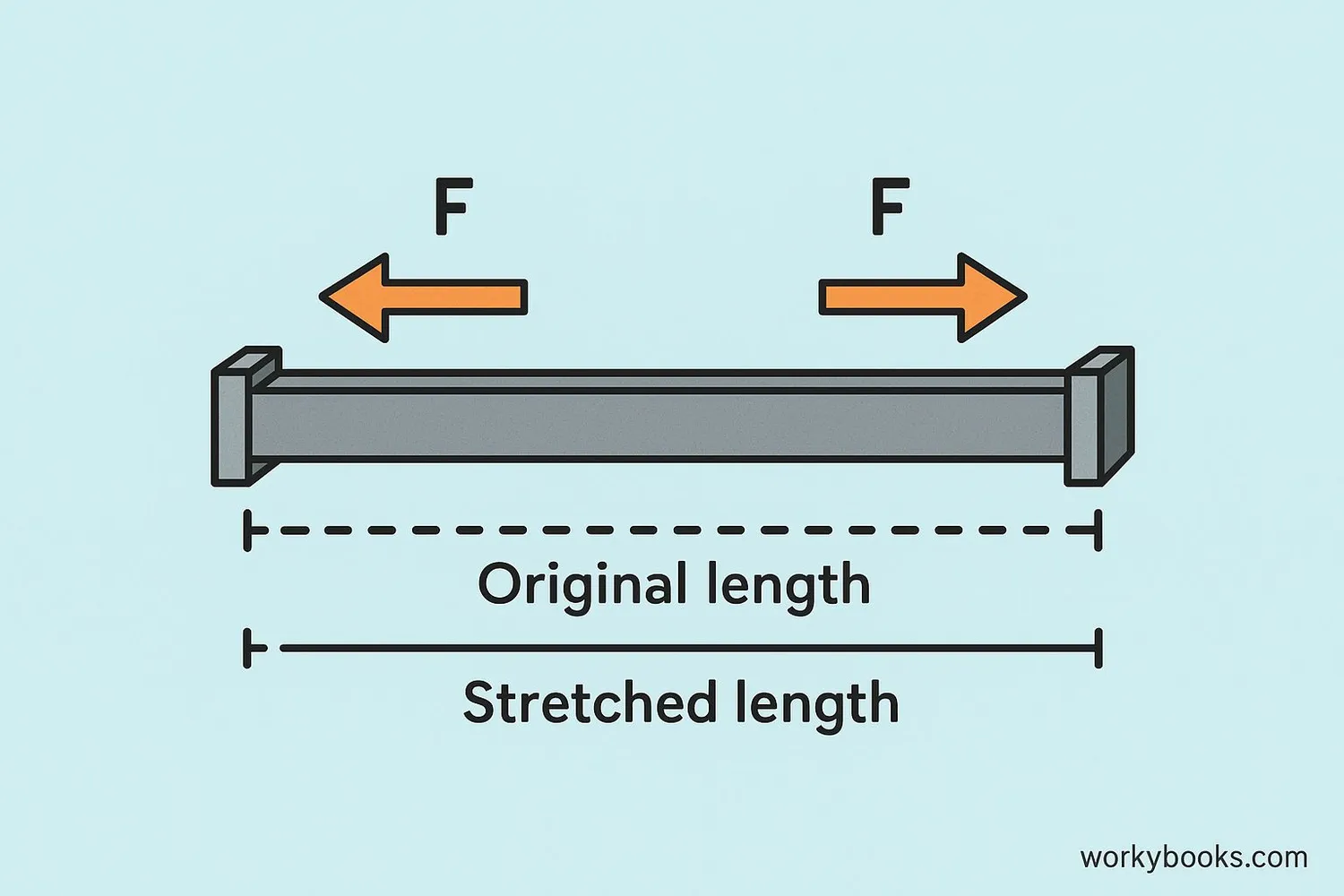
To understand how materials respond to forces, scientists use two important concepts: Stress and Strain.
Stress is the force applied to a material divided by its cross-sectional area. It tells us how much "push" or "pull" each part of the material experiences.
Strain is how much the material stretches compared to its original length. It's the change in length divided by original length.
When we plot stress against strain for an elastic material, we get a straight line (as long as we're within the elastic limit). The slope of this line is called Young's Modulus, which measures how stiff a material is.
Young's Modulus
Named after scientist Thomas Young, this value tells us how much a material will deform under stress. Diamond has a very high Young's modulus (stiff), while rubber has a low value (stretchy).
Elastic Limit
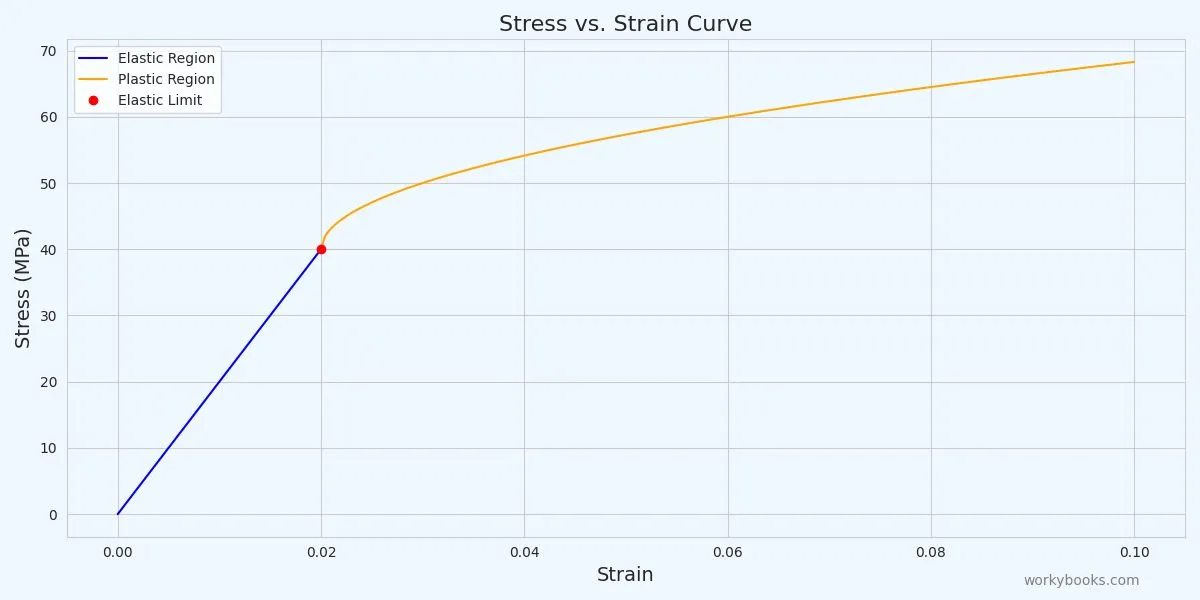
Every material has its limits! The elastic limit is the maximum stress a material can experience and still return to its original shape when the force is removed.
If you apply stress beyond the elastic limit, the material will undergo plastic deformation. This means it will be permanently changed and won't return to its original shape.
Think of a paperclip: if you bend it slightly, it springs back (elastic deformation). But if you bend it too far, it stays bent (plastic deformation).
Elastic Deformation
Material returns to original shape when force is removed
Elastic Limit
The maximum stress before permanent deformation
Plastic Deformation
Material is permanently deformed beyond this point
Material Science
Engineers must understand elastic limits when designing structures like bridges and buildings to ensure they're safe!
Elasticity Quiz
Test your elasticity knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about elasticity:
Fun Elasticity Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about elasticity!
Space Materials
Spacecraft use special elastic materials in their heat shields that can expand and contract with temperature changes from -150°C to over 1,000°C!
Animal Elasticity
A frog's tongue is one of the most elastic natural materials, stretching to about 1.5 times its length in just 0.07 seconds to catch insects!
Molecular Bungee
At the molecular level, rubber's elasticity comes from its long, tangled polymer chains that straighten when pulled but snap back when released.
Ancient Bows
The oldest known use of elasticity is the bow and arrow, invented over 64,000 years ago! Hunters used the elastic properties of wood to store and release energy.





